Memory is a fascinating process that allows us to encode,... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
315
•
10 Feb 2026
•
poppy
@poppy_grad2027
Memory is a fascinating process that allows us to encode,... Show more









Memory is more than just remembering facts for a test - it's the foundation of how we learn and function every day. Memory involves three key processes: encoding (getting information in), storage (keeping it), and retrieval (getting it back out when needed).
There are three main ways we encode information into our memory:
When we need to access stored information, we use three different retrieval methods:
Quick Tip: Understanding how memory works isn't just academic knowledge - it can help you develop better study techniques based on how your brain actually processes information!
Your brain uses different types of memory systems for different purposes. Knowing which type to use can help you learn more effectively.
Episodic memory stores your personal experiences and events. Think of it like your own personal autobiography - remembering your first day of school, your last birthday party, or that holiday to the beach last summer. These memories are unique to you and form part of your life story.
Semantic memory is your storehouse for general knowledge and facts. When you know that London is the capital of England or that water boils at 100°C, you're using semantic memory. These aren't personal memories but shared knowledge that helps you understand the world.
Procedural memory is how you remember to do things - riding a bike, tying your shoelaces, or swimming. Interestingly, procedural memories are stored using a motor code rather than words. That's why showing someone how to swim works better than just explaining it to them!
Remember: When studying a new skill, practising the physical movements is much more effective than just reading about how to do it - your procedural memory needs physical practice to develop!
Wondering why some information sticks in your mind while other details fade away? It all depends on how your brain processes it.
Acoustic encoding happens when you store information as sounds. When someone tells you their phone number and you repeat it to yourself until you can write it down, you're using acoustic encoding. This is useful for temporarily holding information but may not last long.
Visual encoding occurs when you create mental pictures. If you try to remember what your classroom looks like or picture the layout of your town, you're using visual encoding. This type of encoding can be powerful for remembering spatial information.
Semantic encoding involves processing information through its meaning. When you understand a concept deeply enough to explain it in your own words, you're using semantic encoding. This is often the most effective way to remember information for the long term.
How we retrieve memories is just as important as how we store them. Recall involves actively searching your memory (like on a test), recognition is identifying information you've seen before (like multiple choice questions), and re-learning is why you can pick up old skills faster than learning new ones.
Study Hack: Try converting information into different forms - create visual diagrams of written information, explain concepts aloud, or write summaries in your own words to strengthen your memory through multiple encoding methods!

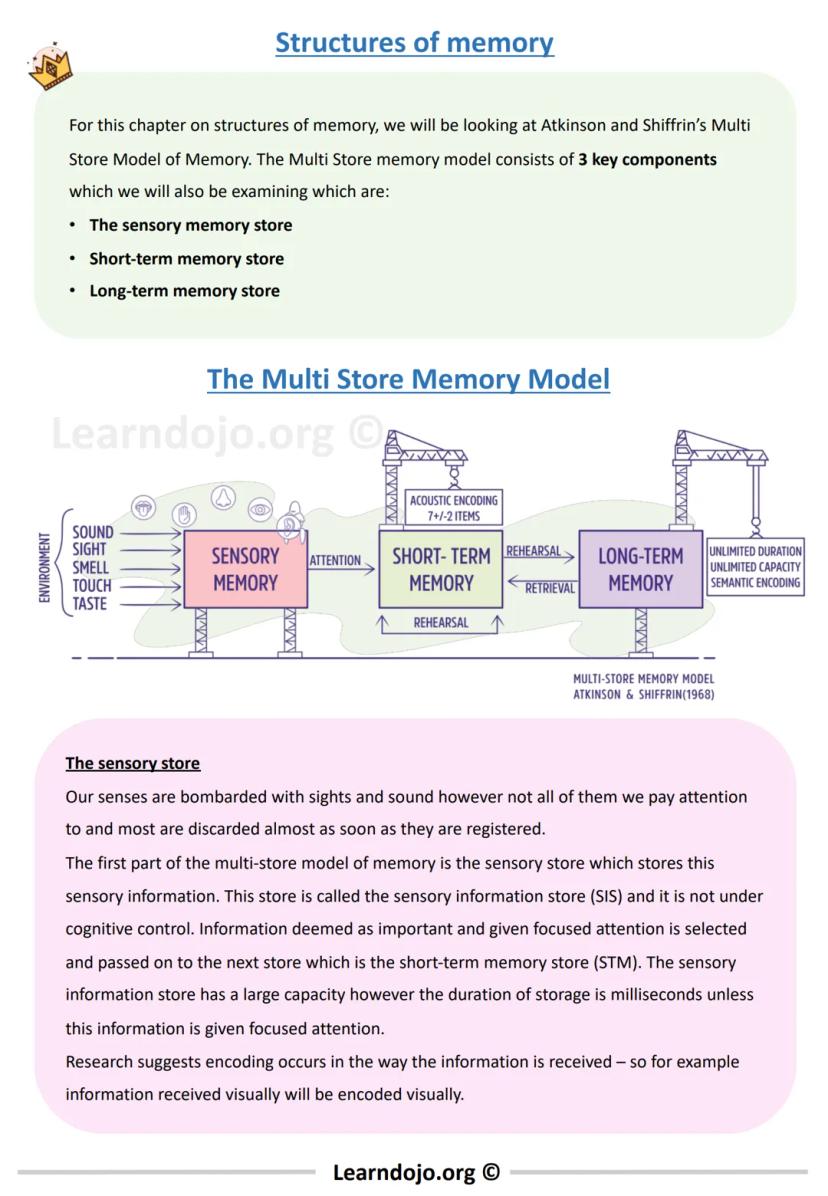
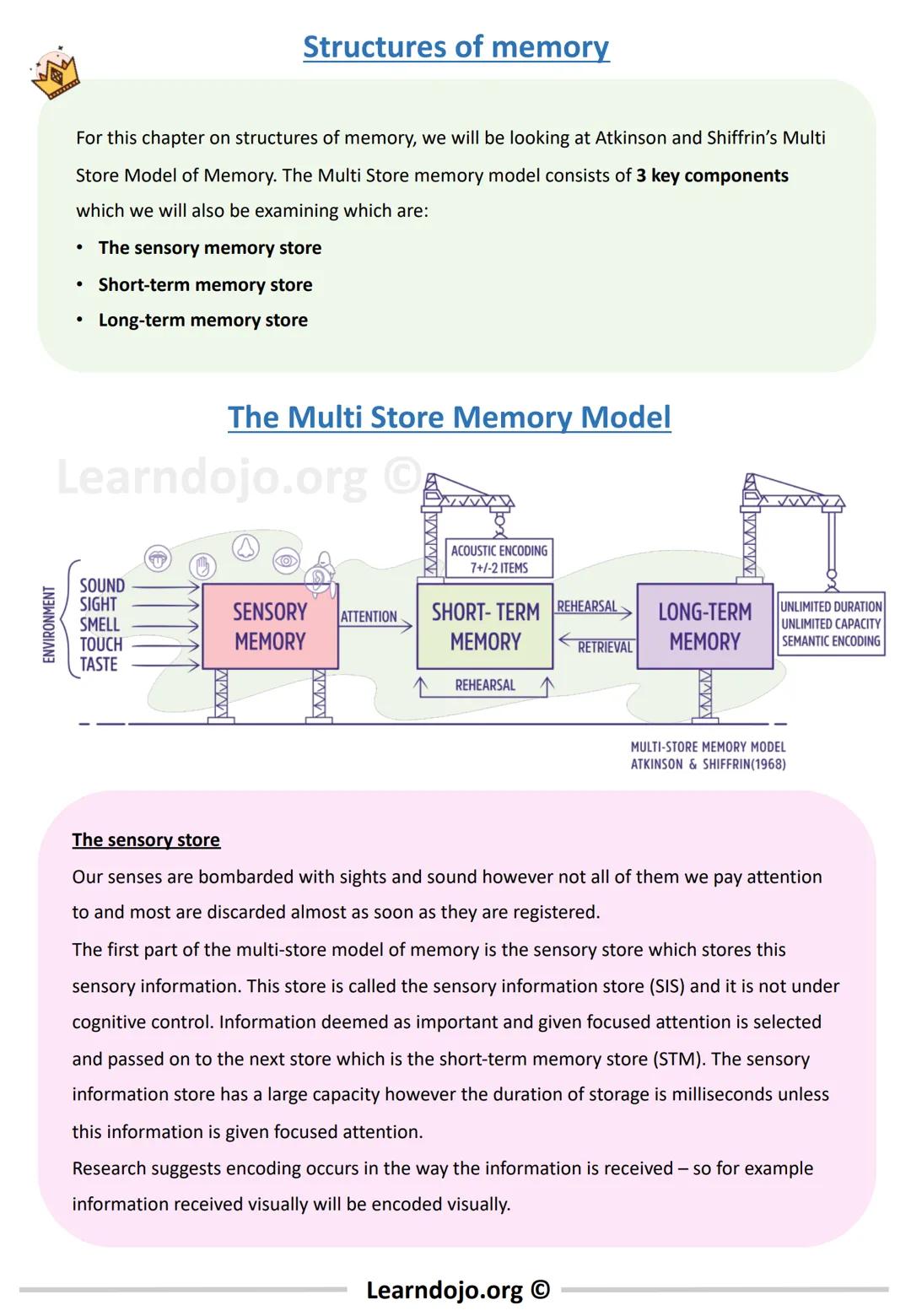
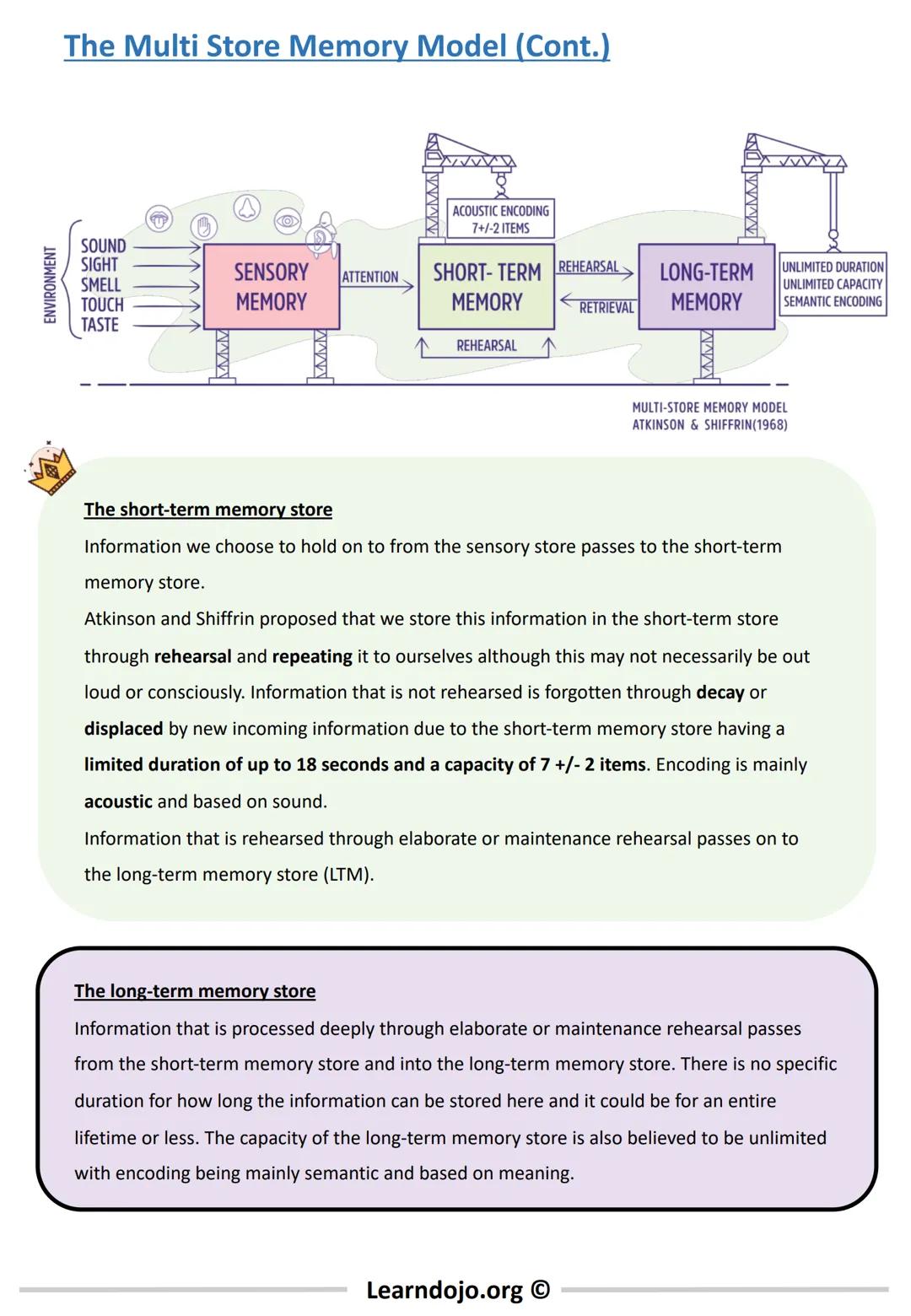
The Multi-Store Memory Model, developed by Atkinson and Shiffrin, explains how memory works through three distinct storage systems that process information in different ways.
First, information enters your sensory memory, which briefly holds all the sights, sounds, smells and other sensations you experience. Most of this information disappears within milliseconds unless you pay attention to it. Your sensory memory has huge capacity but extremely brief duration.
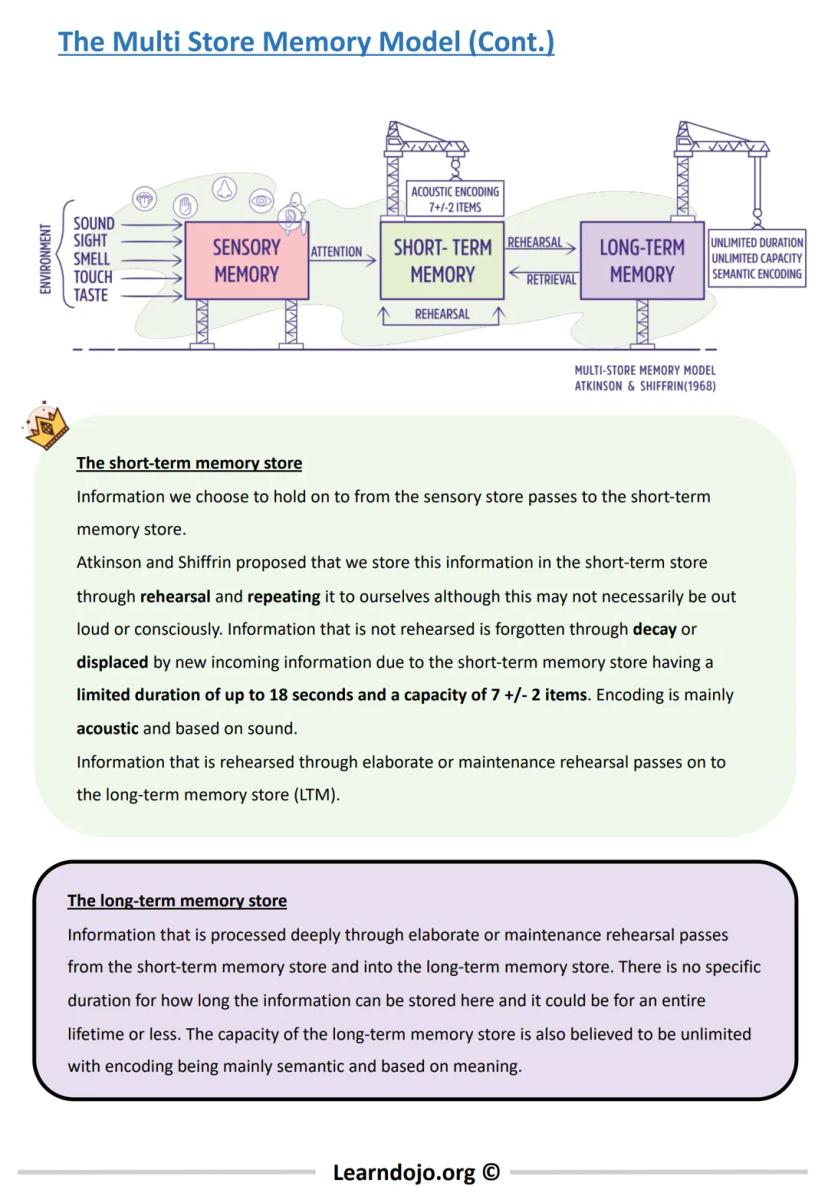
Information you focus on moves to your short-term memory (STM), which can hold about 7±2 items for up to 18 seconds. This is why phone numbers are typically seven digits long! Information in STM is primarily encoded acoustically (by sound). To keep information in your STM longer, you need to rehearse it by repeating it to yourself.
Through rehearsal, information can transfer to your long-term memory (LTM), which has unlimited capacity and can store information for a lifetime. Unlike STM, information in LTM is primarily encoded semantically (by meaning).
Did you know? Brain scans show different parts of your brain activate when using short-term versus long-term memory. The prefrontal cortex handles short-term memory tasks, while the hippocampus is crucial for long-term memory – proving these really are separate systems!

The Multi-Store Memory Model gives us a useful framework for understanding memory, but like all theories, it has both strengths and limitations.
Strengths: The model's predictions are easily testable, which is crucial for any scientific theory. Brain imaging studies support the idea of separate memory stores, showing different brain regions activate during short-term versus long-term memory tasks. The prefrontal cortex lights up during STM tasks, while the hippocampus is active during LTM processes.
Weaknesses: The model struggles to explain why we can sometimes remember things we never rehearsed (like what you had for dinner last week) while forgetting information we've repeatedly rehearsed (like exam material). Simple repetition doesn't always lead to better memory. Understanding the meaning of information (semantic processing) often matters more than rehearsal.
The model also presents memory as too simplistic and linear. Modern research shows memory is more complex and interconnected than the straight path from sensory to short-term to long-term memory that the model suggests.
Exam Tip: When evaluating memory models, remember that real-life memory isn't just about rehearsing information—it's about making meaningful connections between new information and what you already know!

Have you ever noticed that it's easier to remember items from the beginning and end of a list? This phenomenon is known as the primacy and recency effects, and understanding them can help improve your study techniques.
The primacy effect explains why we tend to remember items from the beginning of a list better. When you start learning new information, you have more time and mental energy to rehearse these first items, helping transfer them to your long-term memory.
The recency effect explains why items at the end of a list are also well-remembered. These final items are still fresh in your short-term memory when you're asked to recall them, making them easier to access.
Murdock's Serial Position Curve study (1962) demonstrated these effects clearly. When participants were asked to remember lists of words, they recalled words from the beginning and end much better than those in the middle. This creates a U-shaped curve when graphed—high recall at both ends with a dip in the middle.
Study Strategy: Break your revision into smaller chunks with short breaks between topics. This creates multiple "beginnings" and "endings" in your study session, taking advantage of both primacy and recency effects to boost your memory!
Unlike the Multi-Store Model, which sees memory as a recording device, Bartlett's theory suggests that memories aren't stored exactly as experienced but are reconstructed each time we remember them.
Bartlett proposed that we don't simply record memories like a video camera. Instead, we interpret experiences based on our existing knowledge, beliefs, and expectations—a process he called "effort after meaning". When we recall memories, we unconsciously fill in gaps and adjust details to make them more sensible to us.
In his famous "War of the Ghosts" study (1932), Bartlett had participants read an unfamiliar Native American folk tale and then retell it. As the story passed from person to person:
This study showed that memory is an active process of reconstruction rather than a passive recording. People automatically reshape memories to fit with their understanding of the world.
Real-world application: Understanding reconstructive memory helps explain why eyewitness testimony can be unreliable, and why different people remember the same event differently—we're all reconstructing memories through our own personal lens of experiences and expectations.
Several factors can influence how accurately we remember information, from interference from other memories to the context in which we learn.
Interference occurs when memories compete with each other:
False memories are recollections of events that didn't actually happen. Research by Elizabeth Loftus showed how easily false memories can be created. In one study, participants were convinced they had been lost in a shopping centre as children, with 25% developing detailed memories of an event that never occurred.
Context plays a crucial role in memory. Have you ever walked into a room only to forget why you went there? The environmental cues present when you encoded a memory (sights, sounds, smells) become linked to that memory. Returning to the same environment can trigger recall—explaining why going back to the room where you had the thought often helps you remember what you were looking for.
Memory trick: When studying for an exam, try to recreate the exam environment during revision. If possible, study in a quiet room similar to the exam hall, as these contextual cues may help trigger your memories during the actual test.


Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
poppy
@poppy_grad2027
Memory is a fascinating process that allows us to encode, store and retrieve information. Understanding how memory works can help you perform better in exams and daily life. This guide explores the different types of memory, how they function, and... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
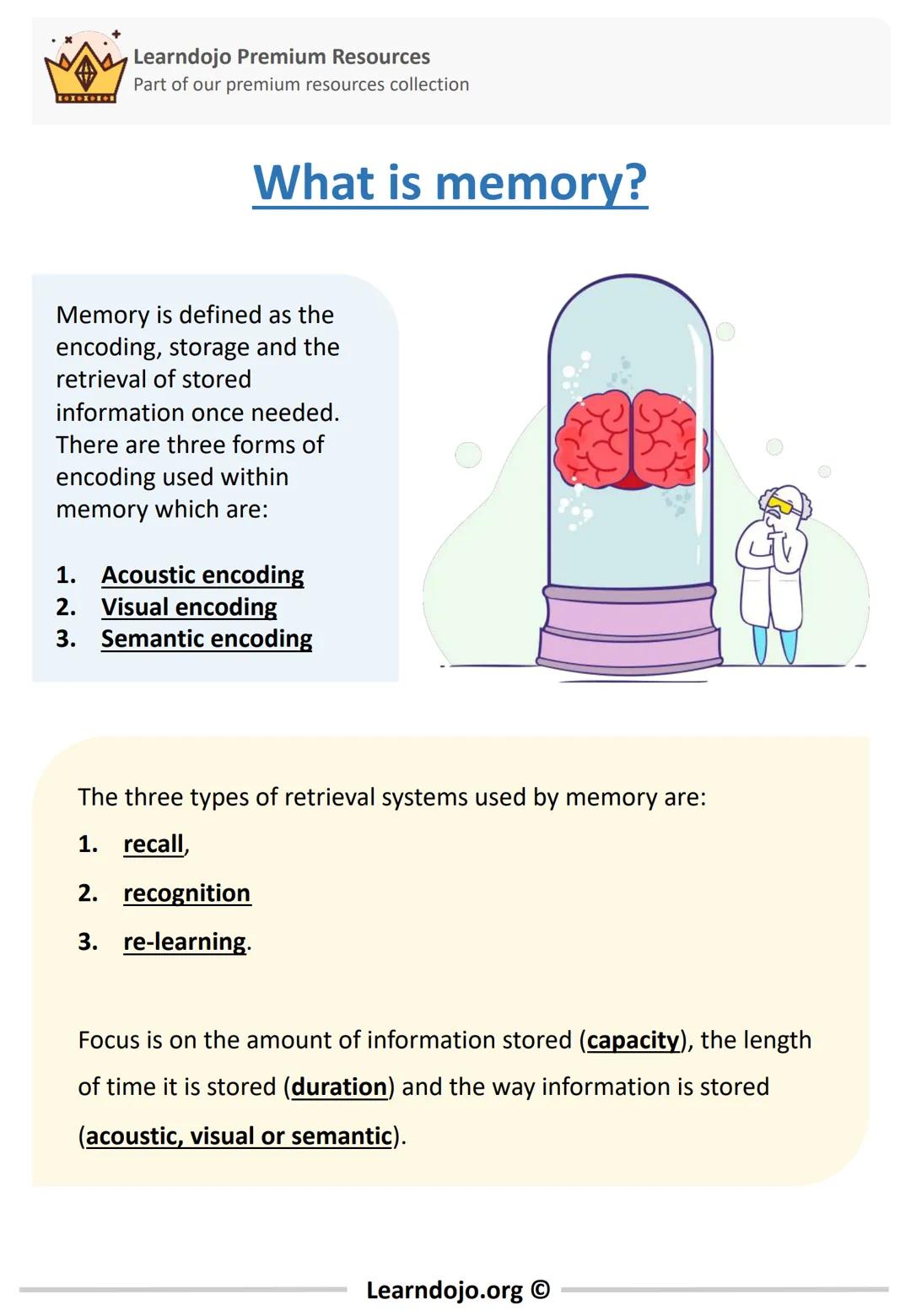
Memory is more than just remembering facts for a test - it's the foundation of how we learn and function every day. Memory involves three key processes: encoding (getting information in), storage (keeping it), and retrieval (getting it back out when needed).
There are three main ways we encode information into our memory:
When we need to access stored information, we use three different retrieval methods:
Quick Tip: Understanding how memory works isn't just academic knowledge - it can help you develop better study techniques based on how your brain actually processes information!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your brain uses different types of memory systems for different purposes. Knowing which type to use can help you learn more effectively.
Episodic memory stores your personal experiences and events. Think of it like your own personal autobiography - remembering your first day of school, your last birthday party, or that holiday to the beach last summer. These memories are unique to you and form part of your life story.
Semantic memory is your storehouse for general knowledge and facts. When you know that London is the capital of England or that water boils at 100°C, you're using semantic memory. These aren't personal memories but shared knowledge that helps you understand the world.
Procedural memory is how you remember to do things - riding a bike, tying your shoelaces, or swimming. Interestingly, procedural memories are stored using a motor code rather than words. That's why showing someone how to swim works better than just explaining it to them!
Remember: When studying a new skill, practising the physical movements is much more effective than just reading about how to do it - your procedural memory needs physical practice to develop!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Wondering why some information sticks in your mind while other details fade away? It all depends on how your brain processes it.
Acoustic encoding happens when you store information as sounds. When someone tells you their phone number and you repeat it to yourself until you can write it down, you're using acoustic encoding. This is useful for temporarily holding information but may not last long.
Visual encoding occurs when you create mental pictures. If you try to remember what your classroom looks like or picture the layout of your town, you're using visual encoding. This type of encoding can be powerful for remembering spatial information.
Semantic encoding involves processing information through its meaning. When you understand a concept deeply enough to explain it in your own words, you're using semantic encoding. This is often the most effective way to remember information for the long term.
How we retrieve memories is just as important as how we store them. Recall involves actively searching your memory (like on a test), recognition is identifying information you've seen before (like multiple choice questions), and re-learning is why you can pick up old skills faster than learning new ones.
Study Hack: Try converting information into different forms - create visual diagrams of written information, explain concepts aloud, or write summaries in your own words to strengthen your memory through multiple encoding methods!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Multi-Store Memory Model, developed by Atkinson and Shiffrin, explains how memory works through three distinct storage systems that process information in different ways.
First, information enters your sensory memory, which briefly holds all the sights, sounds, smells and other sensations you experience. Most of this information disappears within milliseconds unless you pay attention to it. Your sensory memory has huge capacity but extremely brief duration.
Information you focus on moves to your short-term memory (STM), which can hold about 7±2 items for up to 18 seconds. This is why phone numbers are typically seven digits long! Information in STM is primarily encoded acoustically (by sound). To keep information in your STM longer, you need to rehearse it by repeating it to yourself.
Through rehearsal, information can transfer to your long-term memory (LTM), which has unlimited capacity and can store information for a lifetime. Unlike STM, information in LTM is primarily encoded semantically (by meaning).
Did you know? Brain scans show different parts of your brain activate when using short-term versus long-term memory. The prefrontal cortex handles short-term memory tasks, while the hippocampus is crucial for long-term memory – proving these really are separate systems!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Multi-Store Memory Model gives us a useful framework for understanding memory, but like all theories, it has both strengths and limitations.
Strengths: The model's predictions are easily testable, which is crucial for any scientific theory. Brain imaging studies support the idea of separate memory stores, showing different brain regions activate during short-term versus long-term memory tasks. The prefrontal cortex lights up during STM tasks, while the hippocampus is active during LTM processes.
Weaknesses: The model struggles to explain why we can sometimes remember things we never rehearsed (like what you had for dinner last week) while forgetting information we've repeatedly rehearsed (like exam material). Simple repetition doesn't always lead to better memory. Understanding the meaning of information (semantic processing) often matters more than rehearsal.
The model also presents memory as too simplistic and linear. Modern research shows memory is more complex and interconnected than the straight path from sensory to short-term to long-term memory that the model suggests.
Exam Tip: When evaluating memory models, remember that real-life memory isn't just about rehearsing information—it's about making meaningful connections between new information and what you already know!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Have you ever noticed that it's easier to remember items from the beginning and end of a list? This phenomenon is known as the primacy and recency effects, and understanding them can help improve your study techniques.
The primacy effect explains why we tend to remember items from the beginning of a list better. When you start learning new information, you have more time and mental energy to rehearse these first items, helping transfer them to your long-term memory.
The recency effect explains why items at the end of a list are also well-remembered. These final items are still fresh in your short-term memory when you're asked to recall them, making them easier to access.
Murdock's Serial Position Curve study (1962) demonstrated these effects clearly. When participants were asked to remember lists of words, they recalled words from the beginning and end much better than those in the middle. This creates a U-shaped curve when graphed—high recall at both ends with a dip in the middle.
Study Strategy: Break your revision into smaller chunks with short breaks between topics. This creates multiple "beginnings" and "endings" in your study session, taking advantage of both primacy and recency effects to boost your memory!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Unlike the Multi-Store Model, which sees memory as a recording device, Bartlett's theory suggests that memories aren't stored exactly as experienced but are reconstructed each time we remember them.
Bartlett proposed that we don't simply record memories like a video camera. Instead, we interpret experiences based on our existing knowledge, beliefs, and expectations—a process he called "effort after meaning". When we recall memories, we unconsciously fill in gaps and adjust details to make them more sensible to us.
In his famous "War of the Ghosts" study (1932), Bartlett had participants read an unfamiliar Native American folk tale and then retell it. As the story passed from person to person:
This study showed that memory is an active process of reconstruction rather than a passive recording. People automatically reshape memories to fit with their understanding of the world.
Real-world application: Understanding reconstructive memory helps explain why eyewitness testimony can be unreliable, and why different people remember the same event differently—we're all reconstructing memories through our own personal lens of experiences and expectations.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Several factors can influence how accurately we remember information, from interference from other memories to the context in which we learn.
Interference occurs when memories compete with each other:
False memories are recollections of events that didn't actually happen. Research by Elizabeth Loftus showed how easily false memories can be created. In one study, participants were convinced they had been lost in a shopping centre as children, with 25% developing detailed memories of an event that never occurred.
Context plays a crucial role in memory. Have you ever walked into a room only to forget why you went there? The environmental cues present when you encoded a memory (sights, sounds, smells) become linked to that memory. Returning to the same environment can trigger recall—explaining why going back to the room where you had the thought often helps you remember what you were looking for.
Memory trick: When studying for an exam, try to recreate the exam environment during revision. If possible, study in a quiet room similar to the exam hall, as these contextual cues may help trigger your memories during the actual test.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
7
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user