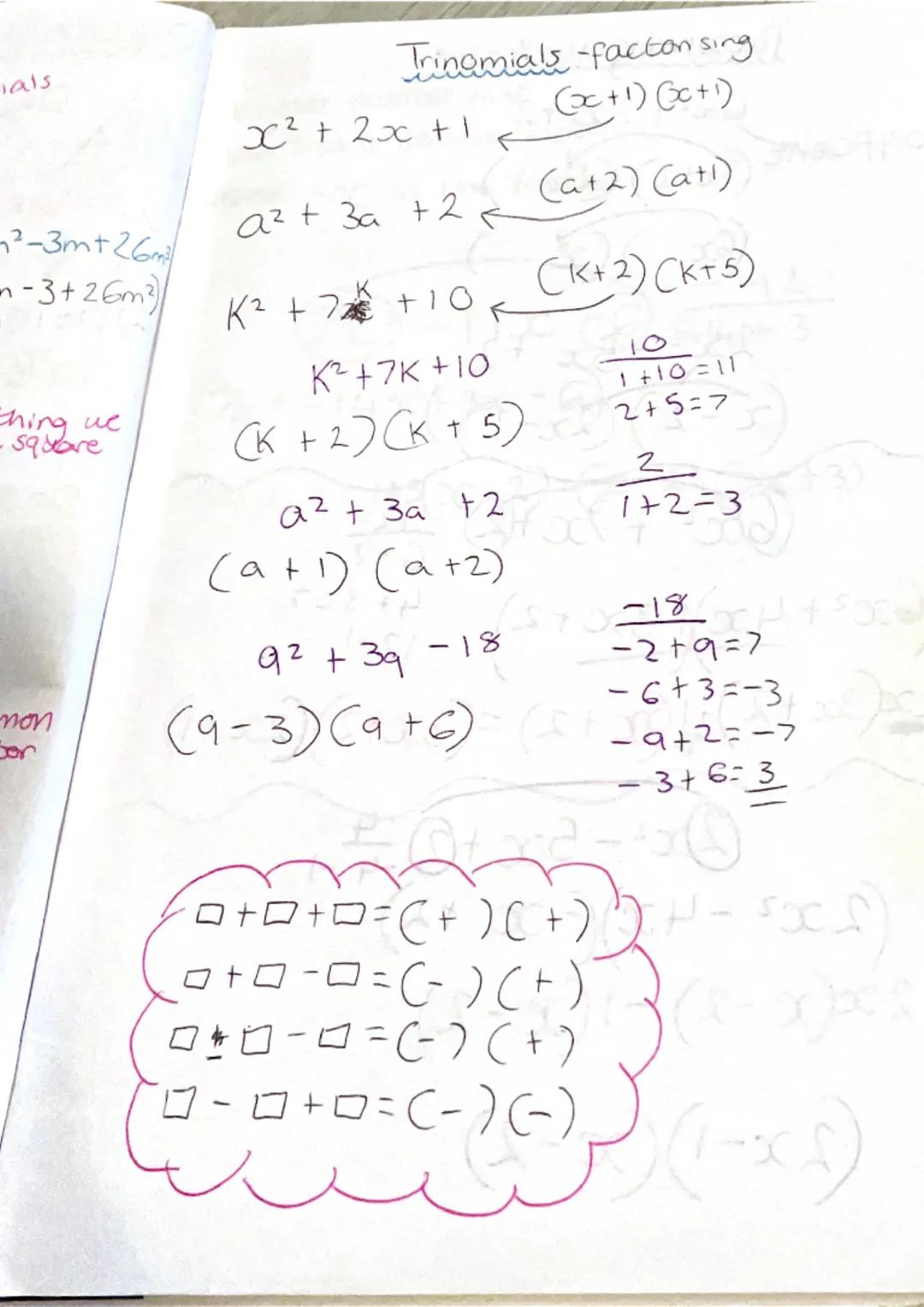Factoring Trinomials
This page focuses on factoring trinomials, particularly quadratic expressions.
Definition: A trinomial is an algebraic expression consisting of three terms, often in the form ax² + bx + c.
The page provides several examples of factoring trinomials:
Example: x² + 7x + 10 = x+2x+5
Example: a² + 3a + 2 = a+1a+2
Highlight: When factoring trinomials, look for two numbers that multiply to give the constant term and add to give the coefficient of x.
The page also covers the special case of perfect square trinomials:
Example: x² + 2x + 1 = x+1x+1 = x+1²
It concludes with a method for checking factorization by expanding the factors:
Example: For x+2x+5:
2 + 5 = 7 (coefficient of x)
2 × 5 = 10 (constant term)
This method provides a quick way to verify if the factorization is correct.