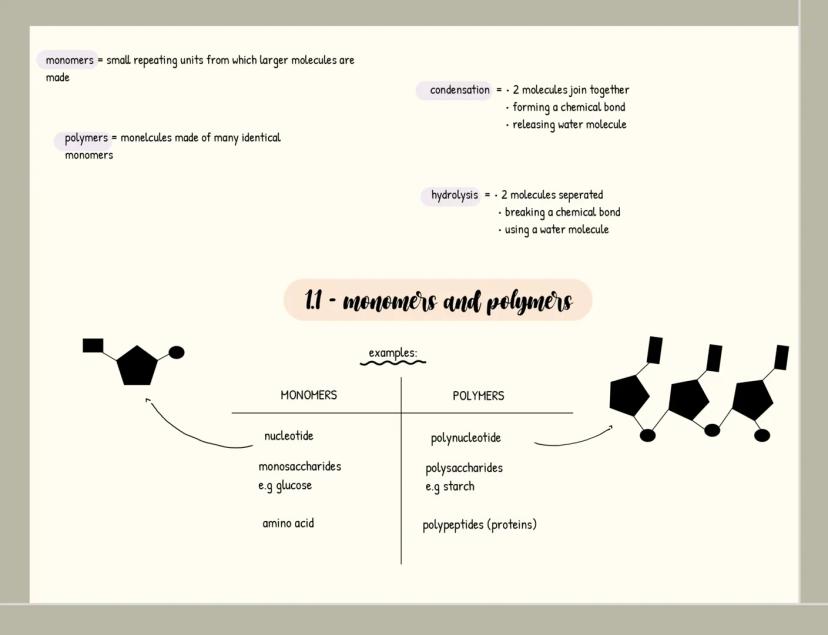
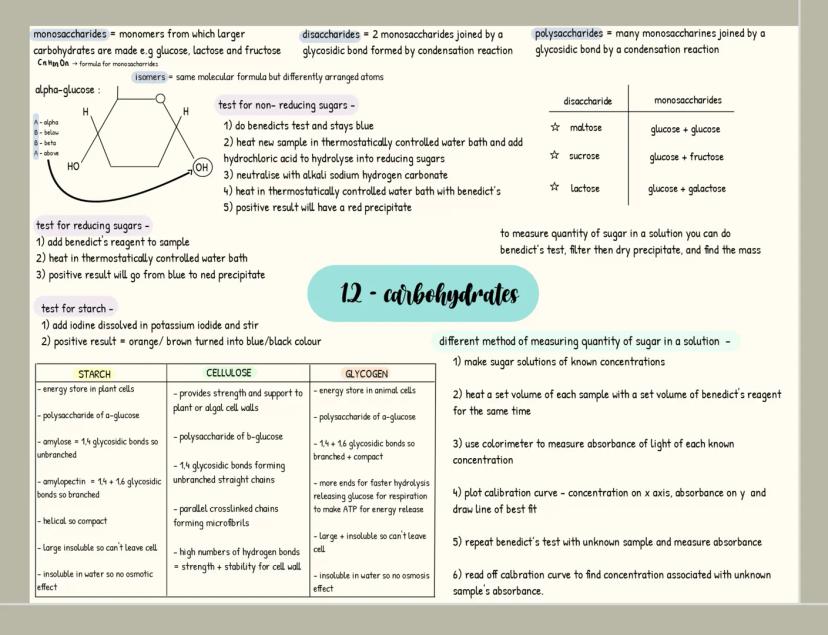
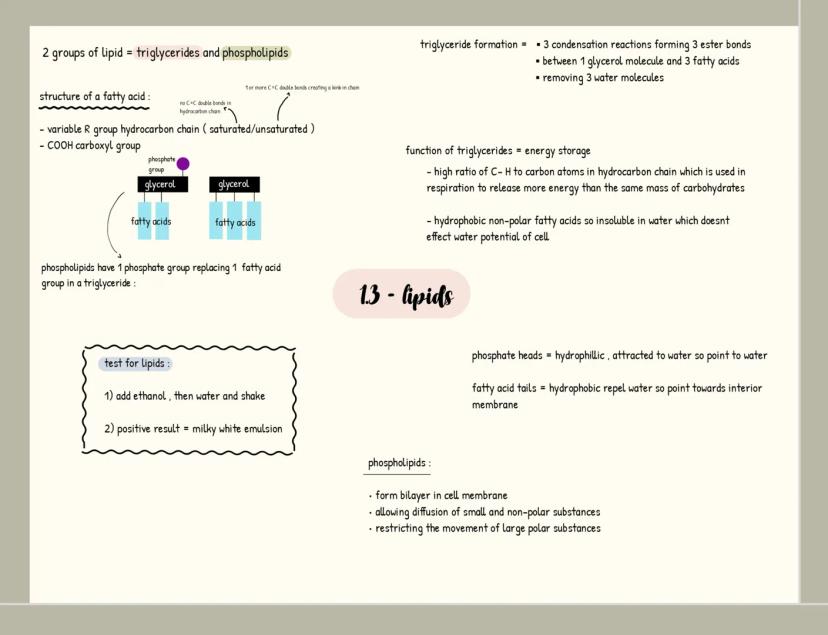
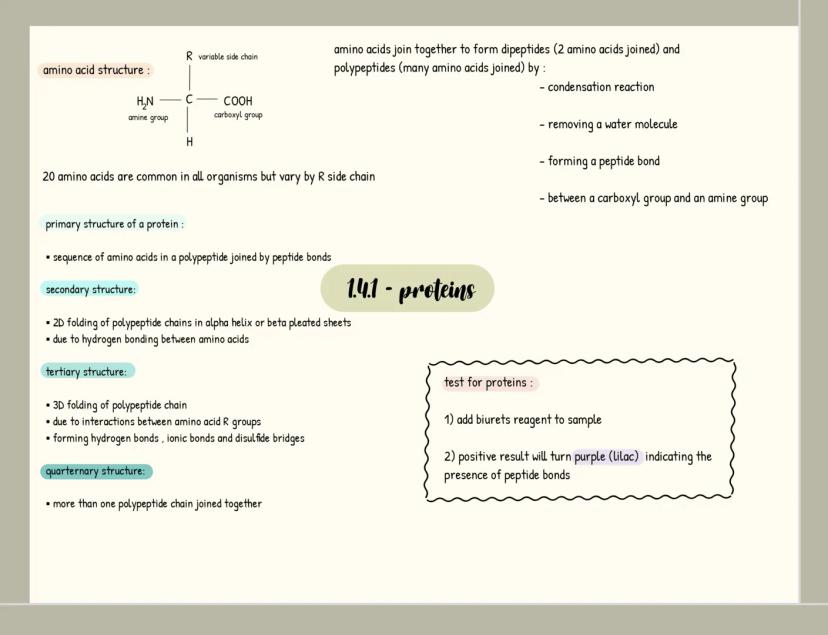
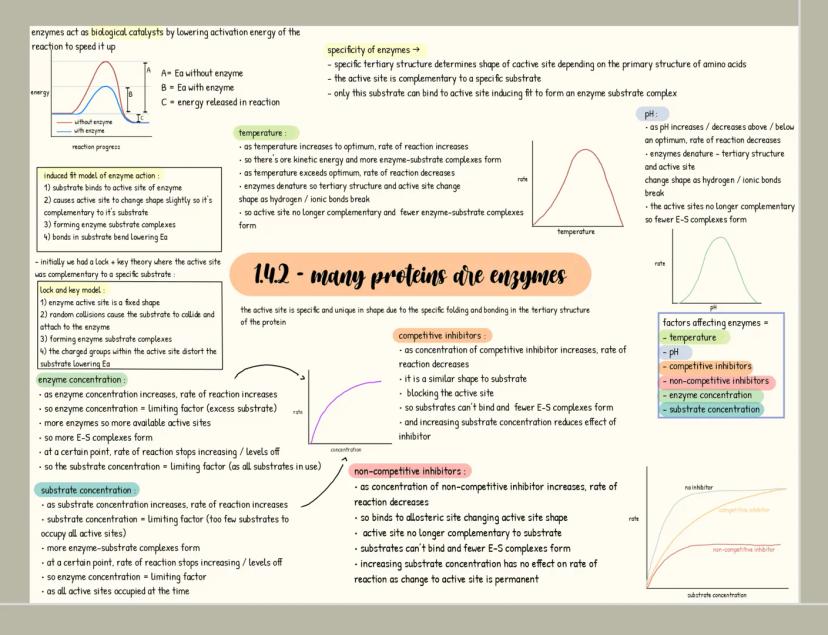
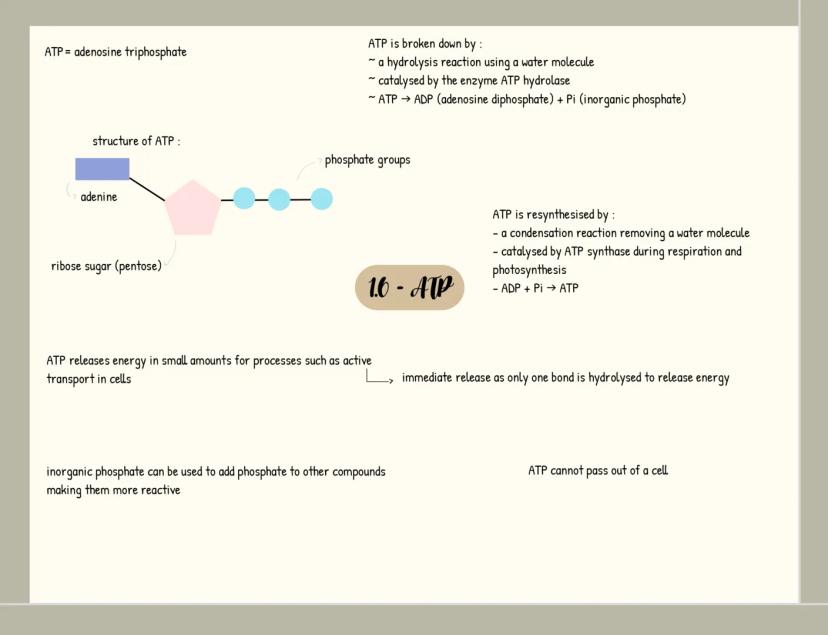
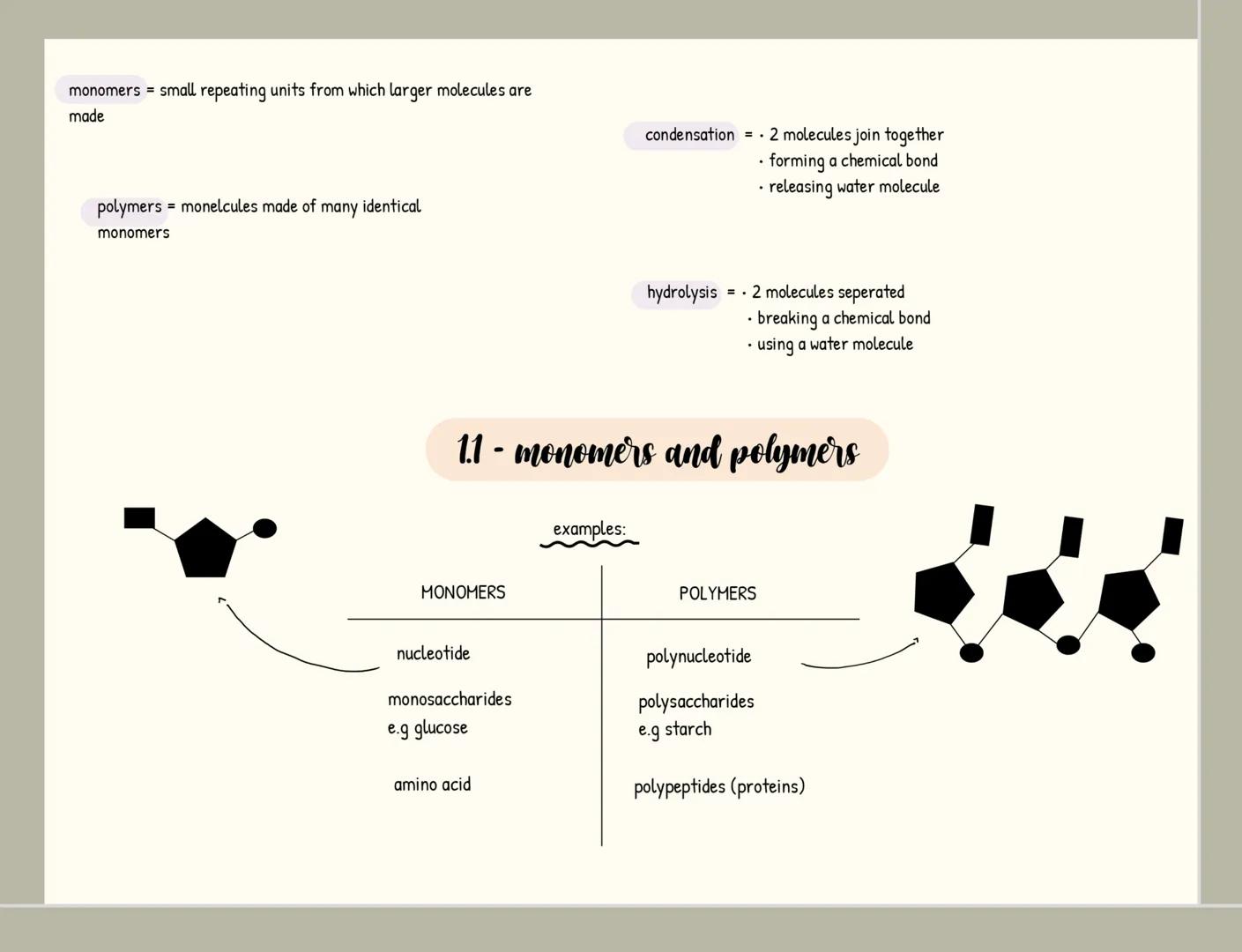
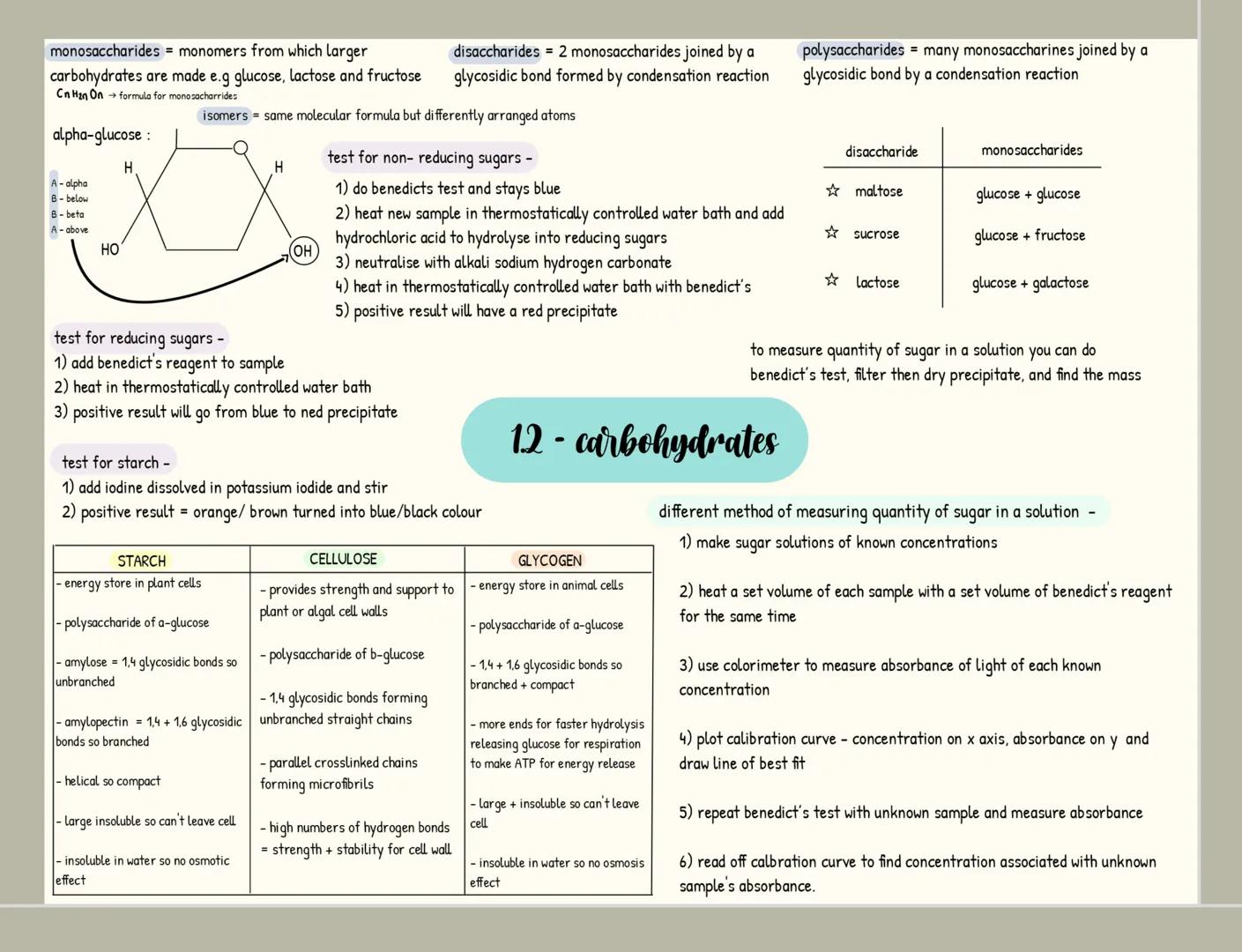
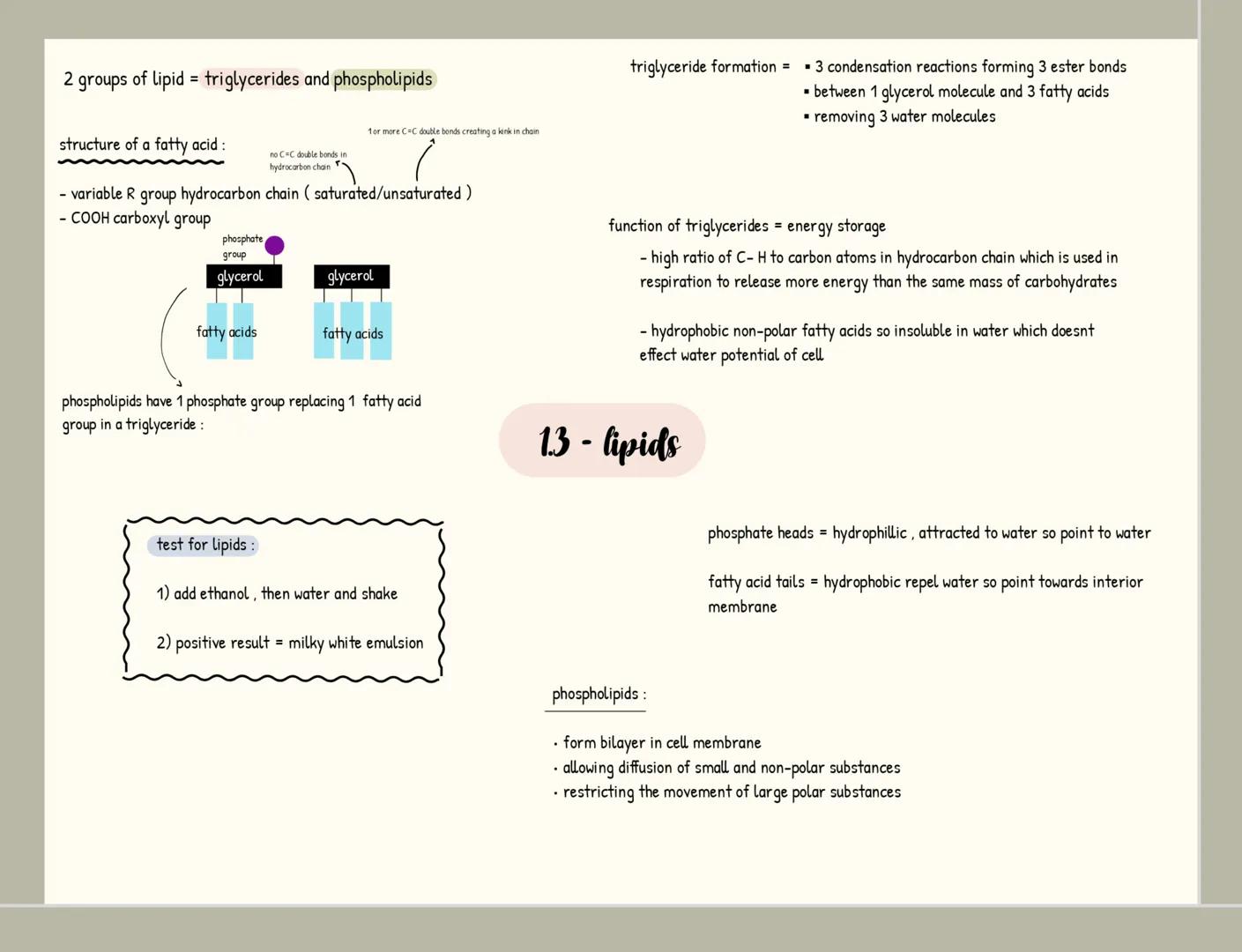
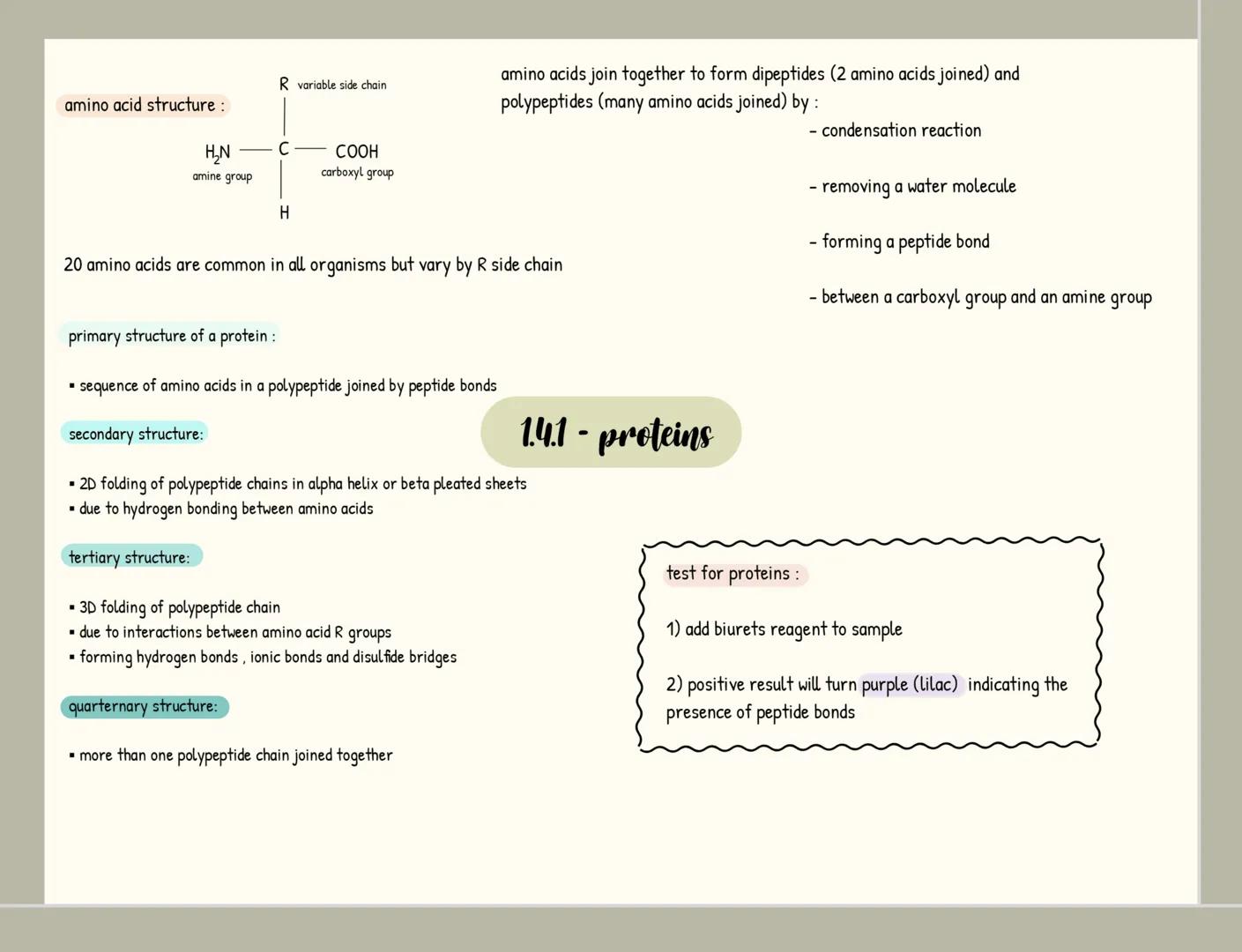
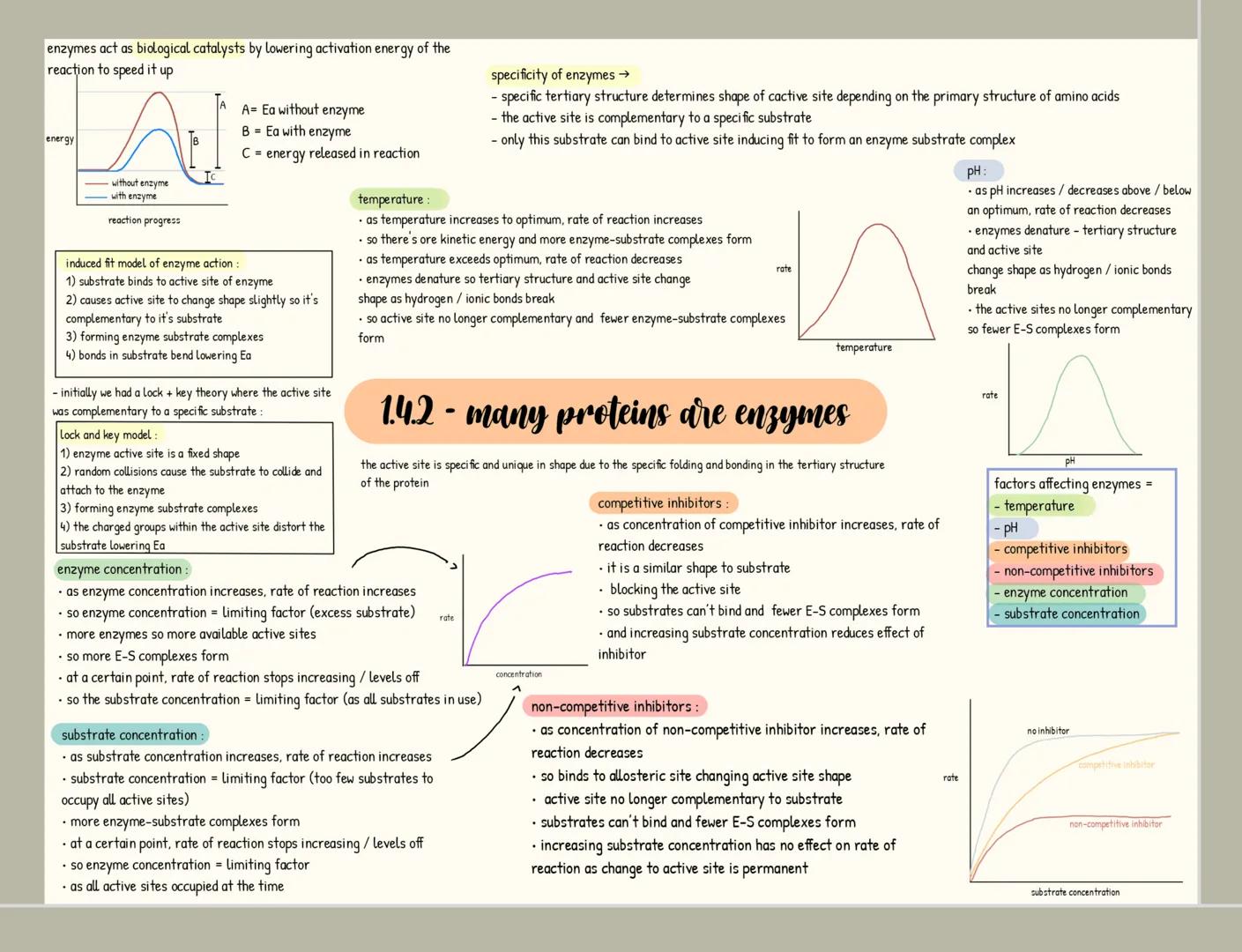
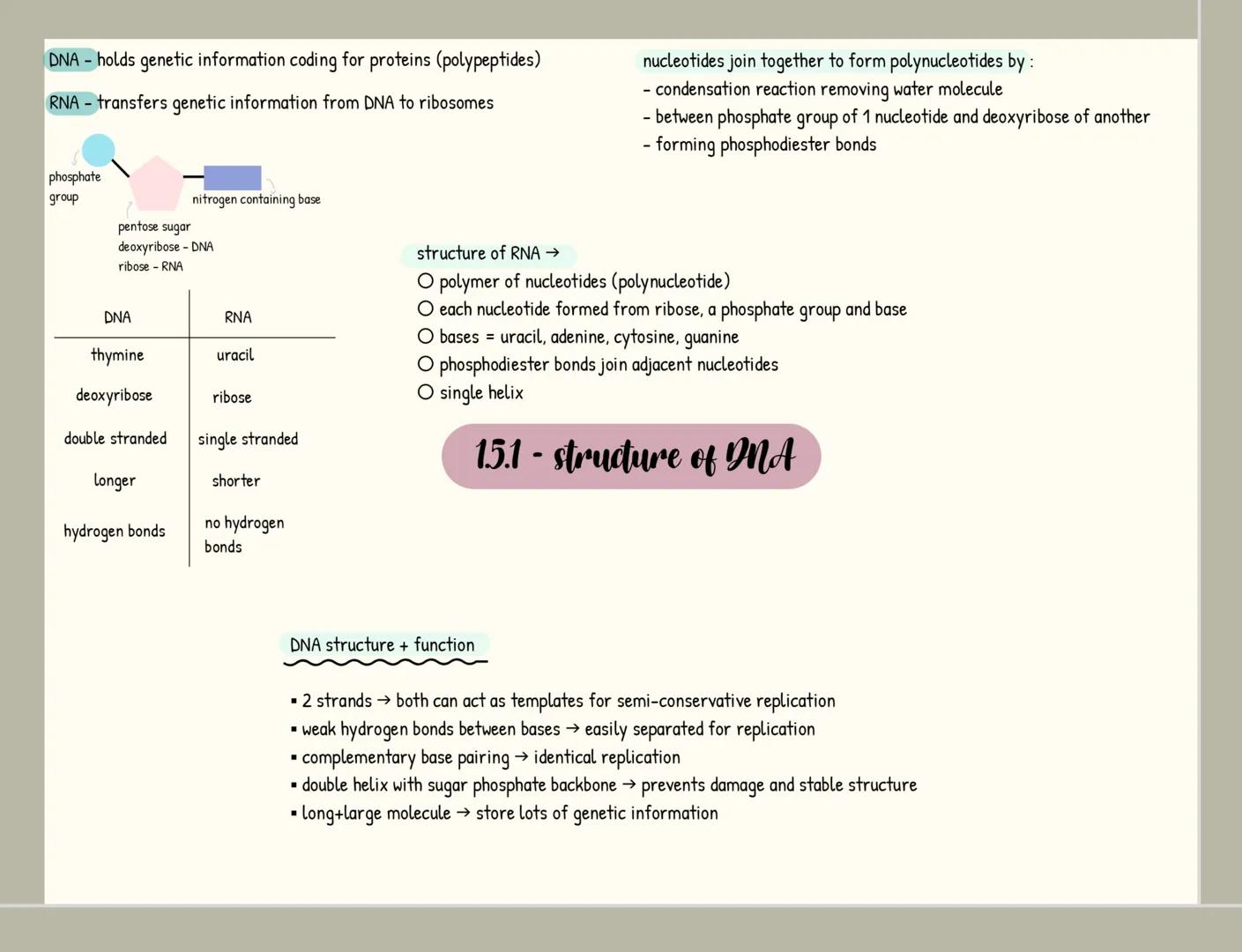
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are your body's primary energy source and have the formula C₍ₙ₎H₍₂ₙ₎O₍ₙ₎. Monosaccharides like glucose are single sugar units, while disaccharides form when two monosaccharides join through a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction (examples include maltose, sucrose and lactose).
When many monosaccharides link together, they form polysaccharides like starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Each serves a distinct purpose: starch stores energy in plants, glycogen stores energy in animals, and cellulose provides structural support in plant cell walls.
You can identify carbohydrates through simple tests. For reducing sugars, Benedict's test produces a red precipitate when positive. For non-reducing sugars, acid hydrolysis is needed before Benedict's test. Starch turns blue-black when iodine solution is added.
🧪 Laboratory tip: When measuring sugar concentration, you can create a calibration curve using known concentrations with Benedict's reagent and a colorimeter, then compare your unknown sample's absorbance to determine its concentration!