The Weimar Republic faced massive challenges from the start, dealing... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
1,123
•
Updated 25 Feb 2026
•
java73):?
@mjh375_pfwi
The Weimar Republic faced massive challenges from the start, dealing... Show more










Germany was absolutely shattered after WWI - 11 million men fought and over half became casualties. The British naval blockade caused 750,000 Germans to starve, whilst government debt tripled to 150 billion marks. When the Kaiser abdicated in 1918, Germany needed a completely fresh start.
Friedrich Ebert stepped up to lead the new Weimar Republic, creating Germany's first proper democracy. The new constitution introduced proportional representation, meaning parties got seats based on their vote percentage. Sounds fair, right? Well, it also meant extremist parties could gain power more easily.
The constitution had some serious flaws though. Article 48 gave the president emergency powers during crises - and Ebert used this 136 times! This would later prove dangerous when democracy was already hanging by a thread.
Key Point: The Weimar Republic was born from defeat and crisis, making it vulnerable to attack from extremist groups who blamed it for Germany's problems.
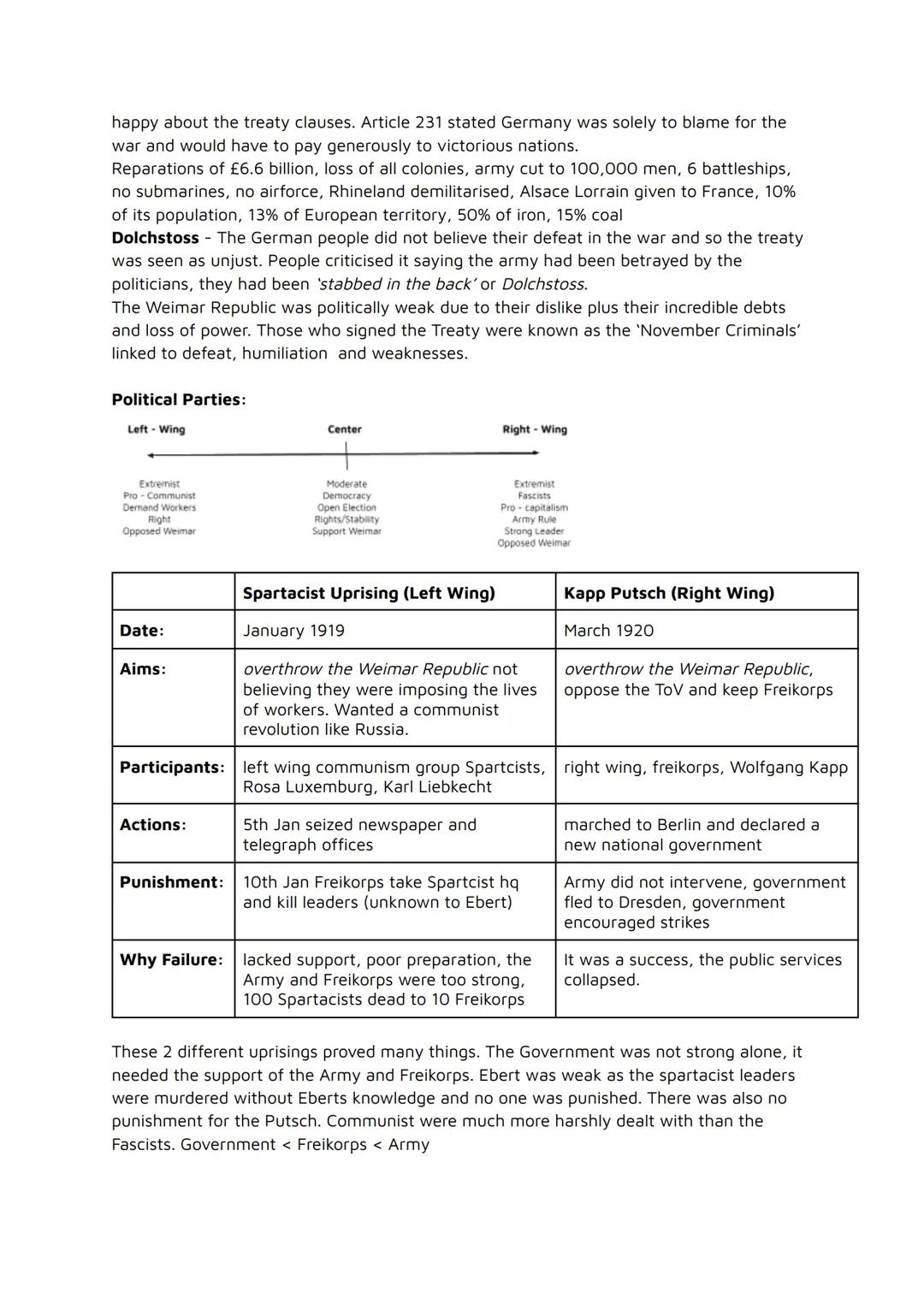
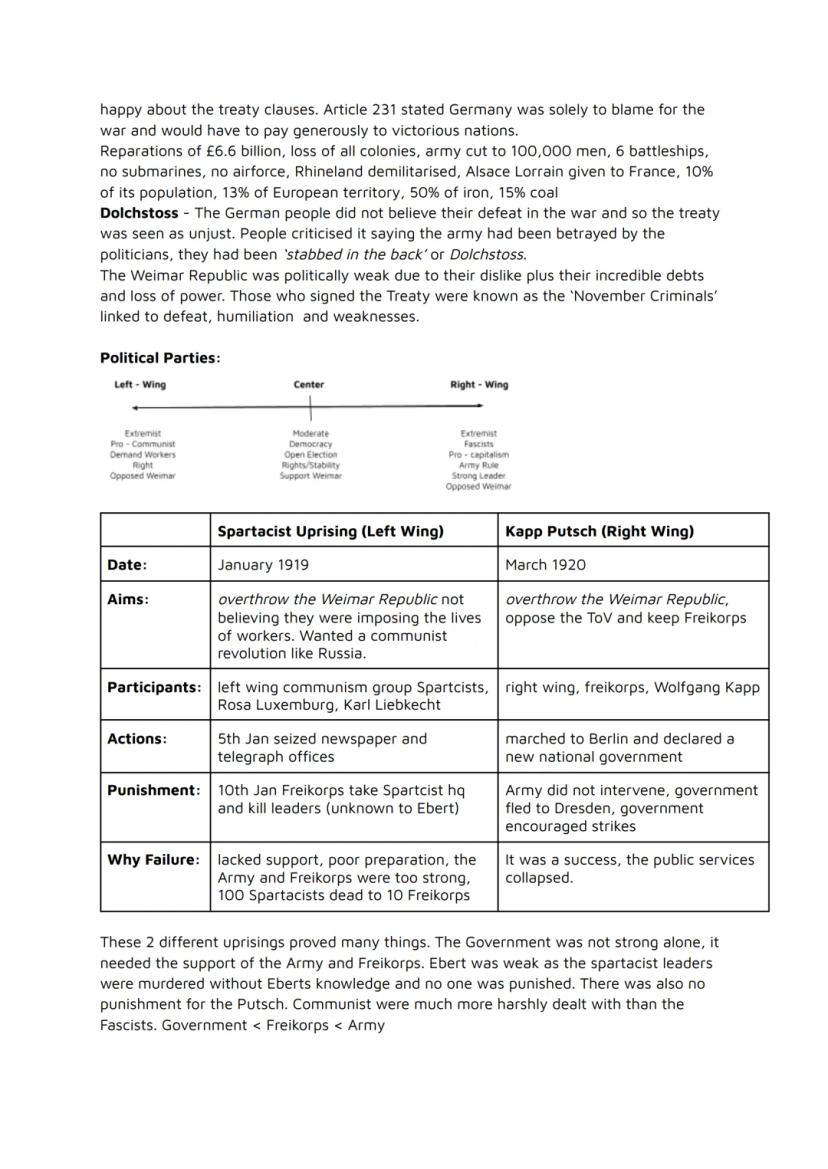
The Treaty of Versailles was brutal for Germany. They lost 10% of their population, 13% of European territory, and had to pay £6.6 billion in reparations. Germans felt betrayed, calling politicians who signed it the "November Criminals" and spreading the Dolchstoss myth - claiming the army was "stabbed in the back" by politicians.
Two major uprisings tested the weak republic. The Spartacist Uprising (1919) saw communists try to overthrow the government, but the Freikorps brutally crushed them, killing leaders Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht. The Kapp Putsch (1920) was a right-wing attempt that only failed when public services went on strike.
These uprisings revealed the government's weakness - it couldn't survive without the army and Freikorps. Worryingly, communists were treated far more harshly than right-wing rebels, showing where the real power lay.
Key Point: The government was caught between left and right-wing extremists, proving it lacked the strength to protect democracy on its own.

Everything went wrong in 1923. When Germany couldn't pay reparations, French troops occupied the Ruhr valley - Germany's industrial heartland containing 80% of their remaining resources. The government's "passive resistance" failed miserably, leaving factories closed and workers unemployed.
Desperate for money, the government started printing cash, triggering hyperinflation so severe that people needed wheelbarrows of money to buy bread. Workers were paid twice daily because prices changed so rapidly. Anyone with savings was wiped out, though some businesses actually benefited by paying off debts with worthless money.
This chaos set the stage for Hitler's Munich Putsch - his failed attempt to copy Mussolini's march on Rome. Though it ended with Hitler in prison, the trial gave him national publicity and taught him he needed to gain power legally through elections rather than violence.
The crisis proved how fragile the republic was when faced with economic collapse and foreign pressure.
Key Point: The 1923 crisis of hyperinflation and French occupation nearly destroyed the Weimar Republic and gave extremist groups like the Nazis their first real opportunity.

Things actually got much better for a while! The Dawes Plan (1924) saw American loans of £25 billion help Germany pay reparations, whilst the new Rentenmark currency ended hyperinflation. Industrial production increased by 40%, unemployment fell, and wages rose by 25%.
Internationally, Germany was making friends again. The Locarno Pact (1925) secured Germany's borders, whilst joining the League of Nations (1926) restored their status as a "great power". The Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928) saw 61 countries, including Germany, promise not to use war for foreign policy.
Working-class people were delighted - better wages, shorter hours (50 to 46 hours per week), and unemployment insurance. Women gained new freedoms, cutting their hair short, smoking, and entering professions like teaching. Young people saw university places increase from 70,000 to 110,000.
However, big businesses felt threatened by higher wages and worker rights, leading some to support right-wing extremist groups. The recovery was also completely dependent on American loans - a dangerous weakness that would soon be exposed.
Key Point: The "Golden Years" showed the Weimar Republic could work when times were good, but this prosperity was built on shaky foundations of foreign loans.

Hitler joined Anton Drexler's tiny German Workers' Party (DAP) as an army spy in 1919, but quickly took control. By 1921, he'd renamed it the Nazi Party (NSDAP) and made himself leader. His powerful speeches attracted crowds, whilst the SA brownshirts provided muscle against opponents.
The failed Munich Putsch (1923) taught Hitler crucial lessons. Instead of violent revolution, he'd gain power legally through elections. While in prison, he wrote Mein Kampf, outlining his racist ideology and plans for German expansion. His trial had already made him famous across Germany.
During the "lean years" (1924-1928), the Nazis struggled to gain support whilst Germany was prosperous. At the Bamberg Conference (1926), Hitler consolidated his control over the party, convincing propaganda chief Goebbels to abandon socialism and focus on nationalism instead.
By 1928, the party had 100,000 members but only won 2.6% of votes. People didn't want extremism when life was improving, employment was rising, and Germany was gaining international respect.
Key Point: Hitler learned that extremist parties only succeed during crisis - when people are desperate, they'll consider radical solutions they'd normally reject.

The Wall Street Crash (1929) destroyed the German economy overnight. American banks demanded their loans back, German banks collapsed, and unemployment rocketed from 1.3 million to 6.6 million by 1933. People lost their savings again, became homeless, and violence increased by 24% in Berlin alone.
Chancellor Brüning's harsh response - raising taxes and cutting benefits - pleased nobody. The Reichstag met less and less (from 94 times in 1930 to just 13 in 1932), whilst presidential decrees increased to 66 in 1932. Democracy was clearly failing.
Both communist and Nazi support surged as desperate people turned to extremes. The Nazis went from 12 seats in 1928 to 230 in July 1932, becoming the largest party. Hitler's brilliant propaganda, led by Goebbels, used aeroplanes, radio broadcasts, and mass rallies to spread their message.
The SA (now 400,000 strong) made the Nazis look organised and powerful compared to the weak government. Hitler cleverly appealed to different groups - promising businesses protection from communism, workers "bread and work", and middle-class families a return to traditional values.
Key Point: Economic crisis gave the Nazis their chance - Hitler offered simple solutions to complex problems, whilst his propaganda machine made him seem like Germany's savior.

Political chaos in 1932 opened the door for Hitler. After Brüning resigned, von Papen became chancellor, believing he could control Hitler by giving the Nazis a few government positions. Big mistake! Hindenburg and other conservative politicians fatally underestimated Hitler's ambition and cunning.
In the July 1932 election, the Nazis won 38% - their highest vote share. Though this dropped to 33% in November, they remained the largest party. When von Schleicher also failed as chancellor, the desperate conservatives turned to Hitler in January 1933, making him chancellor with von Papen as vice-chancellor.
They thought they were using Hitler, but he was using them. Conservative politicians had fatally undermined democracy by constantly using Article 48 and excluding moderate parties from government. Their fear of communism blinded them to the Nazi threat.
Hindenberg, the war hero president, never truly believed in democracy anyway. By appointing Hitler chancellor, he handed power to someone determined to destroy the system from within.
Key Point: Hitler didn't seize power - he was given it by conservative politicians who thought they could control him, proving how dangerous it is to underestimate extremists.

Once in power, Hitler moved fast to destroy democracy. The Reichstag Fire (February 1933) was perfect timing - a Dutch communist was caught and blamed, allowing Hitler to arrest communist leaders and ban their party. Many historians suspect the Nazis started the fire themselves.
The Enabling Act (March 1933) was the final nail in democracy's coffin. This law let Hitler pass laws without the Reichstag for four years. Opposition politicians were intimidated, banned from voting, or threatened into submission. With over 80% support (hardly surprising given the circumstances), Hitler had legal dictatorship.
By July 1933, all political parties except the Nazis were banned. Trade unions were destroyed, their leaders arrested, and local governments replaced with Nazi governors reporting directly to Hitler.
The Night of the Long Knives (1934) saw Hitler eliminate internal threats. Ernst Röhm and SA leaders were murdered when Hitler feared their power. The army, relieved to see the SA crushed, swore loyalty to Hitler personally.
When Hindenburg died in August 1934, Hitler combined the roles of chancellor and president, declaring himself "Führer". A rigged plebiscite gave 90% approval. The Weimar Republic was dead.
Key Point: Hitler used legal methods and manufactured crises to dismantle democracy step by step, showing how quickly democratic institutions can collapse under determined attack.

Hitler controlled Germany through fear and surveillance. The SS replaced the SA as his personal army, controlling all police and security systems. Led by Himmler, they answered only to Hitler and could arrest, torture, or execute anyone they deemed a threat.
The Gestapo secret police spied on ordinary Germans, using a network of informers who could be anyone - neighbours, work colleagues, even family members. People reported "suspicious" behaviour like lacking enthusiasm for Hitler or making critical comments. This created a climate of paranoia where nobody could be trusted.
Concentration camps housed political prisoners, communists, socialists, and anyone who opposed the regime. The threat of being sent to these camps kept most Germans quiet, even if they disagreed with Nazi policies.
The police state was terrifyingly effective because it made resistance seem impossible. When anyone could be an informer and the Gestapo had unlimited powers, most people chose to keep their heads down and conform rather than risk their lives opposing the regime.
Key Point: The Nazi police state worked by making every German complicit in the system of surveillance and terror, destroying trust between people and making organized resistance almost impossible.

Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
java73):?
@mjh375_pfwi
The Weimar Republic faced massive challenges from the start, dealing with Germany's crushing defeat in WWI and the harsh Treaty of Versailles. This period shows how economic crisis and political weakness can lead to the rise of extremism, ultimately allowing... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Germany was absolutely shattered after WWI - 11 million men fought and over half became casualties. The British naval blockade caused 750,000 Germans to starve, whilst government debt tripled to 150 billion marks. When the Kaiser abdicated in 1918, Germany needed a completely fresh start.
Friedrich Ebert stepped up to lead the new Weimar Republic, creating Germany's first proper democracy. The new constitution introduced proportional representation, meaning parties got seats based on their vote percentage. Sounds fair, right? Well, it also meant extremist parties could gain power more easily.
The constitution had some serious flaws though. Article 48 gave the president emergency powers during crises - and Ebert used this 136 times! This would later prove dangerous when democracy was already hanging by a thread.
Key Point: The Weimar Republic was born from defeat and crisis, making it vulnerable to attack from extremist groups who blamed it for Germany's problems.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Treaty of Versailles was brutal for Germany. They lost 10% of their population, 13% of European territory, and had to pay £6.6 billion in reparations. Germans felt betrayed, calling politicians who signed it the "November Criminals" and spreading the Dolchstoss myth - claiming the army was "stabbed in the back" by politicians.
Two major uprisings tested the weak republic. The Spartacist Uprising (1919) saw communists try to overthrow the government, but the Freikorps brutally crushed them, killing leaders Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht. The Kapp Putsch (1920) was a right-wing attempt that only failed when public services went on strike.
These uprisings revealed the government's weakness - it couldn't survive without the army and Freikorps. Worryingly, communists were treated far more harshly than right-wing rebels, showing where the real power lay.
Key Point: The government was caught between left and right-wing extremists, proving it lacked the strength to protect democracy on its own.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Everything went wrong in 1923. When Germany couldn't pay reparations, French troops occupied the Ruhr valley - Germany's industrial heartland containing 80% of their remaining resources. The government's "passive resistance" failed miserably, leaving factories closed and workers unemployed.
Desperate for money, the government started printing cash, triggering hyperinflation so severe that people needed wheelbarrows of money to buy bread. Workers were paid twice daily because prices changed so rapidly. Anyone with savings was wiped out, though some businesses actually benefited by paying off debts with worthless money.
This chaos set the stage for Hitler's Munich Putsch - his failed attempt to copy Mussolini's march on Rome. Though it ended with Hitler in prison, the trial gave him national publicity and taught him he needed to gain power legally through elections rather than violence.
The crisis proved how fragile the republic was when faced with economic collapse and foreign pressure.
Key Point: The 1923 crisis of hyperinflation and French occupation nearly destroyed the Weimar Republic and gave extremist groups like the Nazis their first real opportunity.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Things actually got much better for a while! The Dawes Plan (1924) saw American loans of £25 billion help Germany pay reparations, whilst the new Rentenmark currency ended hyperinflation. Industrial production increased by 40%, unemployment fell, and wages rose by 25%.
Internationally, Germany was making friends again. The Locarno Pact (1925) secured Germany's borders, whilst joining the League of Nations (1926) restored their status as a "great power". The Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928) saw 61 countries, including Germany, promise not to use war for foreign policy.
Working-class people were delighted - better wages, shorter hours (50 to 46 hours per week), and unemployment insurance. Women gained new freedoms, cutting their hair short, smoking, and entering professions like teaching. Young people saw university places increase from 70,000 to 110,000.
However, big businesses felt threatened by higher wages and worker rights, leading some to support right-wing extremist groups. The recovery was also completely dependent on American loans - a dangerous weakness that would soon be exposed.
Key Point: The "Golden Years" showed the Weimar Republic could work when times were good, but this prosperity was built on shaky foundations of foreign loans.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Hitler joined Anton Drexler's tiny German Workers' Party (DAP) as an army spy in 1919, but quickly took control. By 1921, he'd renamed it the Nazi Party (NSDAP) and made himself leader. His powerful speeches attracted crowds, whilst the SA brownshirts provided muscle against opponents.
The failed Munich Putsch (1923) taught Hitler crucial lessons. Instead of violent revolution, he'd gain power legally through elections. While in prison, he wrote Mein Kampf, outlining his racist ideology and plans for German expansion. His trial had already made him famous across Germany.
During the "lean years" (1924-1928), the Nazis struggled to gain support whilst Germany was prosperous. At the Bamberg Conference (1926), Hitler consolidated his control over the party, convincing propaganda chief Goebbels to abandon socialism and focus on nationalism instead.
By 1928, the party had 100,000 members but only won 2.6% of votes. People didn't want extremism when life was improving, employment was rising, and Germany was gaining international respect.
Key Point: Hitler learned that extremist parties only succeed during crisis - when people are desperate, they'll consider radical solutions they'd normally reject.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Wall Street Crash (1929) destroyed the German economy overnight. American banks demanded their loans back, German banks collapsed, and unemployment rocketed from 1.3 million to 6.6 million by 1933. People lost their savings again, became homeless, and violence increased by 24% in Berlin alone.
Chancellor Brüning's harsh response - raising taxes and cutting benefits - pleased nobody. The Reichstag met less and less (from 94 times in 1930 to just 13 in 1932), whilst presidential decrees increased to 66 in 1932. Democracy was clearly failing.
Both communist and Nazi support surged as desperate people turned to extremes. The Nazis went from 12 seats in 1928 to 230 in July 1932, becoming the largest party. Hitler's brilliant propaganda, led by Goebbels, used aeroplanes, radio broadcasts, and mass rallies to spread their message.
The SA (now 400,000 strong) made the Nazis look organised and powerful compared to the weak government. Hitler cleverly appealed to different groups - promising businesses protection from communism, workers "bread and work", and middle-class families a return to traditional values.
Key Point: Economic crisis gave the Nazis their chance - Hitler offered simple solutions to complex problems, whilst his propaganda machine made him seem like Germany's savior.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Political chaos in 1932 opened the door for Hitler. After Brüning resigned, von Papen became chancellor, believing he could control Hitler by giving the Nazis a few government positions. Big mistake! Hindenburg and other conservative politicians fatally underestimated Hitler's ambition and cunning.
In the July 1932 election, the Nazis won 38% - their highest vote share. Though this dropped to 33% in November, they remained the largest party. When von Schleicher also failed as chancellor, the desperate conservatives turned to Hitler in January 1933, making him chancellor with von Papen as vice-chancellor.
They thought they were using Hitler, but he was using them. Conservative politicians had fatally undermined democracy by constantly using Article 48 and excluding moderate parties from government. Their fear of communism blinded them to the Nazi threat.
Hindenberg, the war hero president, never truly believed in democracy anyway. By appointing Hitler chancellor, he handed power to someone determined to destroy the system from within.
Key Point: Hitler didn't seize power - he was given it by conservative politicians who thought they could control him, proving how dangerous it is to underestimate extremists.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Once in power, Hitler moved fast to destroy democracy. The Reichstag Fire (February 1933) was perfect timing - a Dutch communist was caught and blamed, allowing Hitler to arrest communist leaders and ban their party. Many historians suspect the Nazis started the fire themselves.
The Enabling Act (March 1933) was the final nail in democracy's coffin. This law let Hitler pass laws without the Reichstag for four years. Opposition politicians were intimidated, banned from voting, or threatened into submission. With over 80% support (hardly surprising given the circumstances), Hitler had legal dictatorship.
By July 1933, all political parties except the Nazis were banned. Trade unions were destroyed, their leaders arrested, and local governments replaced with Nazi governors reporting directly to Hitler.
The Night of the Long Knives (1934) saw Hitler eliminate internal threats. Ernst Röhm and SA leaders were murdered when Hitler feared their power. The army, relieved to see the SA crushed, swore loyalty to Hitler personally.
When Hindenburg died in August 1934, Hitler combined the roles of chancellor and president, declaring himself "Führer". A rigged plebiscite gave 90% approval. The Weimar Republic was dead.
Key Point: Hitler used legal methods and manufactured crises to dismantle democracy step by step, showing how quickly democratic institutions can collapse under determined attack.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Hitler controlled Germany through fear and surveillance. The SS replaced the SA as his personal army, controlling all police and security systems. Led by Himmler, they answered only to Hitler and could arrest, torture, or execute anyone they deemed a threat.
The Gestapo secret police spied on ordinary Germans, using a network of informers who could be anyone - neighbours, work colleagues, even family members. People reported "suspicious" behaviour like lacking enthusiasm for Hitler or making critical comments. This created a climate of paranoia where nobody could be trusted.
Concentration camps housed political prisoners, communists, socialists, and anyone who opposed the regime. The threat of being sent to these camps kept most Germans quiet, even if they disagreed with Nazi policies.
The police state was terrifyingly effective because it made resistance seem impossible. When anyone could be an informer and the Gestapo had unlimited powers, most people chose to keep their heads down and conform rather than risk their lives opposing the regime.
Key Point: The Nazi police state worked by making every German complicit in the system of surveillance and terror, destroying trust between people and making organized resistance almost impossible.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
26
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the causes and effects of hyperinflation in Weimar Germany (1919-1923) in this detailed summary. Understand the economic policies, the impact of reparations, and the social consequences of the hyperinflation crisis. This resource is ideal for students studying the Weimar Republic and its financial challenges, including the Ruhr occupation and the rise of political instability. Key concepts include deficit financing, inflation dynamics, and the socio-economic landscape of post-WWI Germany.
Explore the social policies in Germany from 1918 to 1945, focusing on the Weimar Republic, Nazi state, and wartime impacts. This summary covers women's roles, youth indoctrination, workers' rights, and the treatment of various social groups, providing essential insights for A-Level History students studying Democracy and Nazism (AQA).
Explore the critical factors behind the Nazis' ascent to power in 1933, focusing on the economic turmoil from 1923 and the inherent weaknesses of the Weimar Republic. This analysis delves into the impact of hyperinflation, the Great Depression, and the political miscalculations of opponents, highlighting how these elements combined to facilitate Hitler's rise. Ideal for students studying the complexities of post-WWI Germany and the dynamics of political power.
Explore key themes in German history, including the rise of nationalism post-Napoleon, the Weimar Republic's challenges, and the ascent of Hitler and the Nazi Party. This summary covers significant events and concepts such as the unification of Germany, the impact of the Treaty of Versailles, and the socio-political dynamics leading to the Nazi dictatorship. Ideal for higher history students preparing for essays and exams.
Explore the key reasons behind public dissatisfaction with the Treaty of Versailles, including the 'stabbed-in-the-back' myth, the role of the Weimar Government, and the harsh terms imposed on Germany. This summary provides insights into the historical context of post-World War I Germany and the impact of the treaty on the rise of Nazi sentiment. Ideal for students studying Nazi Germany and the Weimar Republic.
Explore the establishment of the Weimar Republic from 1918-1919, focusing on the rise of socialism, key political reforms, and the abdication of the Kaiser. This summary highlights the social unrest, the role of the Social Democratic Party (SPD), and significant events leading to Germany's transition to democracy. Ideal for A-Level History students studying Democracy and Nazism (AQA).
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user