Chemical bonding determines how atoms stick together and shapes the... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
368
•
Updated 24 Feb 2026
•
M
@iamjungkook
Chemical bonding determines how atoms stick together and shapes the... Show more










Ever wondered why salt dissolves in water but doesn't conduct electricity until it does? Ionic bonding happens when electrons jump from metal atoms to non-metal atoms, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other like magnets.
These ionic compounds always form lattice structures - think of them as 3D networks of alternating positive and negative ions. They're always solid at room temperature because breaking apart that giant lattice structure requires loads of energy.
Here's the clever bit: ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water. In solid form, the ions are locked in place and can't move to carry charge. But melt them or dissolve them, and those charge-carrying ions become free to move around.
Quick Tip: Remember that ionic compounds are brittle - they shatter easily because when you hit them, like charges can line up and repel each other, causing the structure to break apart.

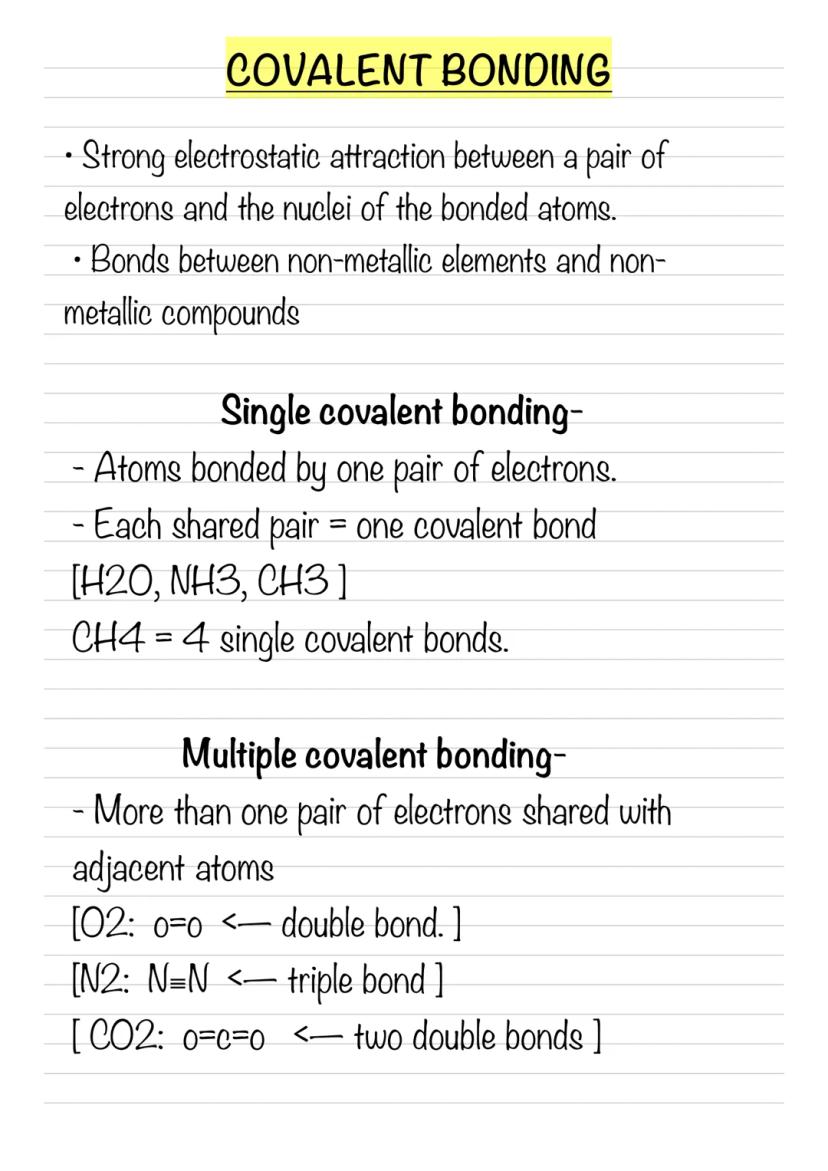
Unlike ionic bonding where electrons transfer completely, covalent bonding is all about sharing. Non-metal atoms share pairs of electrons, creating strong attractions between the shared electrons and both atomic nuclei.
Single covalent bonds involve one shared pair of electrons. Think of methane (CH₄) - carbon shares one pair with each of four hydrogen atoms, creating four single bonds. It's like a molecular handshake between atoms.
But atoms can be greedy and share more! Multiple covalent bonds occur when atoms share two or three pairs of electrons. Oxygen gas (O₂) has a double bond , whilst nitrogen gas (N₂) has an incredibly strong triple bond (N≡N).
Remember: The more electron pairs shared between atoms, the stronger and shorter the bond becomes.

Sometimes one atom is generous and provides both electrons in a shared pair - that's dative covalent bonding. The atom donating the pair has a lone pair of electrons, whilst the receiving atom is electron deficient.
The classic example is when ammonia (NH₃) meets a hydrogen ion (H⁺) to form NH₄⁺. Nitrogen donates its lone pair to the hydrogen, shown with an arrow (N→H). Once formed, this dative bond is identical to regular covalent bonds.
Think of it like lending someone your phone charger - once they're using it, it works just like their own charger would. The lone pair creates a concentrated negative charge region that attracts positive ions.
Average bond enthalpy measures how strong covalent bonds are. Higher values mean stronger bonds that require more energy to break.
Key Point: Dative bonds look different when forming (one atom gives both electrons) but behave identically to normal covalent bonds once established.

Imagine trying to arrange magnets around a central point - they'd push apart to get as far from each other as possible. Electron pairs behave similarly, determining molecular shapes by minimising repulsion between negative charges.
The key insight is that lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. Lone pairs are closer to the central atom and occupy more space because they're not stretched between two nuclei. This means they push other electron pairs away more strongly.
The repulsion strength order is: lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pair-bonding pair. Each lone pair reduces bond angles by about 2.5°.
Steric number tells you the total number of atoms and lone pairs directly attached to a central atom. This number determines the basic molecular geometry before lone pairs modify the angles.
Memory Aid: Think "LP > BP" - Lone Pairs cause more repulsion than Bonding Pairs, so they dominate molecular shape.

Linear molecules have two bonding pairs arranged at 180° - perfectly straight like BeF₂. Trigonal planar molecules have three bonding pairs at 120° angles, all in the same plane like BF₃.
Tetrahedral molecules are 3D with four electron pairs. Methane (CH₄) is perfectly tetrahedral with 109.5° bond angles. But add a lone pair like in ammonia (NH₃), and the angles squeeze down to 107° because that lone pair pushes the bonding pairs closer together.
Water (H₂O) has two lone pairs on oxygen, creating a bent shape with bond angles around 104.5°. The more lone pairs present, the more the bond angles get compressed from the ideal tetrahedral angle.
These shapes aren't just academic - they determine how molecules interact, fit together, and react with each other in biological systems and chemical reactions.
Exam Tip: Always count lone pairs carefully - they're invisible in molecular formulas but crucial for predicting shapes and angles.
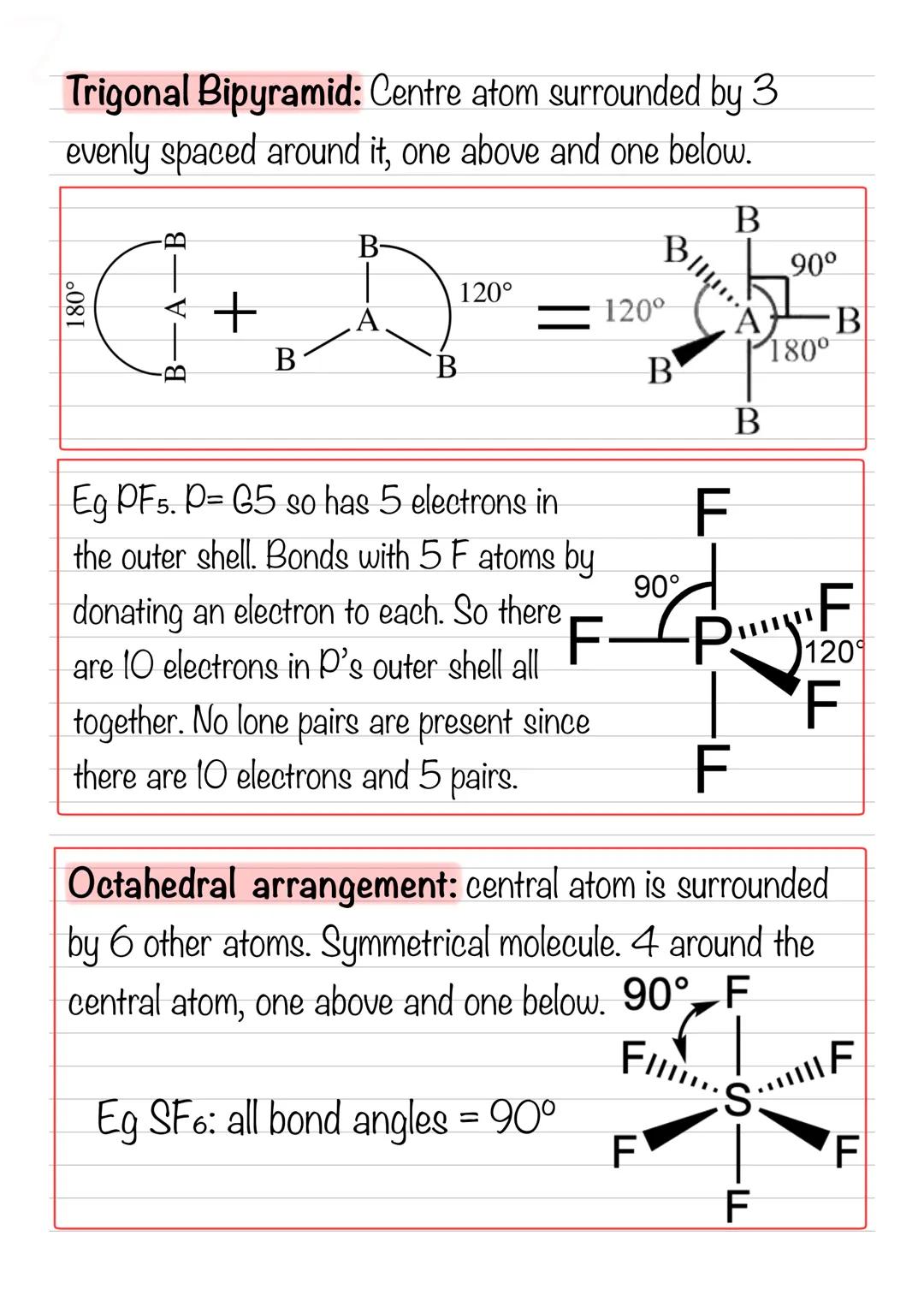
When you have five electron pairs, you get a trigonal bipyramid - imagine three atoms around the equator with one above and one below. PF₅ is a perfect example with 120° angles around the middle and 90° angles to the top and bottom.
Octahedral molecules like SF₆ have six bonding pairs creating a symmetrical shape with all bond angles at 90°. Picture a central atom with four others around it in a square, plus one above and one below.
These complex shapes follow the same electron repulsion principles but in three dimensions. The electron pairs arrange themselves to minimise repulsion, creating these distinctive geometries.
Understanding these shapes helps predict molecular behaviour, especially in coordination chemistry and complex biological molecules where metal centres often adopt octahedral geometries.
Visual Tip: Use molecular models or draw 3D sketches - these complex shapes are much easier to understand when you can visualise them properly.

Electronegativity measures an atom's pulling power for electrons in covalent bonds. Think of it as atomic greed - fluorine is the most electronegative element (4.0 on the Pauling scale) and desperately wants to hog electrons.
Three factors determine electronegativity: nuclear charge , atomic radius (smaller atoms hold electrons tighter), and shielding (inner electrons block the nuclear attraction).
Across a period, electronegativity increases because atoms get smaller whilst gaining more protons. Down a group, it decreases because atoms get bigger and inner electrons shield the outer ones from nuclear attraction.
The nuclear charge increases down groups, but this effect is overwhelmed by the increased distance and shielding from additional electron shells.
Pattern Recognition: Electronegativity increases going right and up the periodic table, with fluorine at the top right being the champion electron-hog.

Moving across a period, electronegativity increases because atoms shrink whilst gaining protons. The nuclear charge grows stronger, but shielding stays constant, creating a tighter grip on electrons.
Going down a group, electronegativity decreases despite increasing nuclear charge. The atoms get bigger, more inner shells create shielding, and the increased distance weakens the attraction between nucleus and bonding electrons.
You can predict bond types using electronegativity differences: equal values give pure covalent bonds, slight differences create polar covalent bonds, and large differences result in ionic bonds.
This prediction system helps you understand why some compounds conduct electricity, dissolve in water, or have particular melting points - it all comes down to the electronegativity differences between atoms.
Quick Check: If electronegativity difference is roughly >1.7, expect ionic character; <0.5 suggests pure covalent bonding.

Polar bonds form when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally. The more electronegative atom becomes slightly negative (δ-) whilst the other becomes slightly positive (δ+).
Having polar bonds doesn't automatically make a polar molecule though! The molecule's shape matters crucially. Water (H₂O) is polar because its bent shape means the dipoles don't cancel out, but carbon dioxide (CO₂) is non-polar despite having polar bonds because its linear shape makes the dipoles cancel.
A permanent dipole exists when there's a persistent charge difference across a covalent bond. These dipoles can align with each other, creating weak electrostatic attractions between molecules - about 1/100th the strength of covalent bonds.
Non-polar molecules either have no polar bonds at all, or have polar bonds arranged symmetrically so the charges cancel out completely.
Shape Matters: Always consider molecular geometry - symmetrical molecules with polar bonds often end up non-polar overall.

Linear, symmetrical molecules are typically non-polar because dipoles cancel out. However, molecules with OH, NH, or lone H atoms at the ends are usually polar due to the significant electronegativity differences.
Carbon-containing molecules are often non-polar, especially hydrocarbons, but there are important exceptions. Diatomic elements with identical atoms (like Cl₂ or O₂) are always non-polar since there's no electronegativity difference.
C-H and S-H bonds don't produce significant dipoles due to similar electronegativities. When predicting polarity, look for the dipole sum - if individual bond dipoles cancel out, the molecule is non-polar; if they don't cancel, it's polar.
The key is recognising that molecular polarity depends on both individual bond polarities and the overall molecular geometry. Symmetry is your friend for predicting non-polar molecules.
Rule of Thumb: Symmetrical molecules tend to be non-polar even with polar bonds, whilst asymmetrical molecules with polar bonds are usually polar overall.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
M
@iamjungkook
Chemical bonding determines how atoms stick together and shapes the properties of everything around us. Understanding ionic, covalent, and polar bonds will help you predict how molecules behave and why substances have different characteristics like melting points and electrical conductivity.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Ever wondered why salt dissolves in water but doesn't conduct electricity until it does? Ionic bonding happens when electrons jump from metal atoms to non-metal atoms, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other like magnets.
These ionic compounds always form lattice structures - think of them as 3D networks of alternating positive and negative ions. They're always solid at room temperature because breaking apart that giant lattice structure requires loads of energy.
Here's the clever bit: ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water. In solid form, the ions are locked in place and can't move to carry charge. But melt them or dissolve them, and those charge-carrying ions become free to move around.
Quick Tip: Remember that ionic compounds are brittle - they shatter easily because when you hit them, like charges can line up and repel each other, causing the structure to break apart.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Unlike ionic bonding where electrons transfer completely, covalent bonding is all about sharing. Non-metal atoms share pairs of electrons, creating strong attractions between the shared electrons and both atomic nuclei.
Single covalent bonds involve one shared pair of electrons. Think of methane (CH₄) - carbon shares one pair with each of four hydrogen atoms, creating four single bonds. It's like a molecular handshake between atoms.
But atoms can be greedy and share more! Multiple covalent bonds occur when atoms share two or three pairs of electrons. Oxygen gas (O₂) has a double bond , whilst nitrogen gas (N₂) has an incredibly strong triple bond (N≡N).
Remember: The more electron pairs shared between atoms, the stronger and shorter the bond becomes.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Sometimes one atom is generous and provides both electrons in a shared pair - that's dative covalent bonding. The atom donating the pair has a lone pair of electrons, whilst the receiving atom is electron deficient.
The classic example is when ammonia (NH₃) meets a hydrogen ion (H⁺) to form NH₄⁺. Nitrogen donates its lone pair to the hydrogen, shown with an arrow (N→H). Once formed, this dative bond is identical to regular covalent bonds.
Think of it like lending someone your phone charger - once they're using it, it works just like their own charger would. The lone pair creates a concentrated negative charge region that attracts positive ions.
Average bond enthalpy measures how strong covalent bonds are. Higher values mean stronger bonds that require more energy to break.
Key Point: Dative bonds look different when forming (one atom gives both electrons) but behave identically to normal covalent bonds once established.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Imagine trying to arrange magnets around a central point - they'd push apart to get as far from each other as possible. Electron pairs behave similarly, determining molecular shapes by minimising repulsion between negative charges.
The key insight is that lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. Lone pairs are closer to the central atom and occupy more space because they're not stretched between two nuclei. This means they push other electron pairs away more strongly.
The repulsion strength order is: lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pair-bonding pair. Each lone pair reduces bond angles by about 2.5°.
Steric number tells you the total number of atoms and lone pairs directly attached to a central atom. This number determines the basic molecular geometry before lone pairs modify the angles.
Memory Aid: Think "LP > BP" - Lone Pairs cause more repulsion than Bonding Pairs, so they dominate molecular shape.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Linear molecules have two bonding pairs arranged at 180° - perfectly straight like BeF₂. Trigonal planar molecules have three bonding pairs at 120° angles, all in the same plane like BF₃.
Tetrahedral molecules are 3D with four electron pairs. Methane (CH₄) is perfectly tetrahedral with 109.5° bond angles. But add a lone pair like in ammonia (NH₃), and the angles squeeze down to 107° because that lone pair pushes the bonding pairs closer together.
Water (H₂O) has two lone pairs on oxygen, creating a bent shape with bond angles around 104.5°. The more lone pairs present, the more the bond angles get compressed from the ideal tetrahedral angle.
These shapes aren't just academic - they determine how molecules interact, fit together, and react with each other in biological systems and chemical reactions.
Exam Tip: Always count lone pairs carefully - they're invisible in molecular formulas but crucial for predicting shapes and angles.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
When you have five electron pairs, you get a trigonal bipyramid - imagine three atoms around the equator with one above and one below. PF₅ is a perfect example with 120° angles around the middle and 90° angles to the top and bottom.
Octahedral molecules like SF₆ have six bonding pairs creating a symmetrical shape with all bond angles at 90°. Picture a central atom with four others around it in a square, plus one above and one below.
These complex shapes follow the same electron repulsion principles but in three dimensions. The electron pairs arrange themselves to minimise repulsion, creating these distinctive geometries.
Understanding these shapes helps predict molecular behaviour, especially in coordination chemistry and complex biological molecules where metal centres often adopt octahedral geometries.
Visual Tip: Use molecular models or draw 3D sketches - these complex shapes are much easier to understand when you can visualise them properly.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Electronegativity measures an atom's pulling power for electrons in covalent bonds. Think of it as atomic greed - fluorine is the most electronegative element (4.0 on the Pauling scale) and desperately wants to hog electrons.
Three factors determine electronegativity: nuclear charge , atomic radius (smaller atoms hold electrons tighter), and shielding (inner electrons block the nuclear attraction).
Across a period, electronegativity increases because atoms get smaller whilst gaining more protons. Down a group, it decreases because atoms get bigger and inner electrons shield the outer ones from nuclear attraction.
The nuclear charge increases down groups, but this effect is overwhelmed by the increased distance and shielding from additional electron shells.
Pattern Recognition: Electronegativity increases going right and up the periodic table, with fluorine at the top right being the champion electron-hog.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Moving across a period, electronegativity increases because atoms shrink whilst gaining protons. The nuclear charge grows stronger, but shielding stays constant, creating a tighter grip on electrons.
Going down a group, electronegativity decreases despite increasing nuclear charge. The atoms get bigger, more inner shells create shielding, and the increased distance weakens the attraction between nucleus and bonding electrons.
You can predict bond types using electronegativity differences: equal values give pure covalent bonds, slight differences create polar covalent bonds, and large differences result in ionic bonds.
This prediction system helps you understand why some compounds conduct electricity, dissolve in water, or have particular melting points - it all comes down to the electronegativity differences between atoms.
Quick Check: If electronegativity difference is roughly >1.7, expect ionic character; <0.5 suggests pure covalent bonding.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Polar bonds form when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally. The more electronegative atom becomes slightly negative (δ-) whilst the other becomes slightly positive (δ+).
Having polar bonds doesn't automatically make a polar molecule though! The molecule's shape matters crucially. Water (H₂O) is polar because its bent shape means the dipoles don't cancel out, but carbon dioxide (CO₂) is non-polar despite having polar bonds because its linear shape makes the dipoles cancel.
A permanent dipole exists when there's a persistent charge difference across a covalent bond. These dipoles can align with each other, creating weak electrostatic attractions between molecules - about 1/100th the strength of covalent bonds.
Non-polar molecules either have no polar bonds at all, or have polar bonds arranged symmetrically so the charges cancel out completely.
Shape Matters: Always consider molecular geometry - symmetrical molecules with polar bonds often end up non-polar overall.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Linear, symmetrical molecules are typically non-polar because dipoles cancel out. However, molecules with OH, NH, or lone H atoms at the ends are usually polar due to the significant electronegativity differences.
Carbon-containing molecules are often non-polar, especially hydrocarbons, but there are important exceptions. Diatomic elements with identical atoms (like Cl₂ or O₂) are always non-polar since there's no electronegativity difference.
C-H and S-H bonds don't produce significant dipoles due to similar electronegativities. When predicting polarity, look for the dipole sum - if individual bond dipoles cancel out, the molecule is non-polar; if they don't cancel, it's polar.
The key is recognising that molecular polarity depends on both individual bond polarities and the overall molecular geometry. Symmetry is your friend for predicting non-polar molecules.
Rule of Thumb: Symmetrical molecules tend to be non-polar even with polar bonds, whilst asymmetrical molecules with polar bonds are usually polar overall.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
12
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the fundamentals of ionic bonding, including the formation of ions, properties of ionic compounds, and the differences between ionic and covalent bonds. This summary covers key concepts such as ion formation, electrostatic forces, and the characteristics of ionic compounds, making it essential for understanding chemical bonding. Ideal for students preparing for exams or seeking a clear overview of ionic bonding principles.
Explore key periodic trends in Higher Chemistry, including ionization energy, electronegativity, and covalent radius. This summary provides essential insights into how these properties change across periods and down groups, with a focus on their implications in chemical behavior. Ideal for students preparing for exams in Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure.
Explore the key concepts of periodicity in chemistry, including ionization energy, electronegativity, atomic radius, and covalent bonding. This summary covers the periodic trends across groups and periods, detailing the properties of covalent network solids and their structures. Ideal for SQA Higher Chemistry students seeking a comprehensive understanding of the periodic table and its implications.
Explore the shapes of molecules through VSEPR theory, including bond angles, electron domains, and the impact of lone pairs on molecular geometry. This summary covers key concepts such as linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral shapes, providing a clear understanding of molecular structures.
Explore the fundamentals of chemical bonding, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. This summary covers solid structures, molecular shapes, bond polarity, and intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals and hydrogen bonds. Ideal for AS AQA Physical Chemistry students.
Explore the principles of VSEPR theory and molecular shapes in this detailed summary. Understand the impact of lone pairs and bonding pairs on molecular geometry, bond angles, and electron pair repulsion. Ideal for AQA A-Level Chemistry students seeking to master molecular structures.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user