The heart and human body cells work together as a... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
858
•
5 Feb 2026
•
lima
@lima_gbpl
The heart and human body cells work together as a... Show more




Your heart is a pumping organ that keeps blood flowing throughout your body. Its special valves ensure blood flows in the correct direction and prevent it from flowing backwards. The heart has four chambers: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, and right ventricle.
Blood enters the heart through the vena cava and pulmonary vein into the atria. When the atria contract, blood is forced into the ventricles. The ventricles then push blood out through the pulmonary artery and aorta. This creates a continuous cycle as blood flows to organs through arteries and returns through veins.
The heart needs its own blood supply to function. Coronary arteries branch from the aorta and surround the heart, providing it with the oxygenated blood it needs. Other important blood vessels include arteries (which carry blood away from the heart), capillaries (where exchange occurs at tissues), and veins (which return blood to the heart).
Did you know? The heart has its own natural pacemaker! A special group of cells in the right atrium produces electrical impulses that control the heart's rhythm. Some people need artificial pacemakers to help their hearts beat regularly.

Your body contains cells with 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs (half from mum, half from dad). The cell cycle, which takes less than 24 hours, involves mitosis to produce two identical daughter cells. During this process, the genetic material is doubled to ensure each new cell gets a complete set of chromosomes.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into many different cell types. They're incredibly important for growth and development. In humans, egg and sperm cells fuse to form a zygote (a single cell), which then divides and becomes an embryo. The cell cycle has three main stages: growth and DNA replication, division of chromosomes, and division of cytoplasm and cell membrane.
Stem cells have enormous potential for medicine and research. In plants, they can be used to produce clones quickly, which helps preserve rare species from extinction. Scientists can also use them to study how genetic changes affect development.
Important! Enzymes are biological catalysts that control chemical reactions in living organisms. Their specific shape allows them to join with substrate molecules, which is vital for their function.

You can identify different food molecules through simple chemical tests. The general preparation involves grinding up food, mixing it with distilled water, stirring well, and filtering to remove solid bits before testing.
The Benedict's test identifies reducing sugars. After preparing 5cm³ of food sample in a test tube, heat it to 75°C in a water bath with Benedict's solution for 5 minutes. If reducing sugars are present, the solution changes from blue to green, yellow, or brick red depending on concentration.
For starch, use the iodine test - add a few drops of iodine solution to 5cm³ of food sample and gently shake. The solution will change from brownish-orange to black or dark blue if starch is present. The Biuret test identifies proteins - add 2cm³ of Biuret solution to your sample and if it turns from blue to purple, proteins are present. To test for lipids, use the Sudan III test - add 3 drops to your sample and if lipids are present, the mixture separates into two layers with the top layer turning red.
Exam tip: Remember the specific color changes for each test - they're commonly asked about in assessments and practical exams!
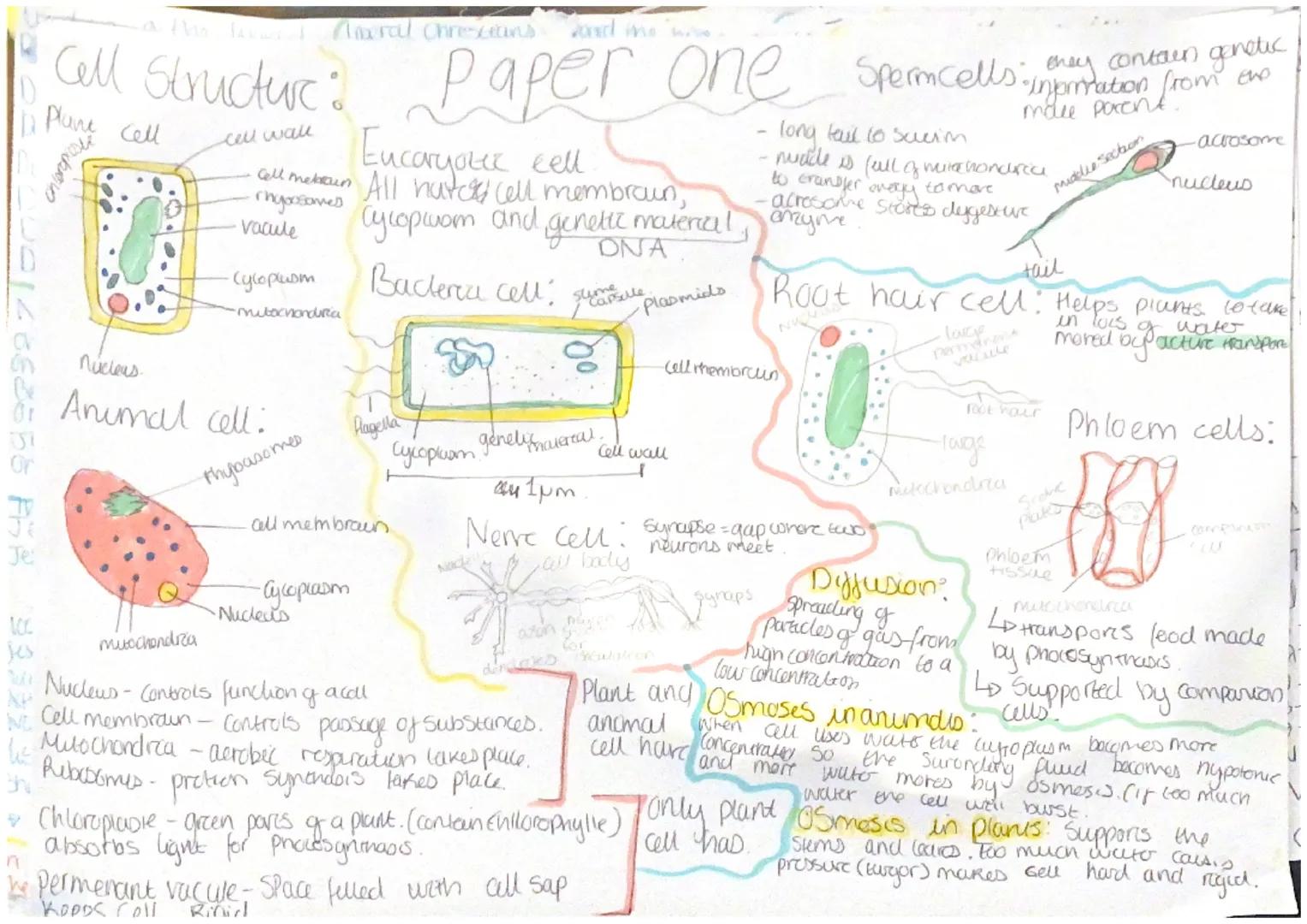
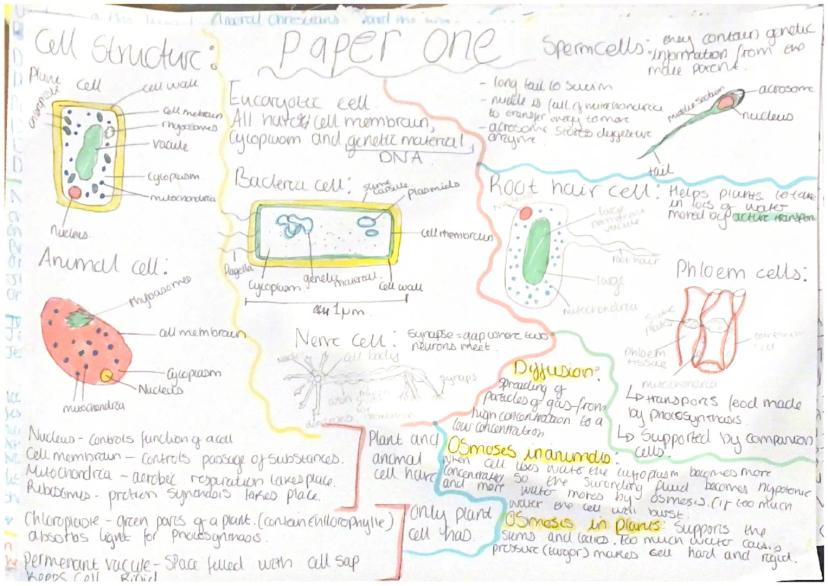
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic cells with important structures. Plant cells have additional features like a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a permanent vacuole. Animal cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondria. The nucleus controls cell function and contains genetic material, while mitochondria are where aerobic respiration takes place.
Specialized cells have adapted structures for specific functions. Sperm cells have a long tail to swim, mitochondria for energy, and an acrosome with digestive enzymes. Root hair cells help plants absorb water and minerals through their large surface area. Nerve cells have long axons for transmitting electrical impulses and form synapses (gaps where neurons meet).
Diffusion is the spreading of particles from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Osmosis is specifically the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane. In plants, osmosis creates turgor pressure which makes cells rigid and supports stems and leaves.
Connect the dots: The transport systems in plants work much like your circulatory system. Phloem tissue transports food made during photosynthesis throughout the plant, similar to how blood carries nutrients around your body.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
lima
@lima_gbpl
The heart and human body cells work together as a remarkable biological system. This summary explores how the heart pumps blood throughout the body, the process of cell division, food testing methods, and the structure of different cell types. Understanding... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your heart is a pumping organ that keeps blood flowing throughout your body. Its special valves ensure blood flows in the correct direction and prevent it from flowing backwards. The heart has four chambers: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, and right ventricle.
Blood enters the heart through the vena cava and pulmonary vein into the atria. When the atria contract, blood is forced into the ventricles. The ventricles then push blood out through the pulmonary artery and aorta. This creates a continuous cycle as blood flows to organs through arteries and returns through veins.
The heart needs its own blood supply to function. Coronary arteries branch from the aorta and surround the heart, providing it with the oxygenated blood it needs. Other important blood vessels include arteries (which carry blood away from the heart), capillaries (where exchange occurs at tissues), and veins (which return blood to the heart).
Did you know? The heart has its own natural pacemaker! A special group of cells in the right atrium produces electrical impulses that control the heart's rhythm. Some people need artificial pacemakers to help their hearts beat regularly.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body contains cells with 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs (half from mum, half from dad). The cell cycle, which takes less than 24 hours, involves mitosis to produce two identical daughter cells. During this process, the genetic material is doubled to ensure each new cell gets a complete set of chromosomes.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into many different cell types. They're incredibly important for growth and development. In humans, egg and sperm cells fuse to form a zygote (a single cell), which then divides and becomes an embryo. The cell cycle has three main stages: growth and DNA replication, division of chromosomes, and division of cytoplasm and cell membrane.
Stem cells have enormous potential for medicine and research. In plants, they can be used to produce clones quickly, which helps preserve rare species from extinction. Scientists can also use them to study how genetic changes affect development.
Important! Enzymes are biological catalysts that control chemical reactions in living organisms. Their specific shape allows them to join with substrate molecules, which is vital for their function.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
You can identify different food molecules through simple chemical tests. The general preparation involves grinding up food, mixing it with distilled water, stirring well, and filtering to remove solid bits before testing.
The Benedict's test identifies reducing sugars. After preparing 5cm³ of food sample in a test tube, heat it to 75°C in a water bath with Benedict's solution for 5 minutes. If reducing sugars are present, the solution changes from blue to green, yellow, or brick red depending on concentration.
For starch, use the iodine test - add a few drops of iodine solution to 5cm³ of food sample and gently shake. The solution will change from brownish-orange to black or dark blue if starch is present. The Biuret test identifies proteins - add 2cm³ of Biuret solution to your sample and if it turns from blue to purple, proteins are present. To test for lipids, use the Sudan III test - add 3 drops to your sample and if lipids are present, the mixture separates into two layers with the top layer turning red.
Exam tip: Remember the specific color changes for each test - they're commonly asked about in assessments and practical exams!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic cells with important structures. Plant cells have additional features like a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a permanent vacuole. Animal cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondria. The nucleus controls cell function and contains genetic material, while mitochondria are where aerobic respiration takes place.
Specialized cells have adapted structures for specific functions. Sperm cells have a long tail to swim, mitochondria for energy, and an acrosome with digestive enzymes. Root hair cells help plants absorb water and minerals through their large surface area. Nerve cells have long axons for transmitting electrical impulses and form synapses (gaps where neurons meet).
Diffusion is the spreading of particles from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Osmosis is specifically the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane. In plants, osmosis creates turgor pressure which makes cells rigid and supports stems and leaves.
Connect the dots: The transport systems in plants work much like your circulatory system. Phloem tissue transports food made during photosynthesis throughout the plant, similar to how blood carries nutrients around your body.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
7
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the stages of mitosis and the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. This summary highlights key processes such as DNA replication, chromosome alignment, and the formation of daughter cells, providing a clear understanding of cell division.
Explore the detailed stages of mitosis, including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. This summary covers key concepts of cell division, cellular regeneration, and the implications of uncontrolled cell division, such as cancer. Ideal for GCSE biology students.
Explore the fundamental concepts of cell biology, including prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, cell specialization, and the organization of tissues and organs. This summary covers the advantages of light and electron microscopes, key cellular structures, and the processes of cell differentiation. Ideal for GCSE Biology students preparing for exams.
Explore the fundamental concepts of cell biology, including cell structure, mitosis, and transport mechanisms. This summary covers key topics such as active transport, diffusion, and the roles of various cellular components. Ideal for students preparing for exams or seeking a concise overview of cellular functions.
Explore the intricacies of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and the regulatory checkpoints that ensure proper cell division. This summary covers key phases such as G1, Synthesis, G2, and mitotic processes, highlighting the importance of DNA replication and error-checking mechanisms. Ideal for A Level Biology students studying OCR A specifications.
Explore the processes of mitosis and cellular differentiation in both plants and animals. This summary covers the stages of mitosis, the role of parent and daughter cells, and how uncontrolled cell division can lead to cancer. Learn about specialized cells and growth patterns, including percentile charts for monitoring child growth. Ideal for biology students studying cell division and growth.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user