This biology revision guide covers everything from the basic building... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
382
•
3 Feb 2026
•
revision
@revision17
This biology revision guide covers everything from the basic building... Show more
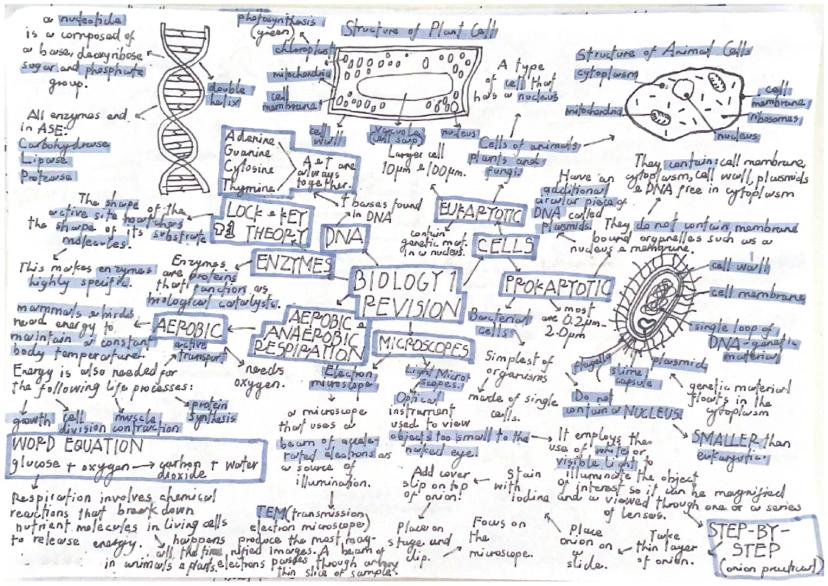
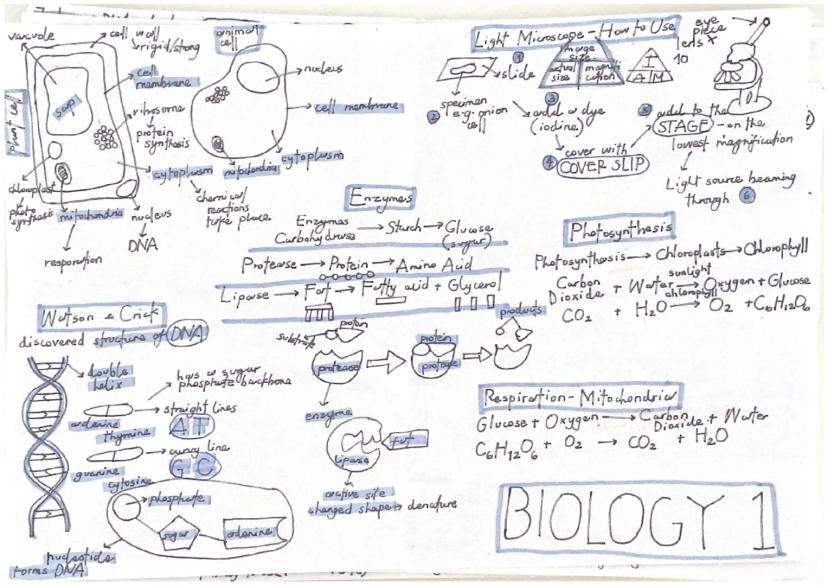
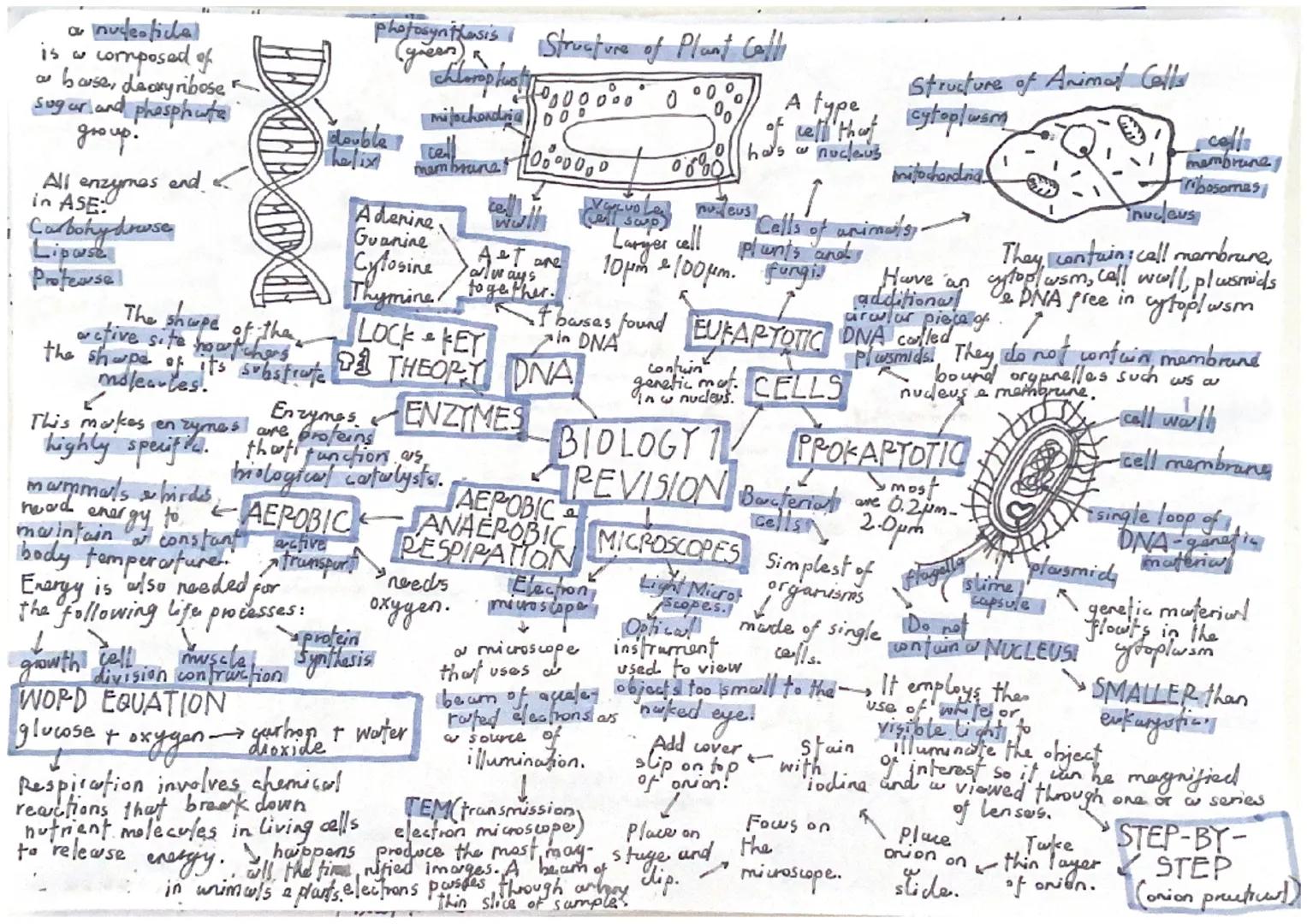
Every living thing is made of cells, and understanding their structure is your foundation for all biology. Animal cells contain a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes. Plant cells have all of these plus a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) are much simpler and smaller than the cells in your body. They don't have a proper nucleus - instead, their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. These bacterial cells are typically 0.2-2.0µm in size, whilst your cells are much larger at 10-100µm.
DNA has a famous double helix structure discovered by Watson and Crick. It's made of four bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Remember that A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C - this is crucial for DNA replication.
Quick Tip: All enzyme names end in "-ase" - carbohydrase breaks down carbohydrates, protease breaks down proteins, and lipase breaks down fats!
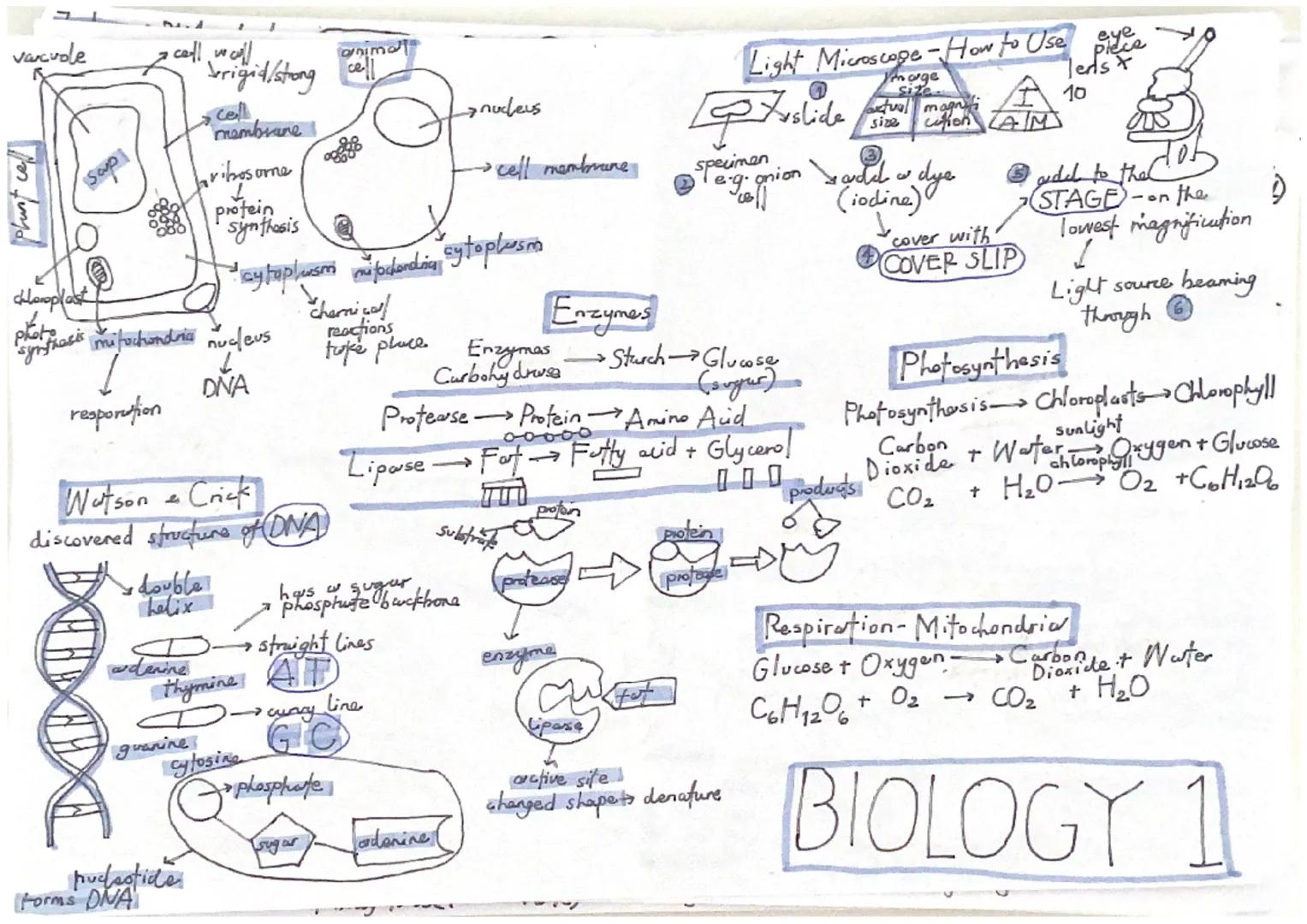
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions in your body using the lock and key theory. Each enzyme has a specific active site that perfectly matches its substrate molecule, making enzymes highly specific. Temperature and pH changes can affect how well enzymes work.
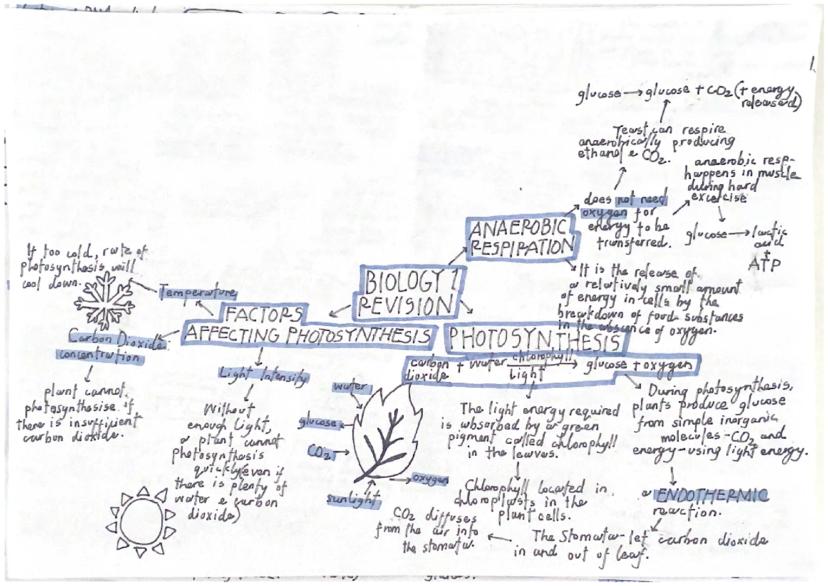
Photosynthesis happens in chloroplasts and uses chlorophyll to capture light energy. The equation is: carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen. This endothermic reaction requires light energy and is affected by light intensity, CO₂ concentration, and temperature.
Respiration occurs in mitochondria and releases energy from glucose. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water. Anaerobic respiration happens without oxygen - in muscles it produces lactic acid, whilst in yeast it produces ethanol and CO₂.
Using microscopes properly is essential for observing cells. Light microscopes use visible light and are great for basic cell observation, whilst electron microscopes provide much higher magnification for detailed structures.
Remember: Photosynthesis makes food using light energy, whilst respiration breaks down food to release energy - they're opposite processes!
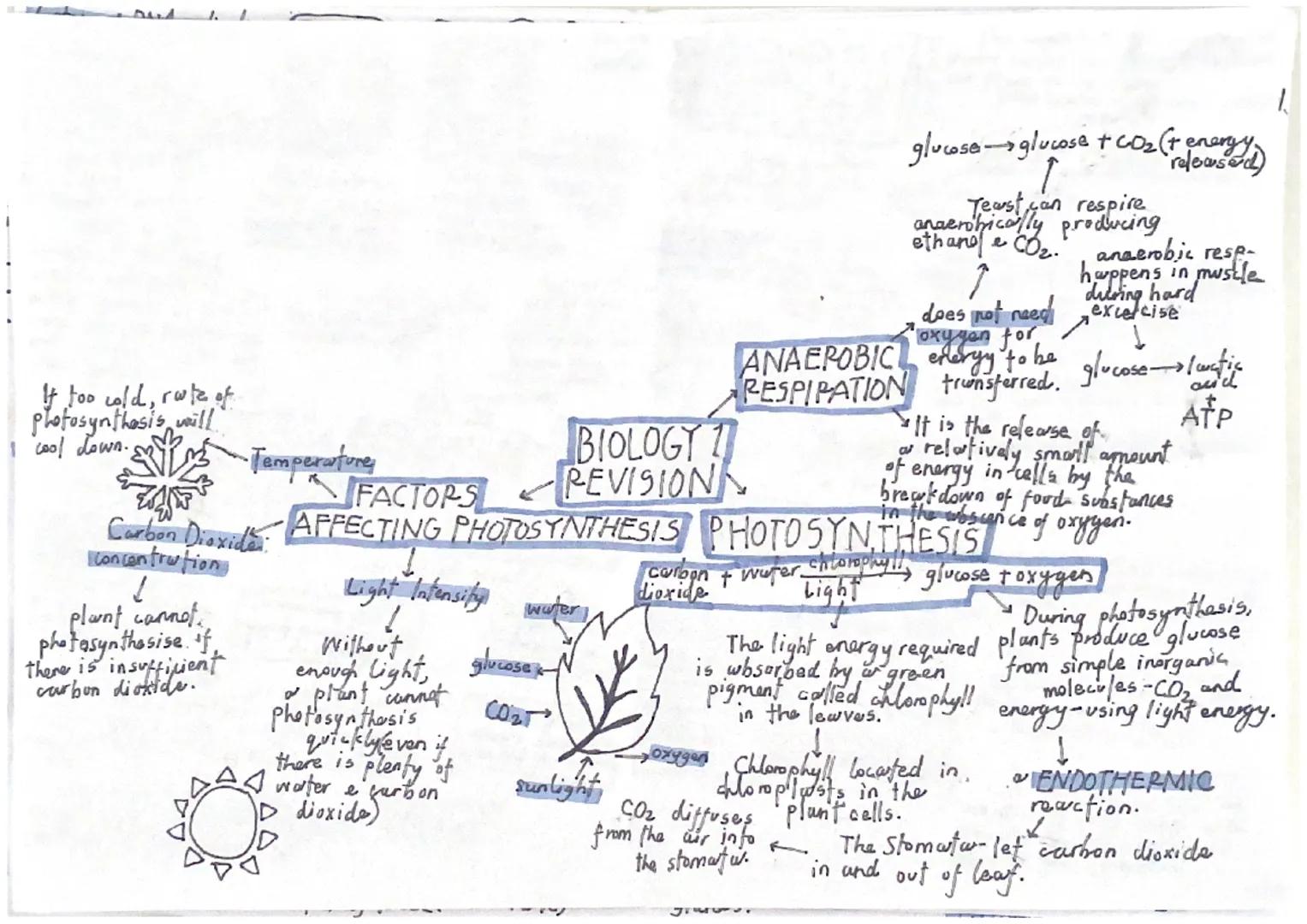
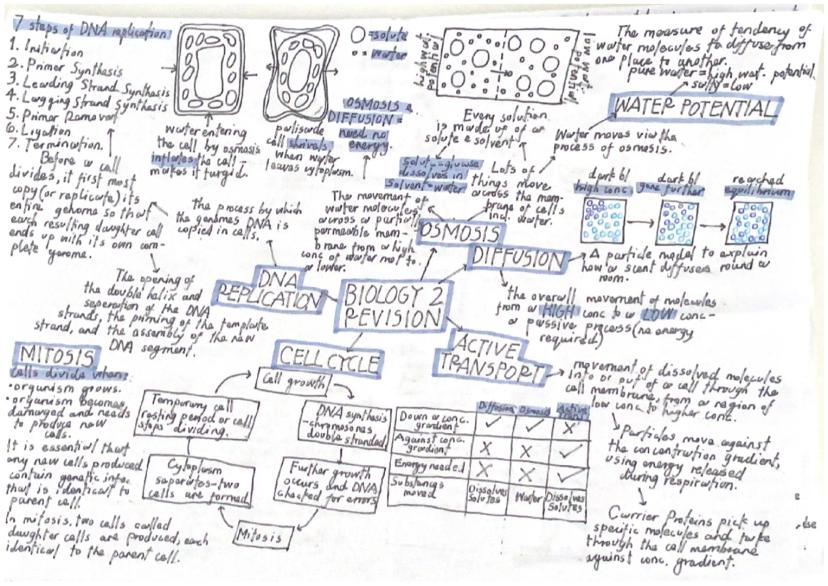
Before any cell divides, it must copy its entire genome through DNA replication. This process has seven key steps: initiation, primer synthesis, leading strand synthesis, lagging strand synthesis, primer removal, ligation, and termination. Each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the parent's DNA.
Mitosis is how your body grows and repairs damage. The cell cycle includes growth phases, DNA synthesis, error-checking, and finally mitosis itself. Two identical daughter cells are produced, each containing the same genetic information as the parent cell.
Understanding factors affecting photosynthesis is crucial for your exams. Without sufficient light intensity, plants cannot photosynthesise quickly even with plenty of water and CO₂. Similarly, inadequate carbon dioxide concentration limits the process, and temperatures that are too cold slow down the rate significantly.
Stomata are tiny pores that let carbon dioxide enter and exit leaves. They're essential for gas exchange during photosynthesis, allowing CO₂ to diffuse from the air into the plant.
Exam Focus: Learn the photosynthesis equation by heart - it appears in most biology papers and understanding it helps with limiting factors questions.
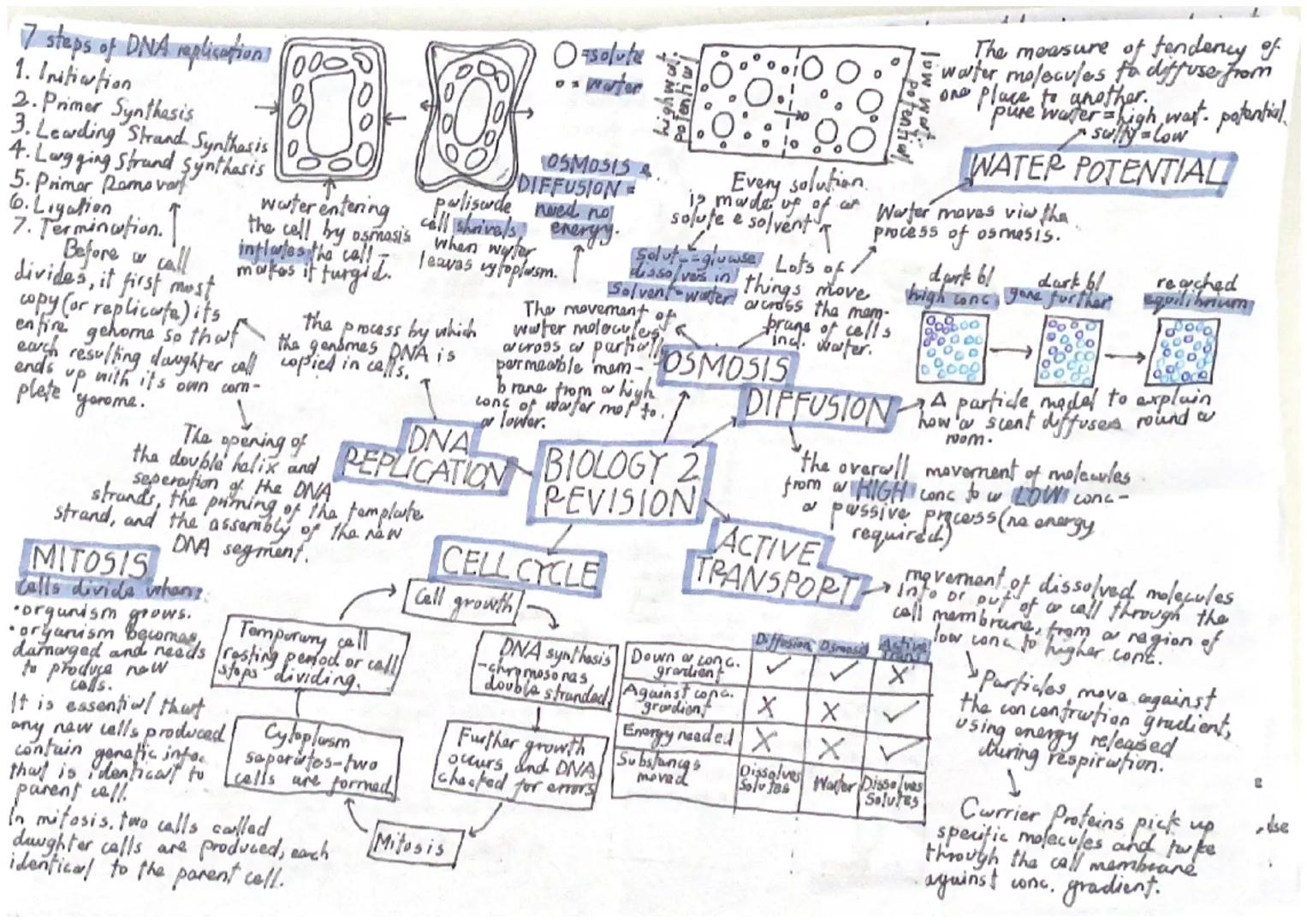
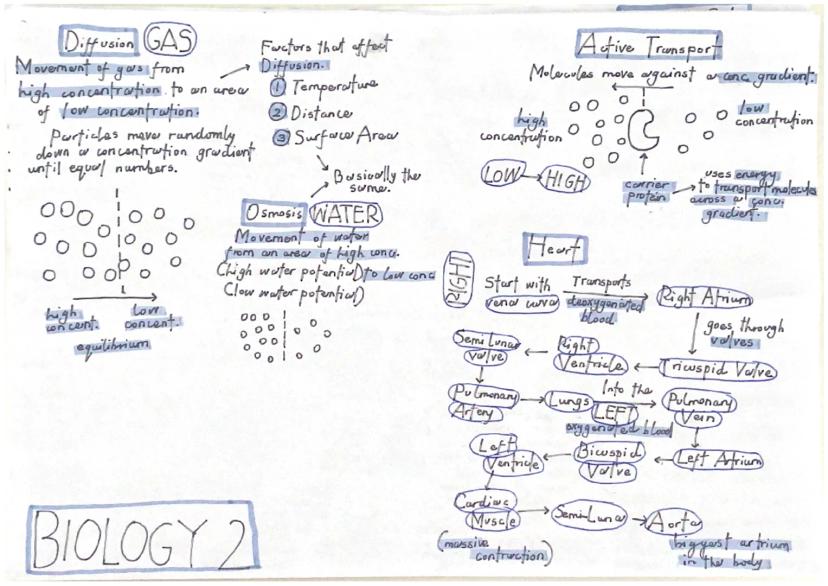
Three main processes move substances across cell membranes: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentration - no energy needed. Think of how a scent spreads across a room.
Osmosis is specifically the movement of water molecules from high water potential to low water potential through a partially permeable membrane. When plant cells gain water by osmosis, they become turgid (swollen). When they lose water, they shrivel.
Active transport is different because it moves substances against the concentration gradient from low to high concentration. This requires energy from respiration and uses special carrier proteins to transport specific molecules across membranes.
Water potential measures the tendency of water molecules to move. Pure water has high water potential, whilst salty solutions have low water potential. Water always moves from high to low water potential via osmosis.
Memory Trick: Active transport goes "uphill" against the gradient, so it needs energy like climbing a mountain needs effort!
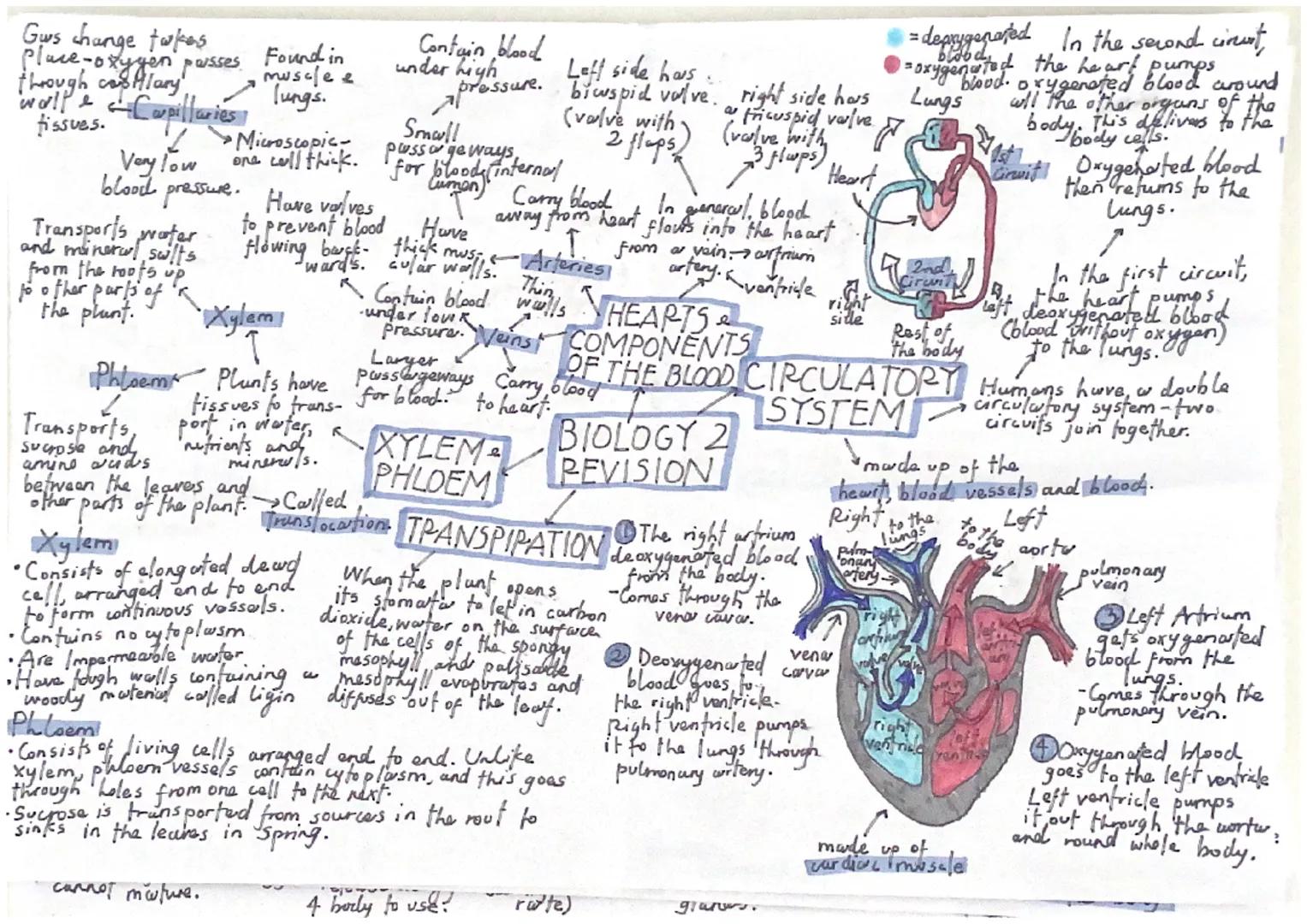
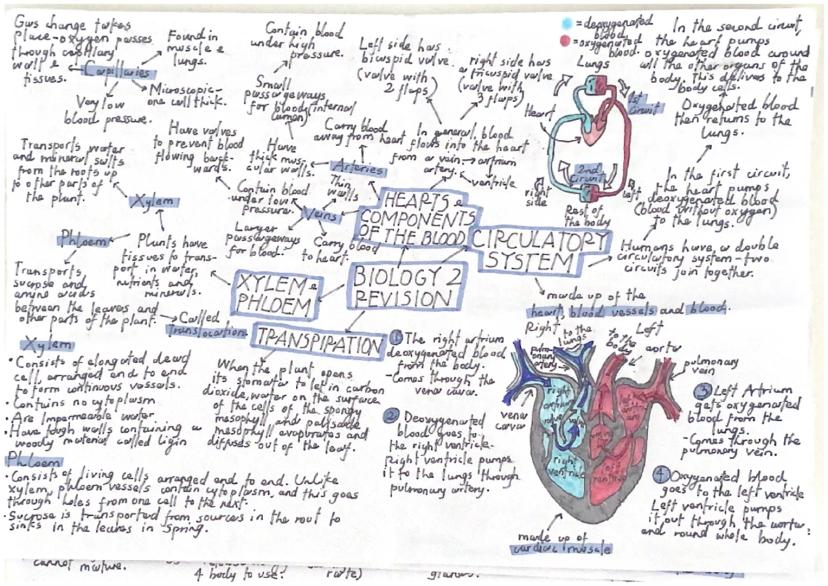
Your heart pumps blood through a double circulatory system with two separate circuits. The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, whilst the left side pumps oxygenated blood around your body. The heart has four chambers with valves preventing backflow.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart under high pressure and have thick muscular walls. Veins return blood to the heart under low pressure and contain valves. Capillaries are microscopic vessels where gas exchange occurs between blood and tissues.
Plants have their own transport systems. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from roots to other plant parts. These vessels are made of dead cells with tough walls containing lignin for strength. Phloem consists of living cells that transport sugars like sucrose around the plant.
Translocation is the movement of dissolved sugars through phloem vessels. In spring, sucrose moves from storage areas in roots to growing areas like leaves and shoots where it's needed for growth.
Quick Check: Remember that xylem transports water UP from roots, whilst phloem transports sugars in ALL directions depending on the plant's needs.
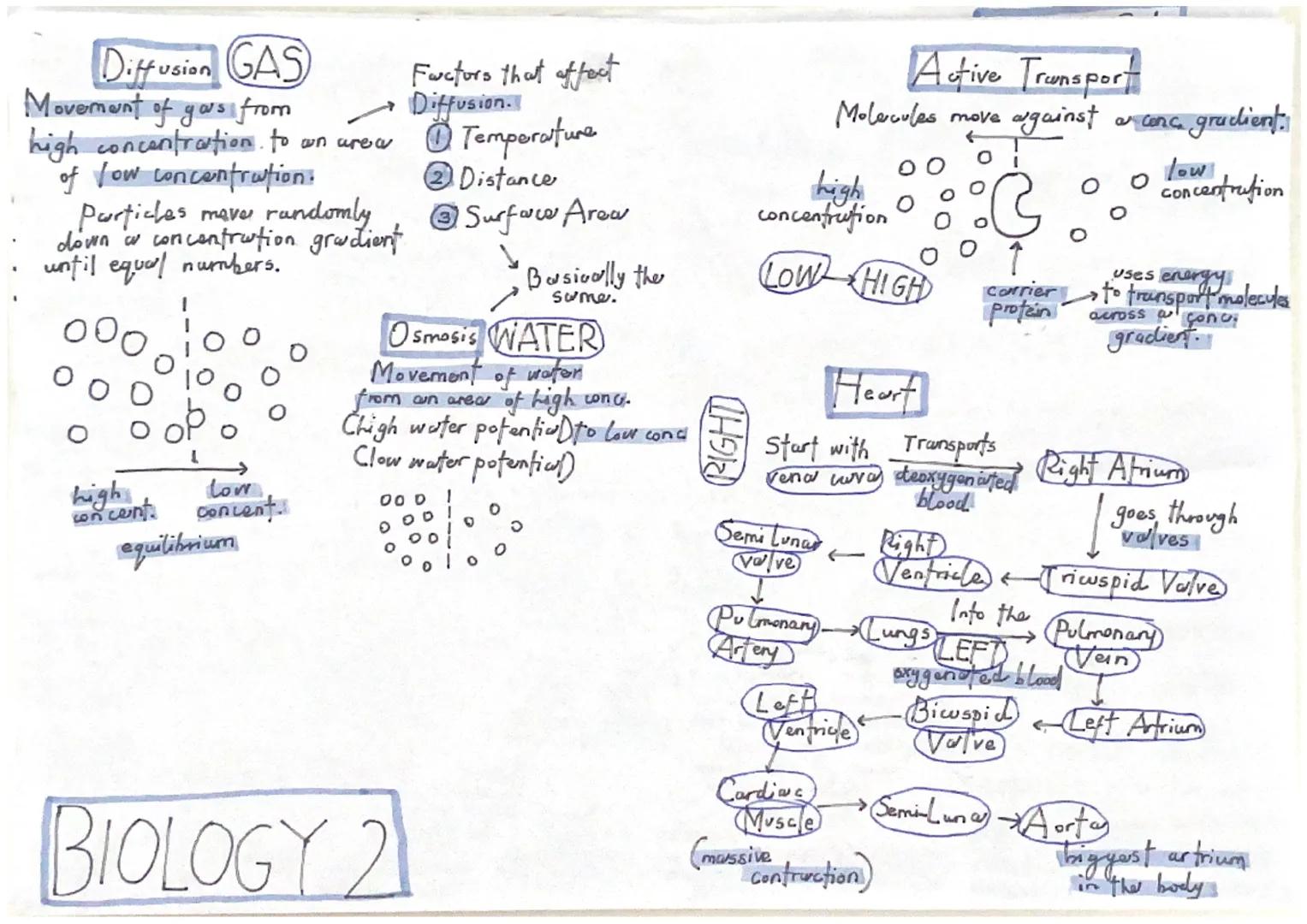
Gas exchange happens through diffusion - oxygen moves from areas of high concentration in your lungs to low concentration in your blood. Carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction. This process is affected by temperature, distance, and surface area.
Understanding how your heart works is essential. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the vena cava, passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle, then gets pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. Oxygenated blood returns through pulmonary veins to the left atrium, passes through the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle, then gets pumped around your body through the aorta.
Active transport requires energy because molecules move against their concentration gradient - from low to high concentration. Carrier proteins embedded in cell membranes facilitate this process, using energy from respiration to transport specific molecules.
The heart's cardiac muscle contracts powerfully to maintain blood circulation. Semi-lunar valves prevent blood flowing backwards into the ventricles after each heartbeat.
Exam Tip: Trace blood flow through the heart step-by-step - right atrium → right ventricle → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → body.
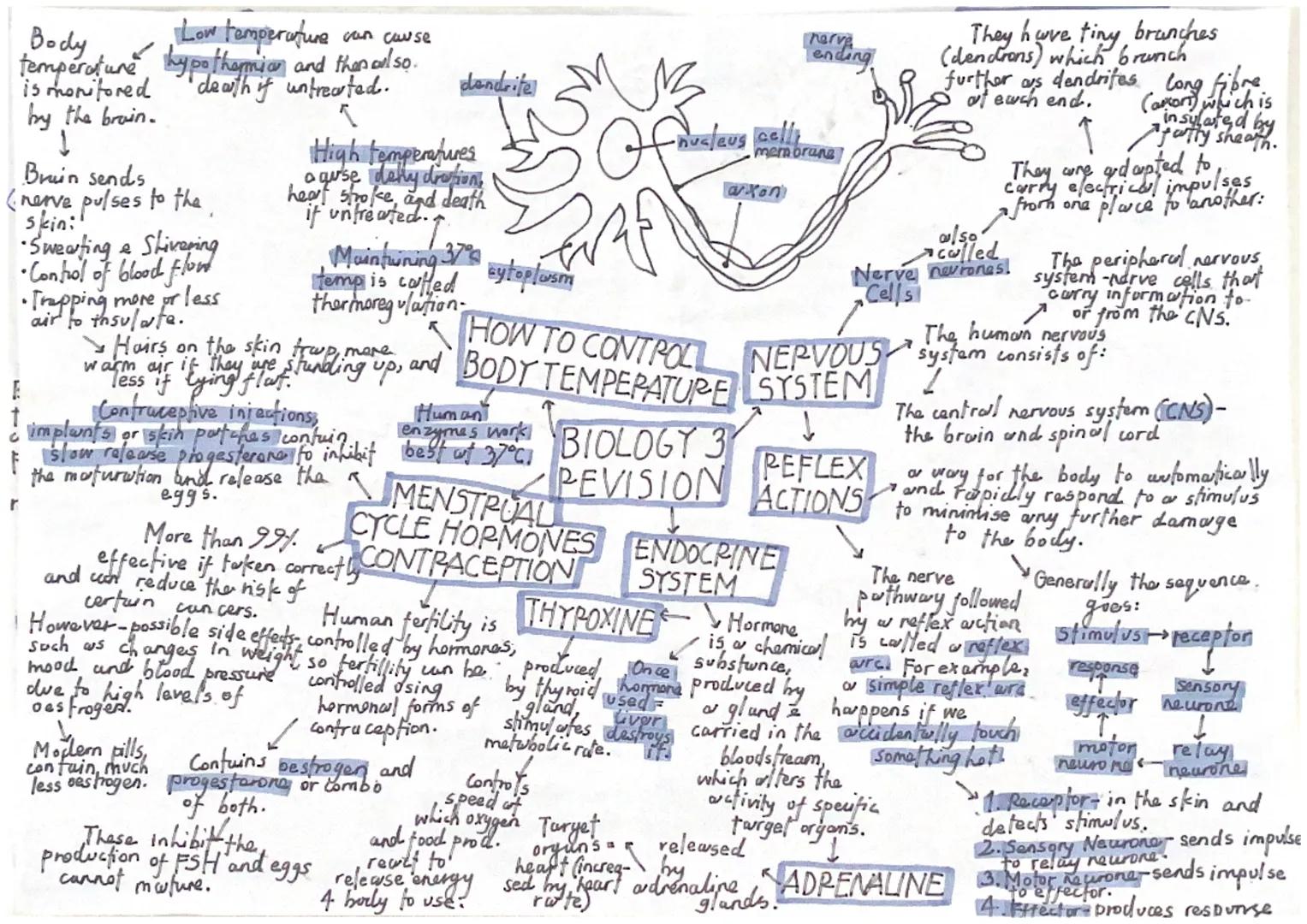
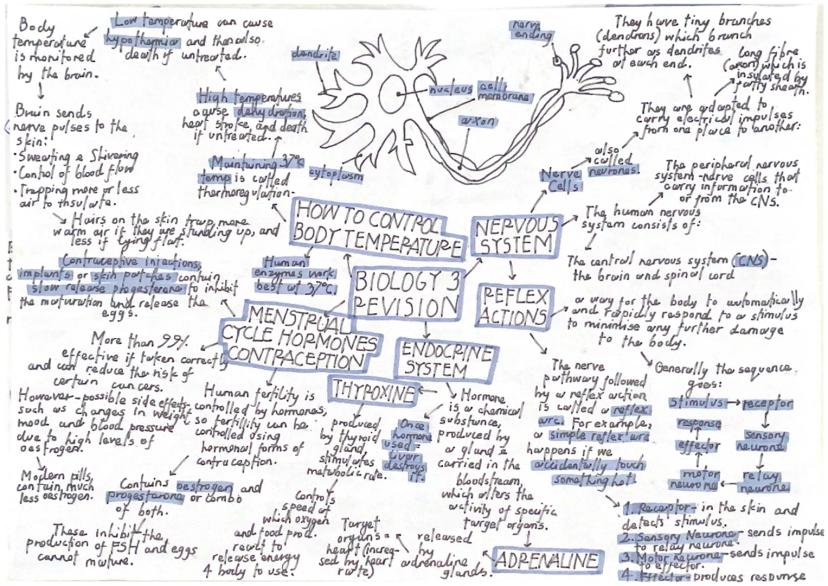
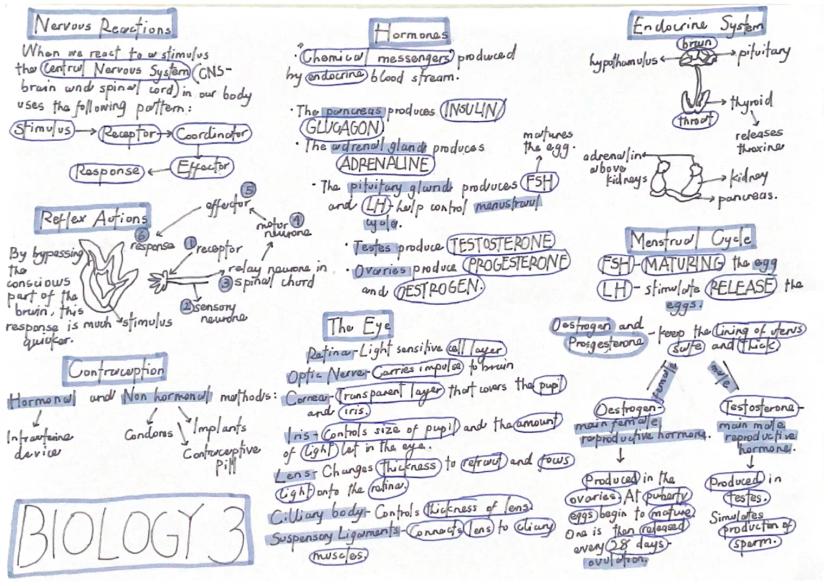
Your nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (all other nerves). Neurons are specially adapted cells with dendrites to receive signals, a long axon to carry impulses, and a fatty sheath for insulation.
Reflex actions protect you from harm by providing automatic, rapid responses. The pathway goes: stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → relay neuron → motor neuron → effector → response. By bypassing conscious thought, reflexes are much faster than normal reactions.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands and carried in your bloodstream to target organs. Adrenaline from adrenal glands increases heart rate and breathing during stress. Thyroxine from the thyroid controls your metabolic rate.
Thermoregulation maintains your body temperature at 37°C because human enzymes work best at this temperature. Your brain monitors temperature and controls responses like sweating, shivering, and blood flow to skin. High temperatures cause heat stroke, whilst low temperatures cause hypothermia.
The contraceptive pill contains oestrogen and progesterone to prevent pregnancy by inhibiting FSH production, stopping egg maturation.
Body Fact: Your nervous system can send signals at speeds up to 120 metres per second - faster than most cars drive through towns!
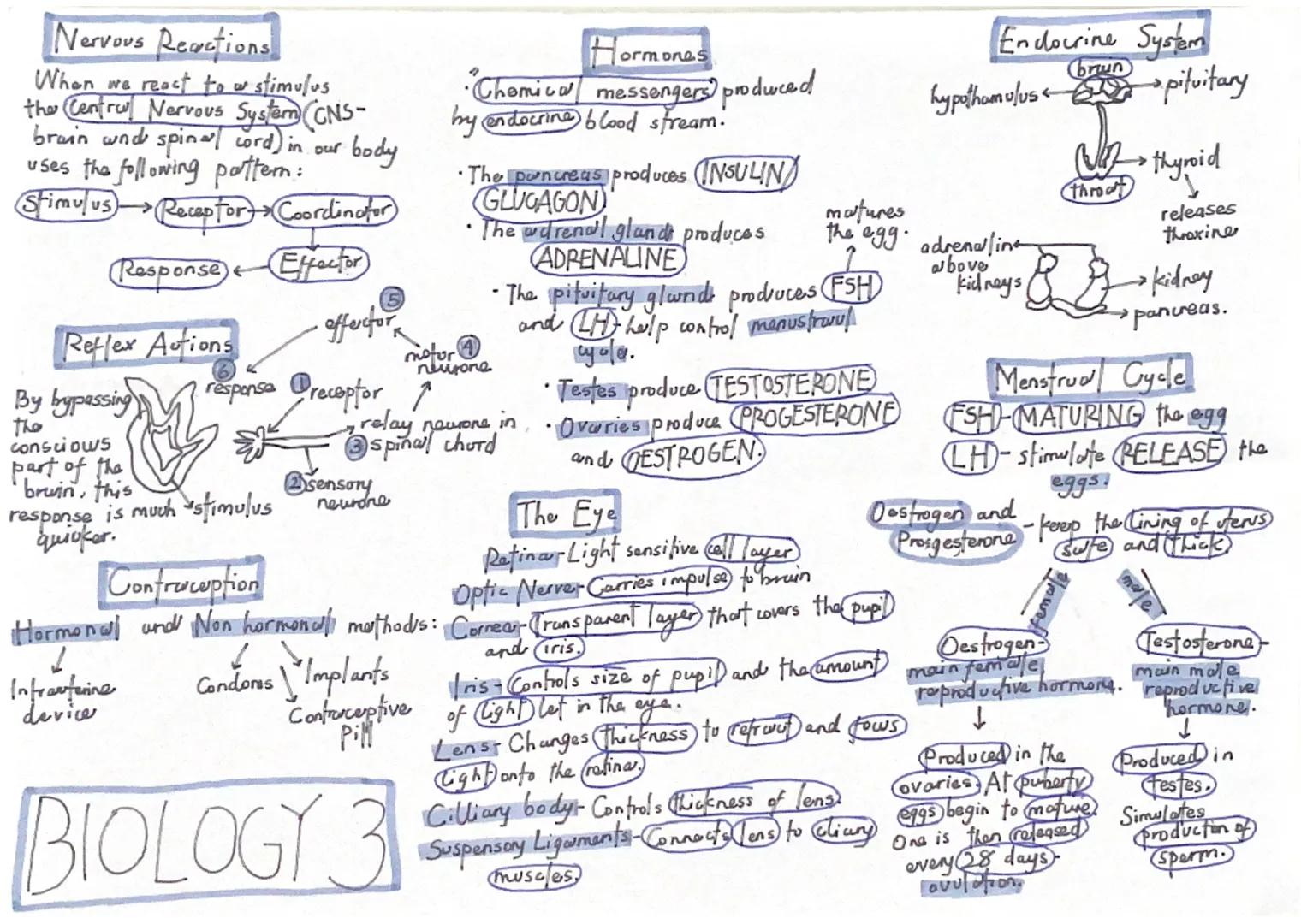
The endocrine system produces hormones that control many body functions. Key glands include the pancreas (insulin and glucagon), adrenal glands (adrenaline), pituitary gland (FSH and LH), testes (testosterone), and ovaries (oestrogen and progesterone).
The menstrual cycle is controlled by four main hormones. FSH causes eggs to mature, LH triggers ovulation (egg release), whilst oestrogen and progesterone maintain the uterus lining. This 28-day cycle repeats from puberty until menopause.
Testosterone is the main male reproductive hormone produced in testes. It stimulates sperm production and controls male secondary sexual characteristics. Oestrogen is the main female reproductive hormone that triggers egg maturation and controls the menstrual cycle.
Your eye is perfectly designed for vision. The cornea and lens focus light onto the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells. The iris controls pupil size to regulate light entry, whilst ciliary muscles change lens thickness for focusing on near or distant objects.
Contraception methods include hormonal options (pills, injections, implants) and barrier methods (condoms, intrauterine devices). Hormonal methods are over 99% effective when used correctly.
Hormone Hub: The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" because it produces hormones that control other glands throughout your body.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
revision
@revision17
This biology revision guide covers everything from the basic building blocks of cells to complex body systems. You'll master essential concepts like DNA structure, how enzymes work, photosynthesis, and how your nervous system controls your body's responses.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Every living thing is made of cells, and understanding their structure is your foundation for all biology. Animal cells contain a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes. Plant cells have all of these plus a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) are much simpler and smaller than the cells in your body. They don't have a proper nucleus - instead, their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. These bacterial cells are typically 0.2-2.0µm in size, whilst your cells are much larger at 10-100µm.
DNA has a famous double helix structure discovered by Watson and Crick. It's made of four bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Remember that A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C - this is crucial for DNA replication.
Quick Tip: All enzyme names end in "-ase" - carbohydrase breaks down carbohydrates, protease breaks down proteins, and lipase breaks down fats!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions in your body using the lock and key theory. Each enzyme has a specific active site that perfectly matches its substrate molecule, making enzymes highly specific. Temperature and pH changes can affect how well enzymes work.
Photosynthesis happens in chloroplasts and uses chlorophyll to capture light energy. The equation is: carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen. This endothermic reaction requires light energy and is affected by light intensity, CO₂ concentration, and temperature.
Respiration occurs in mitochondria and releases energy from glucose. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water. Anaerobic respiration happens without oxygen - in muscles it produces lactic acid, whilst in yeast it produces ethanol and CO₂.
Using microscopes properly is essential for observing cells. Light microscopes use visible light and are great for basic cell observation, whilst electron microscopes provide much higher magnification for detailed structures.
Remember: Photosynthesis makes food using light energy, whilst respiration breaks down food to release energy - they're opposite processes!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Before any cell divides, it must copy its entire genome through DNA replication. This process has seven key steps: initiation, primer synthesis, leading strand synthesis, lagging strand synthesis, primer removal, ligation, and termination. Each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the parent's DNA.
Mitosis is how your body grows and repairs damage. The cell cycle includes growth phases, DNA synthesis, error-checking, and finally mitosis itself. Two identical daughter cells are produced, each containing the same genetic information as the parent cell.
Understanding factors affecting photosynthesis is crucial for your exams. Without sufficient light intensity, plants cannot photosynthesise quickly even with plenty of water and CO₂. Similarly, inadequate carbon dioxide concentration limits the process, and temperatures that are too cold slow down the rate significantly.
Stomata are tiny pores that let carbon dioxide enter and exit leaves. They're essential for gas exchange during photosynthesis, allowing CO₂ to diffuse from the air into the plant.
Exam Focus: Learn the photosynthesis equation by heart - it appears in most biology papers and understanding it helps with limiting factors questions.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Three main processes move substances across cell membranes: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentration - no energy needed. Think of how a scent spreads across a room.
Osmosis is specifically the movement of water molecules from high water potential to low water potential through a partially permeable membrane. When plant cells gain water by osmosis, they become turgid (swollen). When they lose water, they shrivel.
Active transport is different because it moves substances against the concentration gradient from low to high concentration. This requires energy from respiration and uses special carrier proteins to transport specific molecules across membranes.
Water potential measures the tendency of water molecules to move. Pure water has high water potential, whilst salty solutions have low water potential. Water always moves from high to low water potential via osmosis.
Memory Trick: Active transport goes "uphill" against the gradient, so it needs energy like climbing a mountain needs effort!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your heart pumps blood through a double circulatory system with two separate circuits. The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, whilst the left side pumps oxygenated blood around your body. The heart has four chambers with valves preventing backflow.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart under high pressure and have thick muscular walls. Veins return blood to the heart under low pressure and contain valves. Capillaries are microscopic vessels where gas exchange occurs between blood and tissues.
Plants have their own transport systems. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from roots to other plant parts. These vessels are made of dead cells with tough walls containing lignin for strength. Phloem consists of living cells that transport sugars like sucrose around the plant.
Translocation is the movement of dissolved sugars through phloem vessels. In spring, sucrose moves from storage areas in roots to growing areas like leaves and shoots where it's needed for growth.
Quick Check: Remember that xylem transports water UP from roots, whilst phloem transports sugars in ALL directions depending on the plant's needs.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Gas exchange happens through diffusion - oxygen moves from areas of high concentration in your lungs to low concentration in your blood. Carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction. This process is affected by temperature, distance, and surface area.
Understanding how your heart works is essential. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the vena cava, passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle, then gets pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. Oxygenated blood returns through pulmonary veins to the left atrium, passes through the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle, then gets pumped around your body through the aorta.
Active transport requires energy because molecules move against their concentration gradient - from low to high concentration. Carrier proteins embedded in cell membranes facilitate this process, using energy from respiration to transport specific molecules.
The heart's cardiac muscle contracts powerfully to maintain blood circulation. Semi-lunar valves prevent blood flowing backwards into the ventricles after each heartbeat.
Exam Tip: Trace blood flow through the heart step-by-step - right atrium → right ventricle → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → body.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (all other nerves). Neurons are specially adapted cells with dendrites to receive signals, a long axon to carry impulses, and a fatty sheath for insulation.
Reflex actions protect you from harm by providing automatic, rapid responses. The pathway goes: stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → relay neuron → motor neuron → effector → response. By bypassing conscious thought, reflexes are much faster than normal reactions.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands and carried in your bloodstream to target organs. Adrenaline from adrenal glands increases heart rate and breathing during stress. Thyroxine from the thyroid controls your metabolic rate.
Thermoregulation maintains your body temperature at 37°C because human enzymes work best at this temperature. Your brain monitors temperature and controls responses like sweating, shivering, and blood flow to skin. High temperatures cause heat stroke, whilst low temperatures cause hypothermia.
The contraceptive pill contains oestrogen and progesterone to prevent pregnancy by inhibiting FSH production, stopping egg maturation.
Body Fact: Your nervous system can send signals at speeds up to 120 metres per second - faster than most cars drive through towns!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The endocrine system produces hormones that control many body functions. Key glands include the pancreas (insulin and glucagon), adrenal glands (adrenaline), pituitary gland (FSH and LH), testes (testosterone), and ovaries (oestrogen and progesterone).
The menstrual cycle is controlled by four main hormones. FSH causes eggs to mature, LH triggers ovulation (egg release), whilst oestrogen and progesterone maintain the uterus lining. This 28-day cycle repeats from puberty until menopause.
Testosterone is the main male reproductive hormone produced in testes. It stimulates sperm production and controls male secondary sexual characteristics. Oestrogen is the main female reproductive hormone that triggers egg maturation and controls the menstrual cycle.
Your eye is perfectly designed for vision. The cornea and lens focus light onto the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells. The iris controls pupil size to regulate light entry, whilst ciliary muscles change lens thickness for focusing on near or distant objects.
Contraception methods include hormonal options (pills, injections, implants) and barrier methods (condoms, intrauterine devices). Hormonal methods are over 99% effective when used correctly.
Hormone Hub: The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" because it produces hormones that control other glands throughout your body.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
8
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the key processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in this comprehensive summary. Understand the roles of chlorophyll, glucose, and the factors affecting photosynthesis rates. Learn about aerobic and anaerobic respiration, their significance in energy transfer, and how organisms utilize energy for growth and movement. Ideal for GCSE AQA Biology students.
Explore the key processes of photosynthesis, including the role of chlorophyll, chloroplasts, and the factors affecting plant growth. This summary covers the photosynthesis equation, leaf adaptations, and practical experiments for testing starch presence. Ideal for AQA GCSE Biology students seeking to enhance their understanding of plant productivity and respiration.
Explore the impact of temperature and pH on enzyme activity, along with essential food tests for carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. This summary covers key concepts in biological molecules and enzyme kinetics, ideal for IGCSE Edexcel Biology students aiming for top grades.
Explore the key concepts of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, including aerobic and anaerobic processes, energy transfer, and the impact of environmental factors. This summary covers essential topics such as glucose metabolism, oxygen debt, and the role of chloroplasts in energy production. Ideal for AQA GCSE Biology students preparing for exams.
Explore the essential processes of photosynthesis and respiration in this comprehensive overview. Understand the key steps, equations, and factors affecting these metabolic pathways. This summary covers light-dependent and light-independent reactions, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, and the role of glucose in energy production. Ideal for students seeking clarity on bioenergetics concepts.
Prepare for your Year 10 Biology exam with this comprehensive overview covering key topics such as cellular respiration, the immune system, enzymes, and photosynthesis. Understand the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration, the role of enzymes in digestion, and the mechanisms of vaccination and antibiotic resistance. This summary is essential for mastering biological concepts and excelling in your mock exams.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user