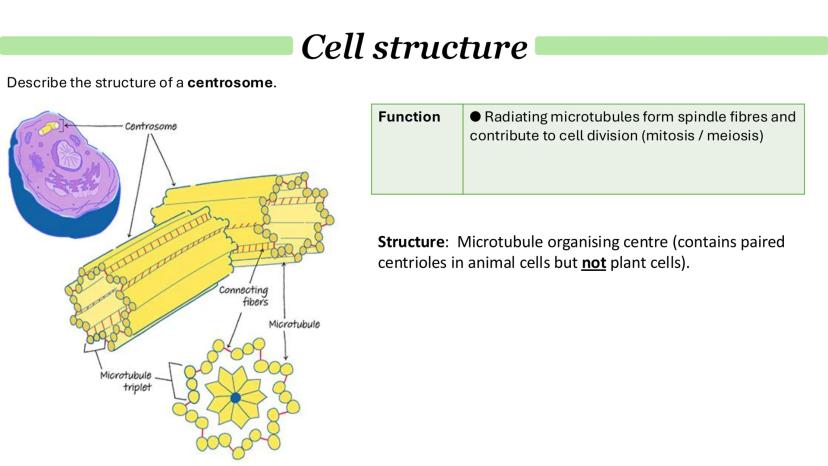
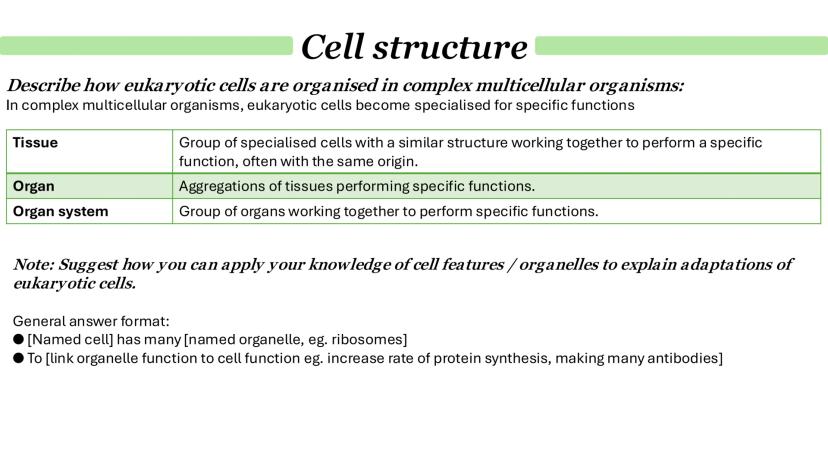
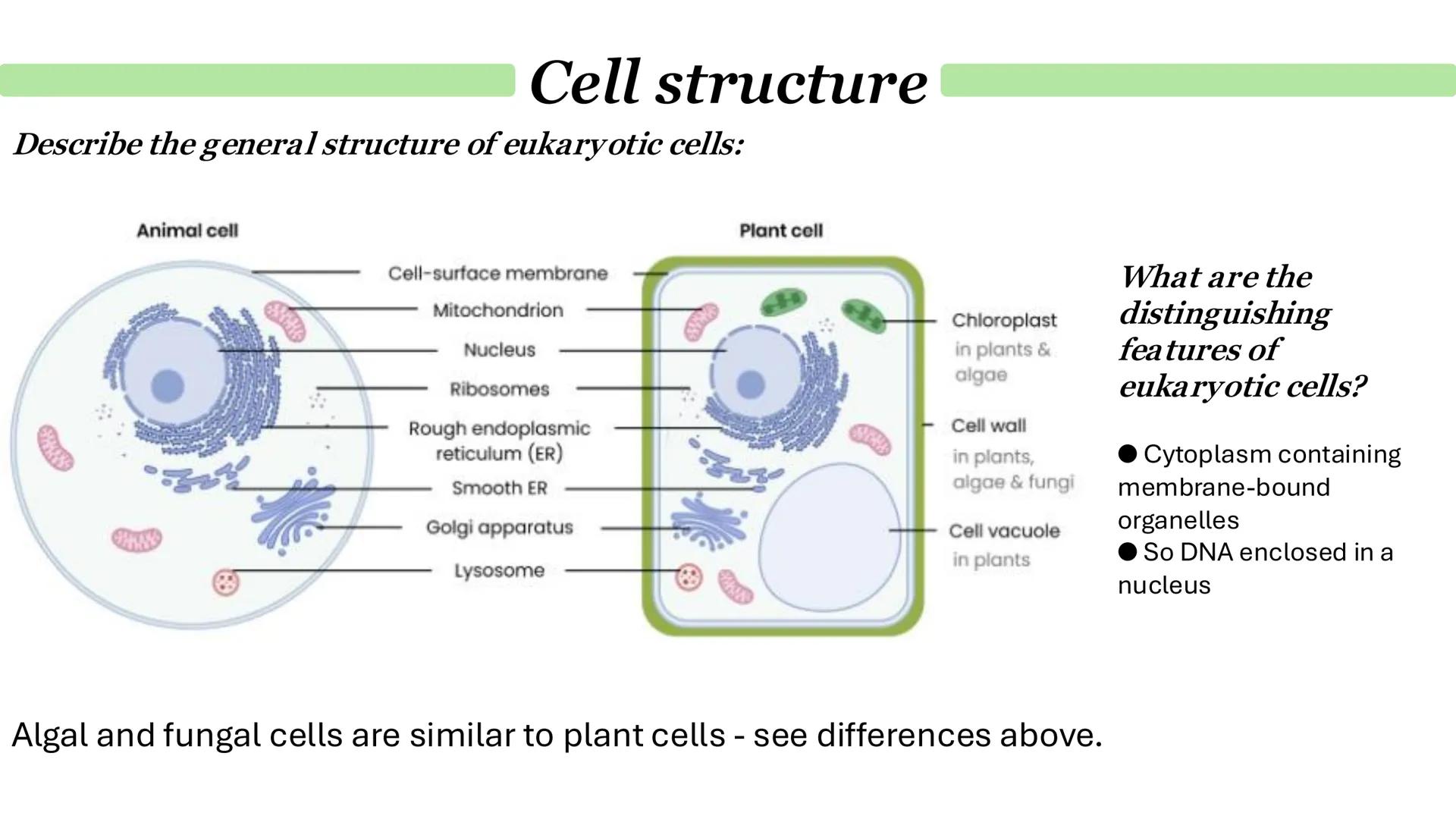
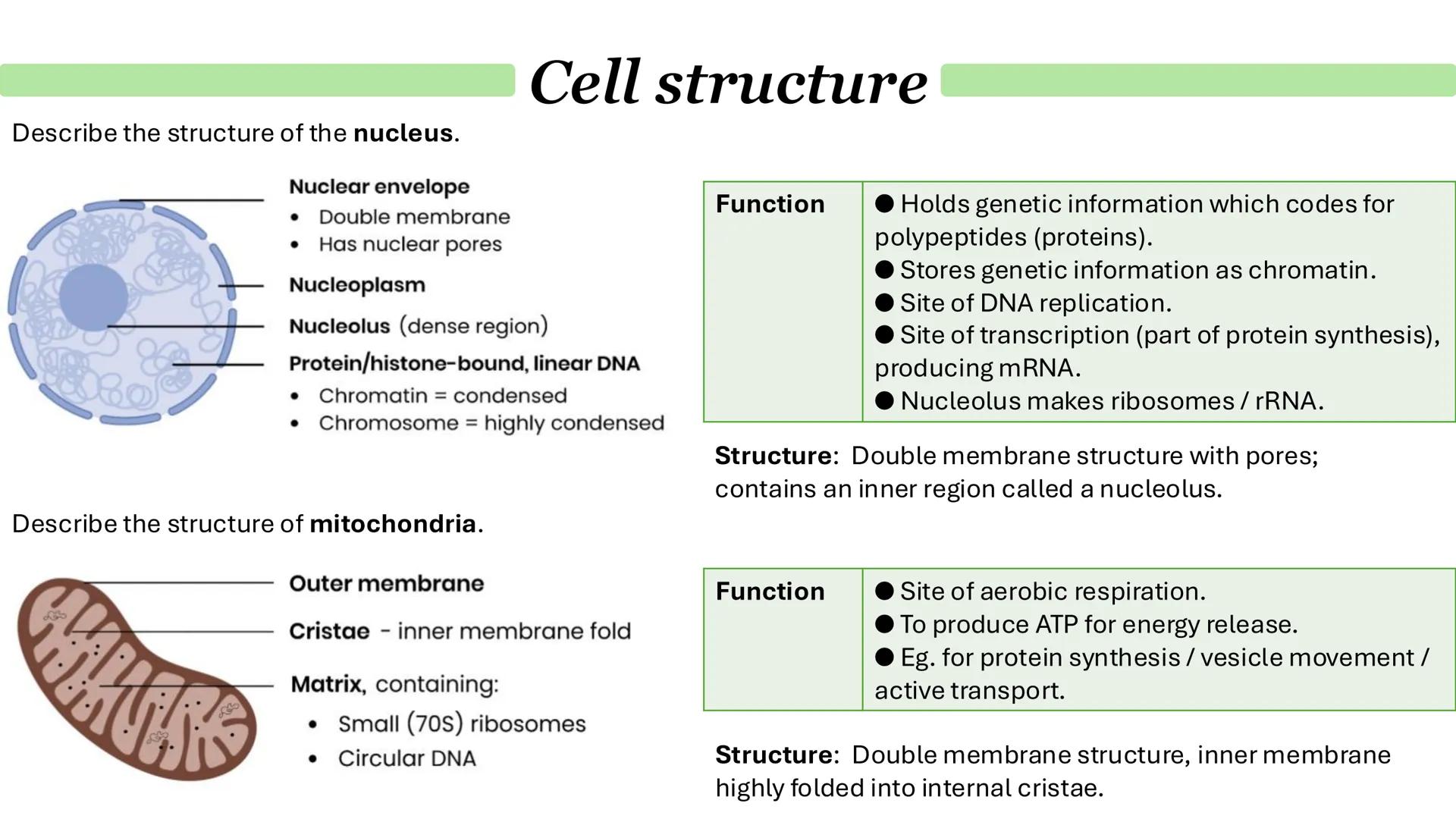
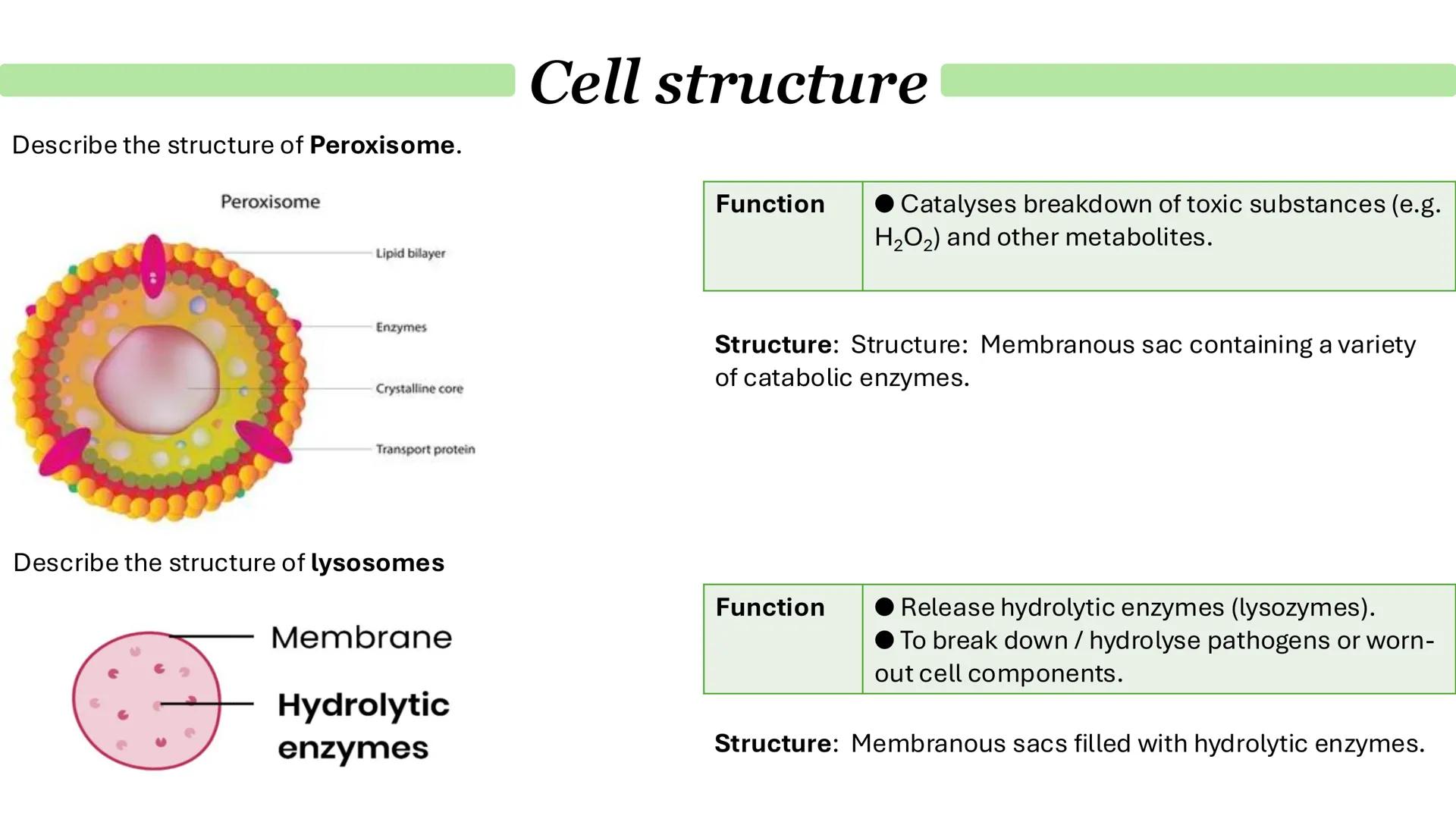
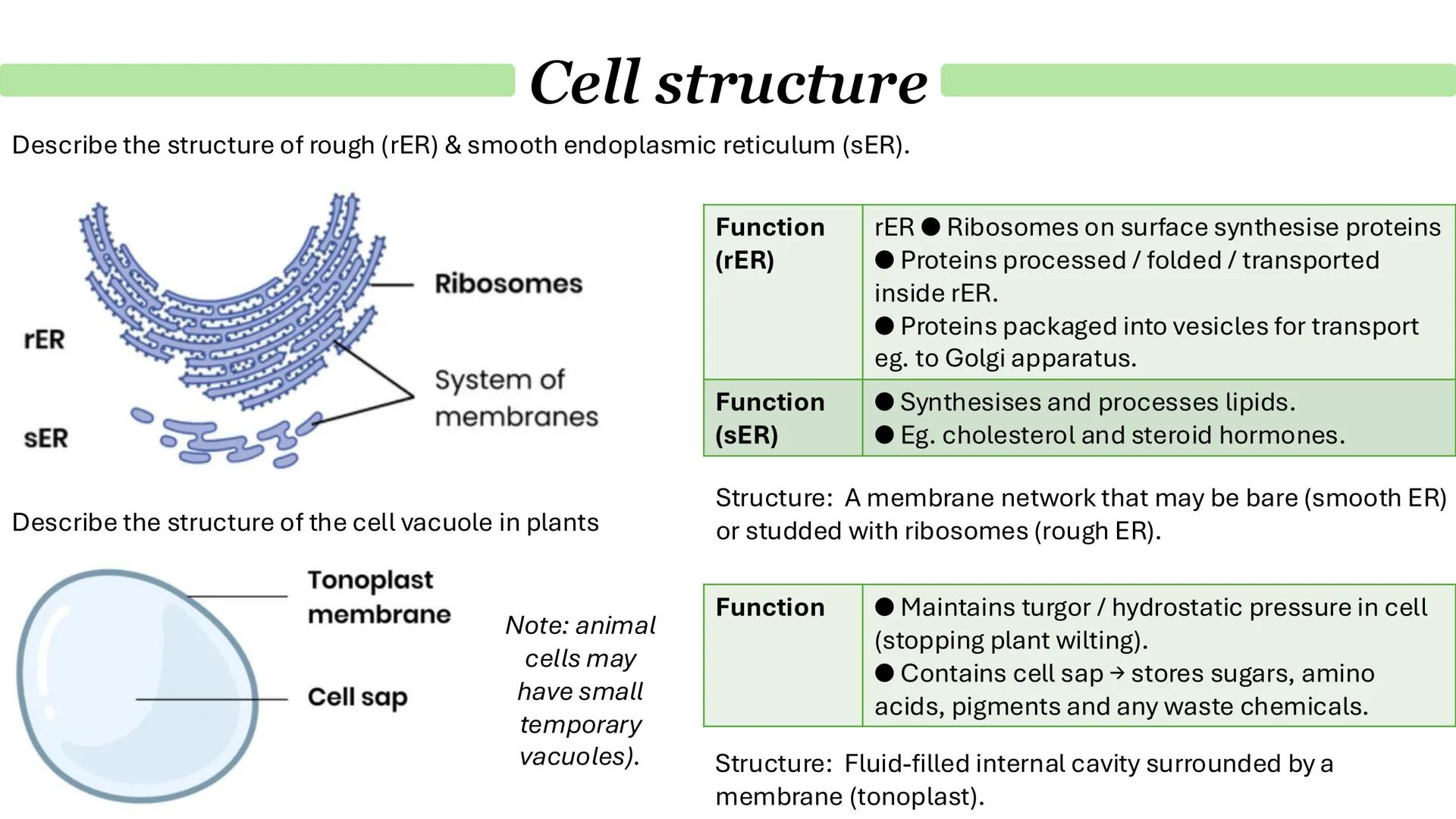
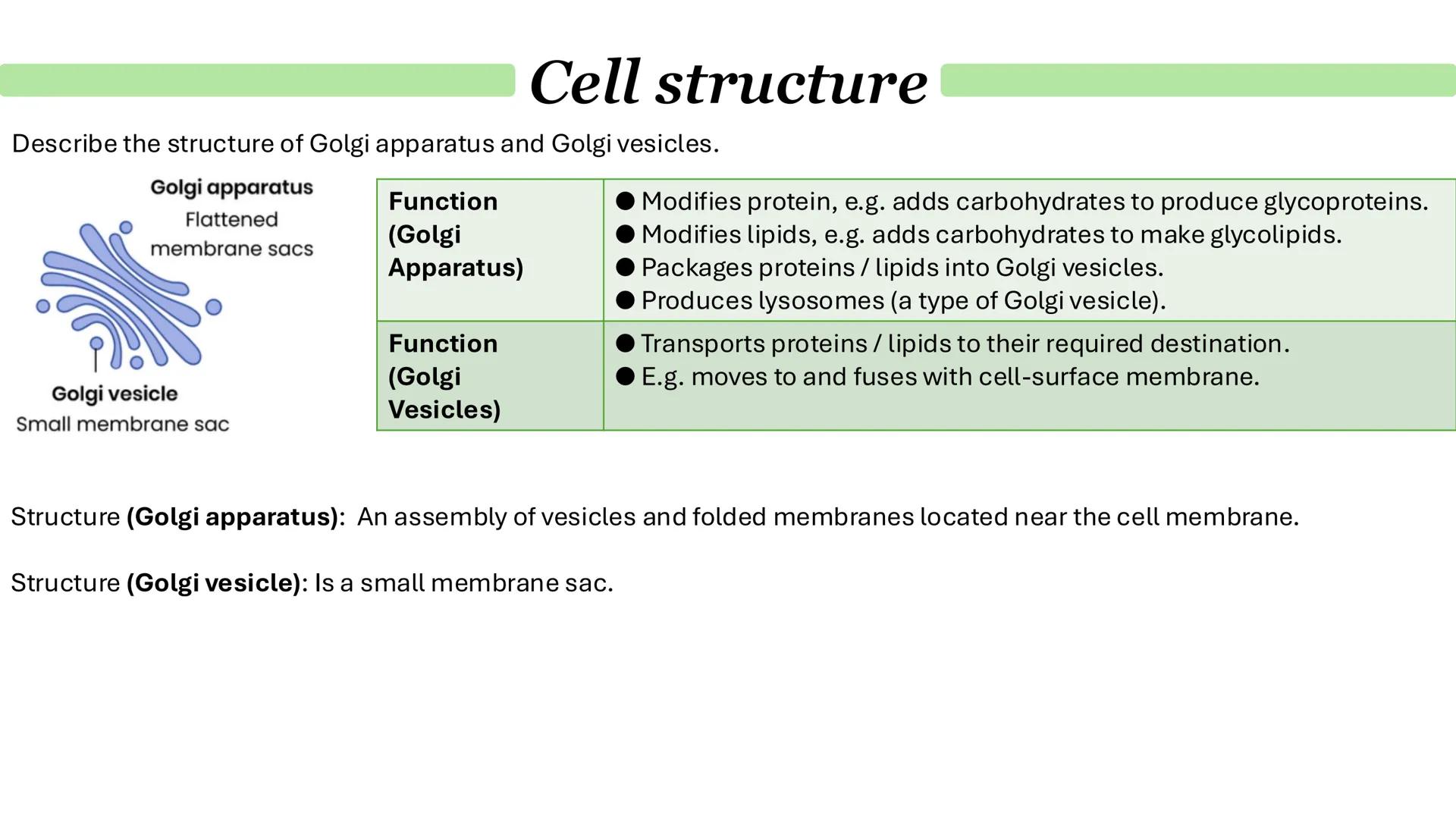
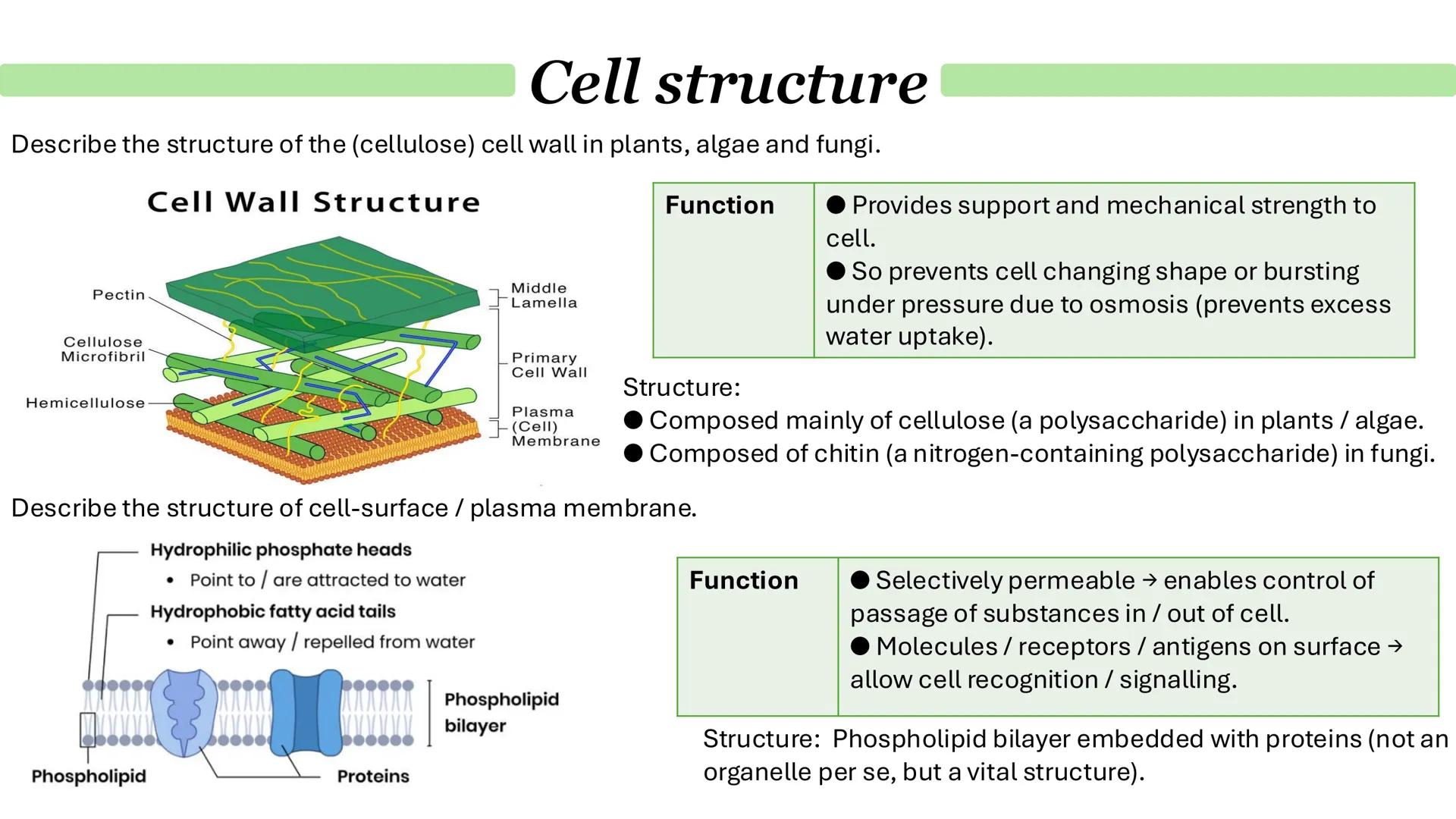
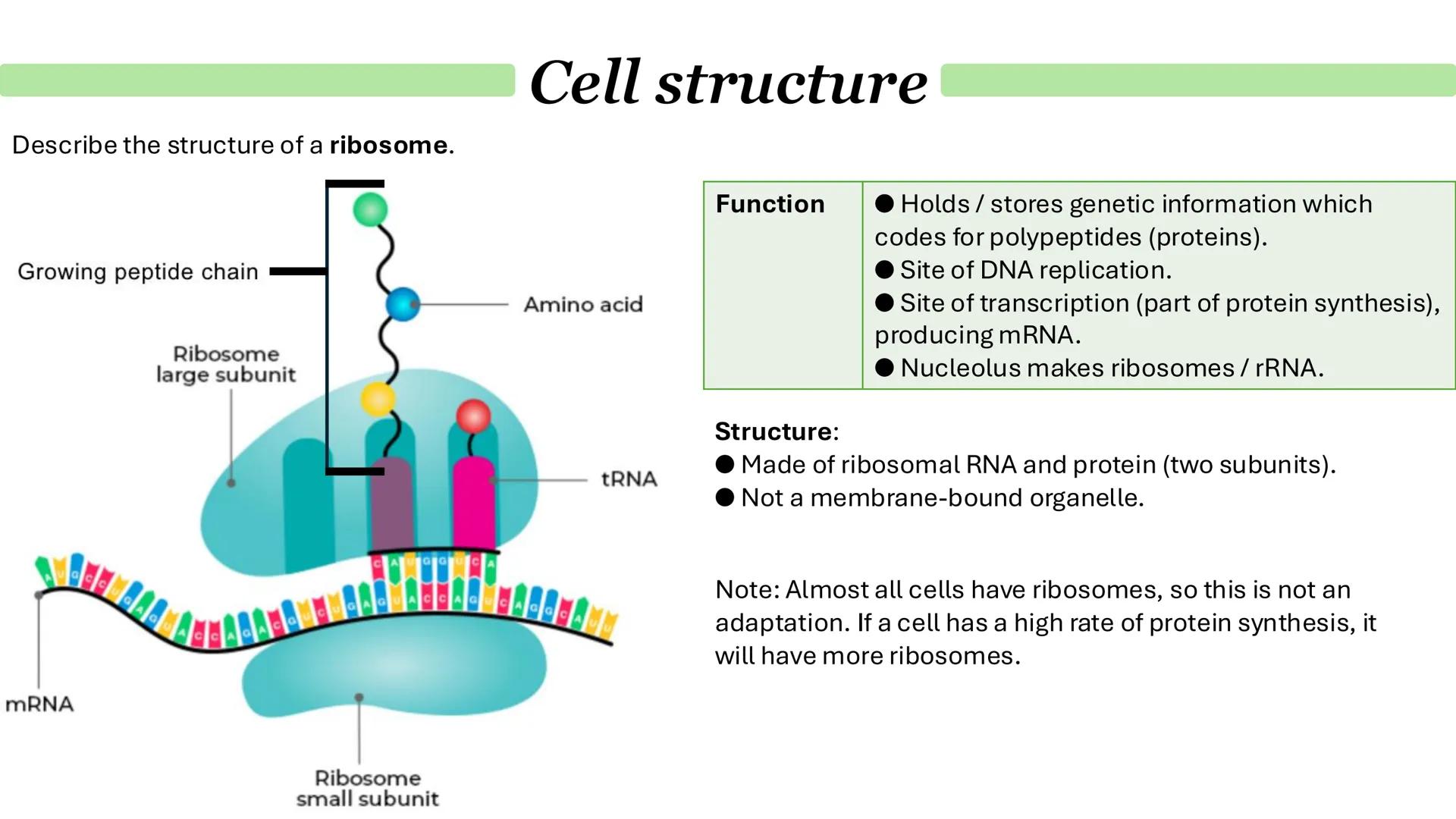
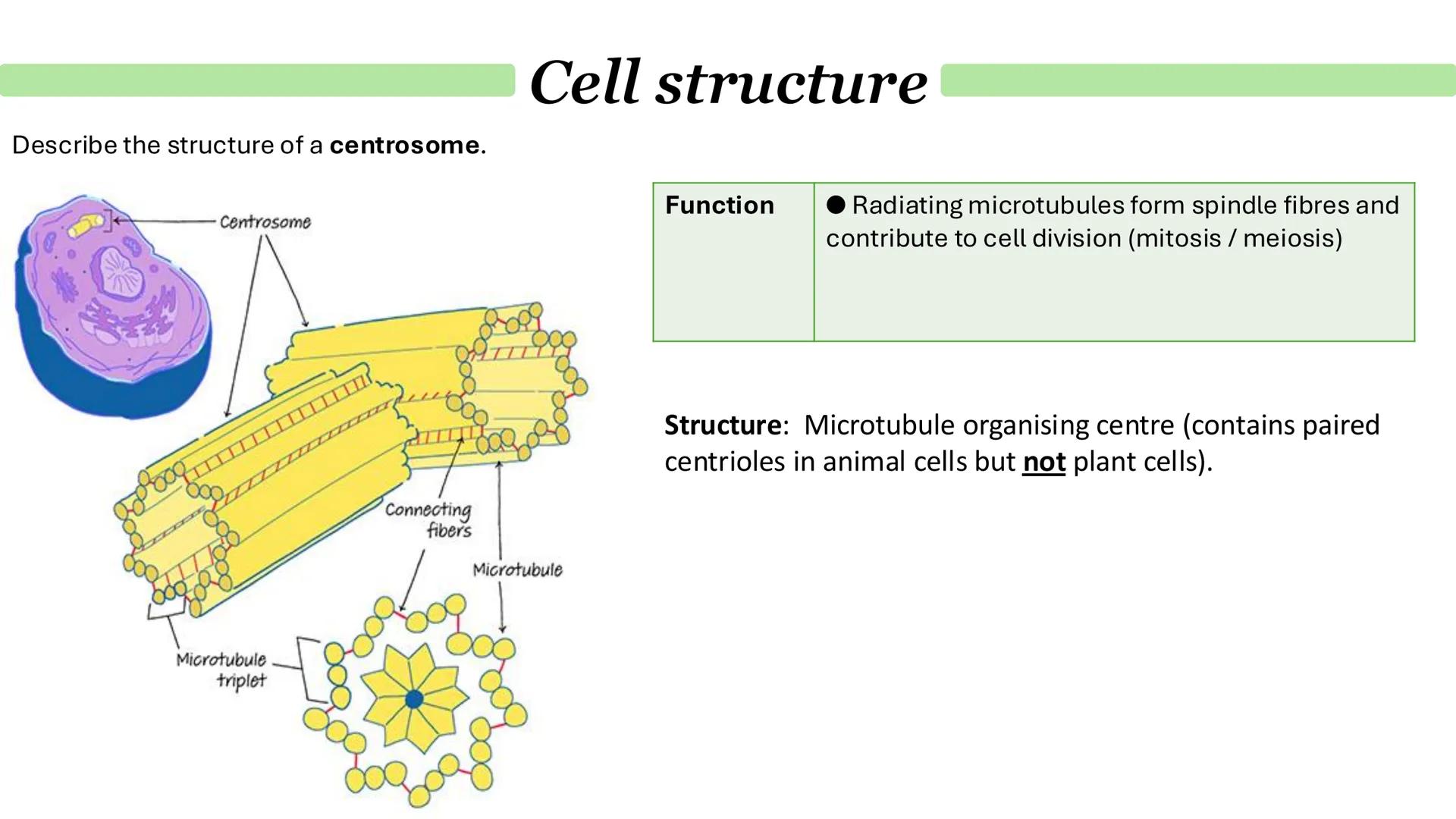
Chloroplasts and Endosymbiosis
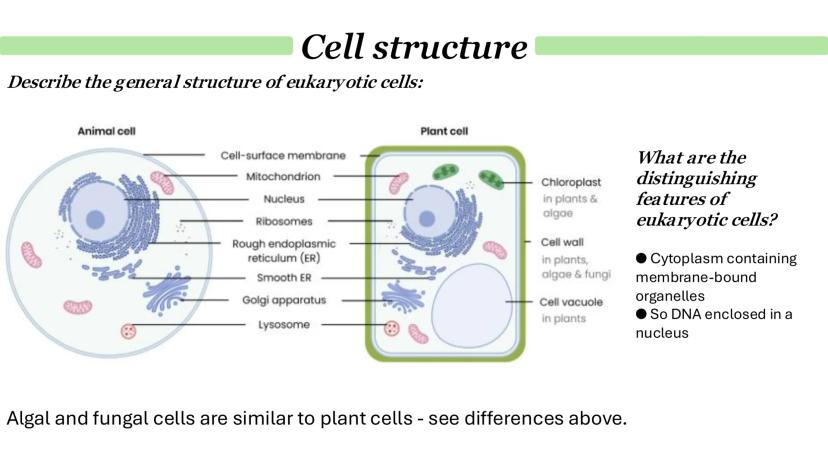
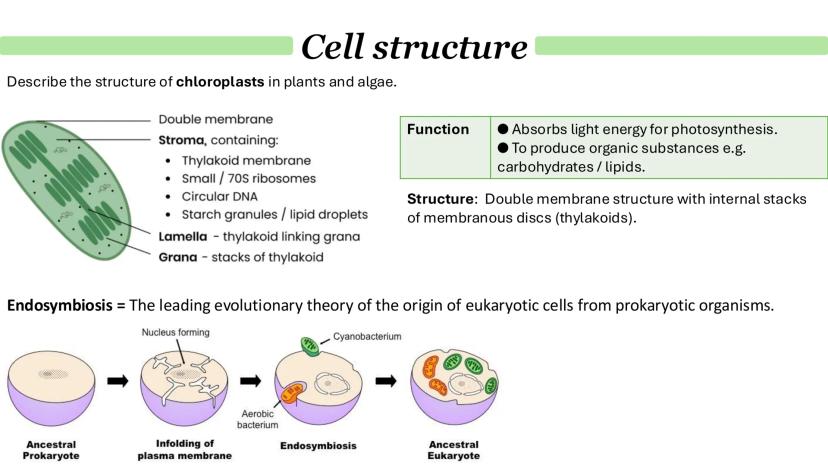
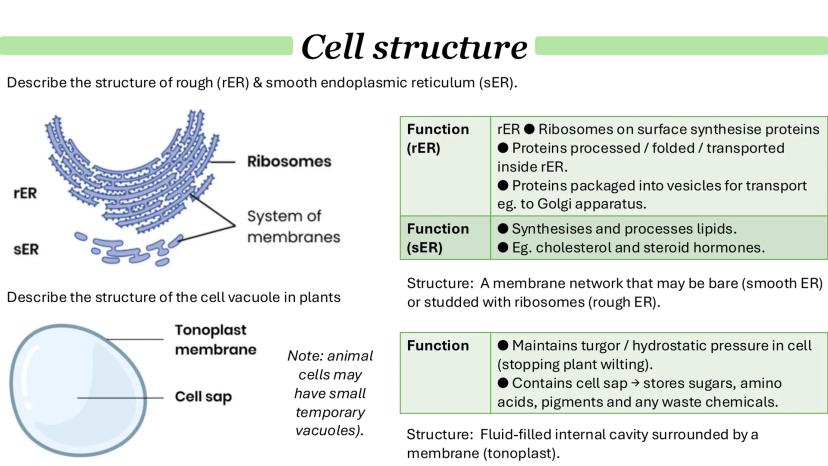
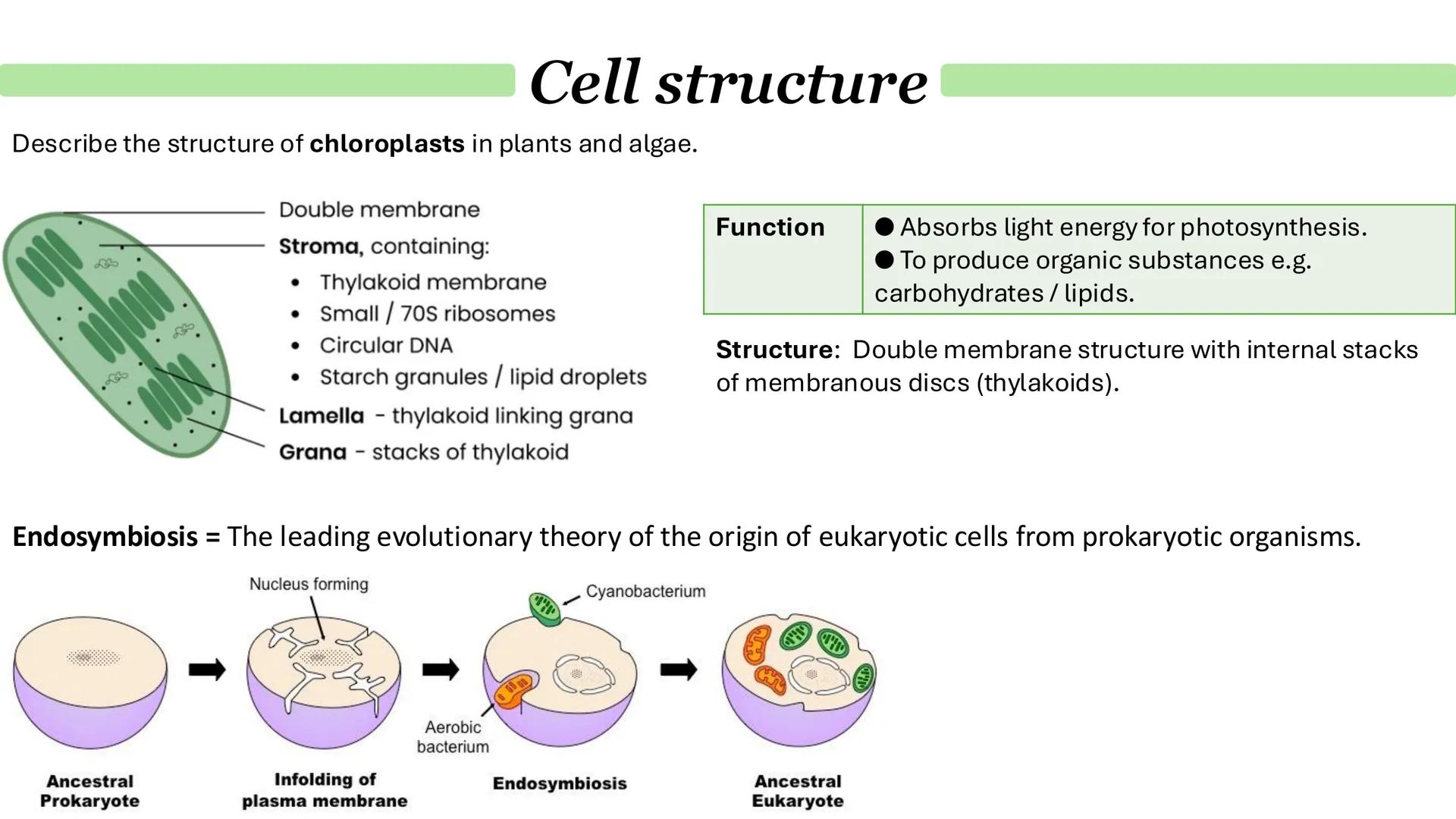
Chloroplasts are found only in plants and algae, and they're responsible for photosynthesis - converting light energy into chemical energy. Like mitochondria, they have a double membrane, but inside they contain thylakoids stacked into grana, connected by lamella.
The stroma (the fluid inside chloroplasts) contains enzymes, circular DNA, ribosomes, and starch granules. This is where the chemical reactions of photosynthesis actually happen.
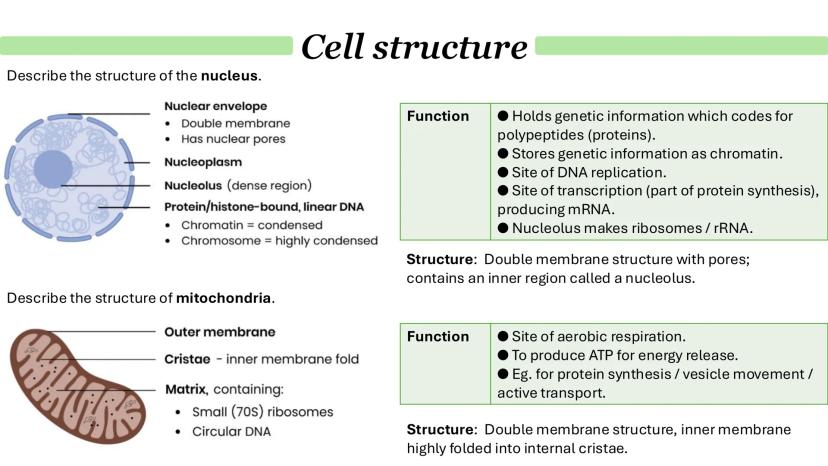
The endosymbiosis theory explains how eukaryotic cells evolved. Basically, ancient prokaryotic cells engulfed other bacteria that became mitochondria and chloroplasts. This explains why these organelles have their own DNA and ribosomes - they were once free-living organisms!
Fascinating fact: Every time you see a green plant, you're looking at the result of an ancient bacterial partnership!