Physics is a subject that explains how our universe works,... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
996
•
5 Feb 2026
•
olivia
@oliviarx
Physics is a subject that explains how our universe works,... Show more









Ever wondered why objects move or stay still? It all comes down to forces and Newton's laws.
Scalars have only magnitude (size) and no direction. Examples include speed, distance, time, mass and energy. Vectors have both magnitude and direction and can be negative. Examples include velocity, displacement, acceleration and force.
Velocity is speed in a certain direction, making it a vector quantity. To calculate speed: Speed = distance (m) ÷ time (s).
Remember: Newton's first law states that an object maintains constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force. No resultant force means no acceleration!
Newton's second law tells us that Force (N) = mass (kg) × acceleration , or F = ma. This helps us calculate how objects accelerate when forces act on them. Meanwhile, Newton's third law states that every action force has an equal and opposite reaction force .
Momentum (mass × velocity) is always conserved in collisions when there are no external forces. This conservation principle is crucial for understanding everything from car crashes to billiard ball collisions.

When a vehicle needs to stop, physics explains exactly why it can't do so instantly.
The stopping distance consists of two parts: thinking distance (how far you travel during reaction time) and braking distance (how far you travel while braking). Together, these determine how much space you need to stop safely.
Several factors affect stopping distances. Thinking distance increases with higher speed, poor concentration, tiredness, distractions, or drugs/alcohol. Braking distance increases with higher speed, poor road conditions, bald tyres, worn brake pads, or greater vehicle mass.
Road safety fact: At 70mph, the typical stopping distance is 96 metres – about the length of a football pitch!
The relationship between speed and braking distance is not linear. Doubling your speed quadruples your braking distance because braking distance is proportional to the square of initial velocity. This is because work done to stop = initial kinetic energy = ½mv².
Large decelerations during crashes are particularly dangerous. When a vehicle stops suddenly from high speed, there's a large change in momentum over a very short time, creating enormous forces that can cause serious injuries. That's why safety features like crumple zones and airbags are designed to extend the stopping time.
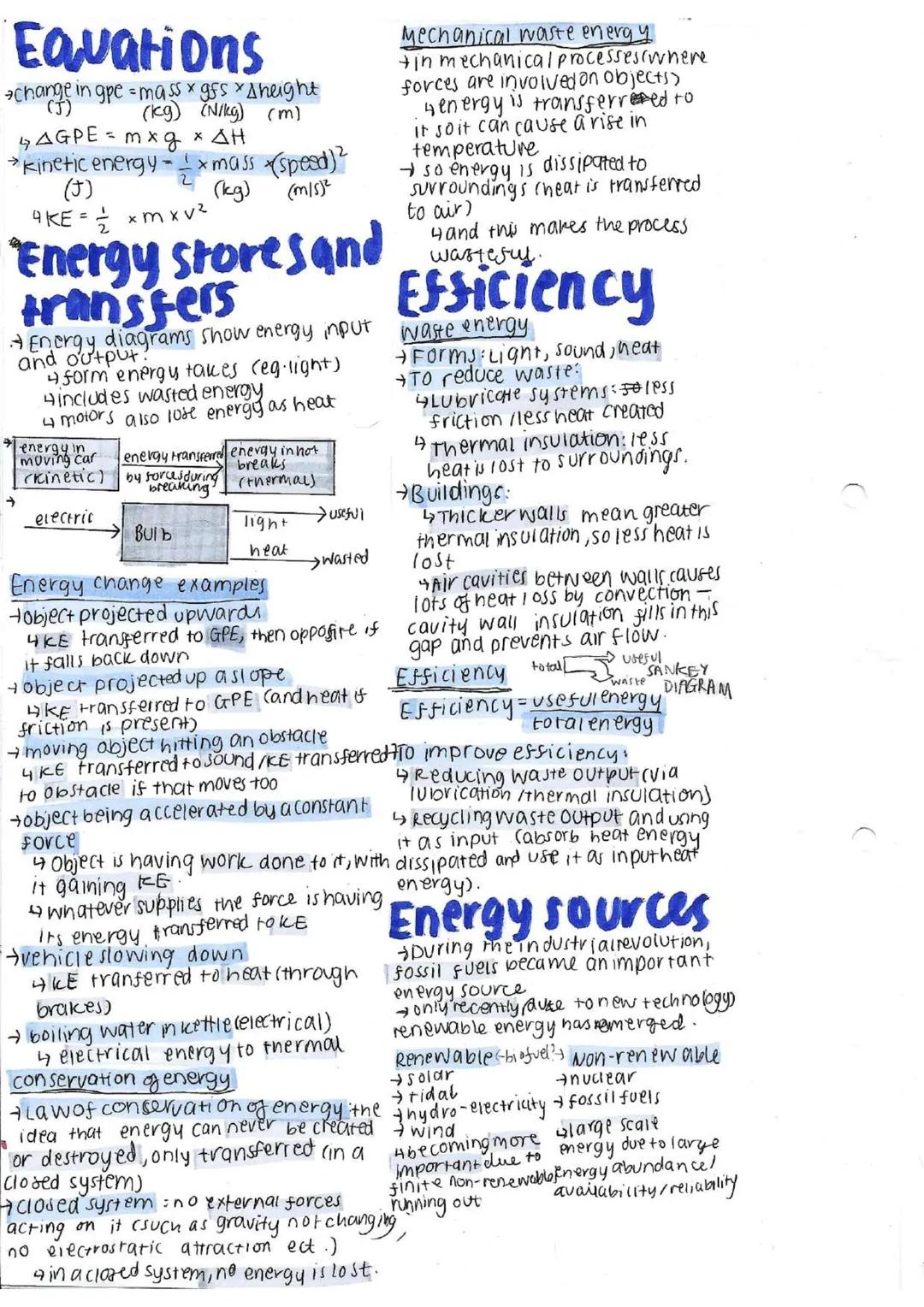
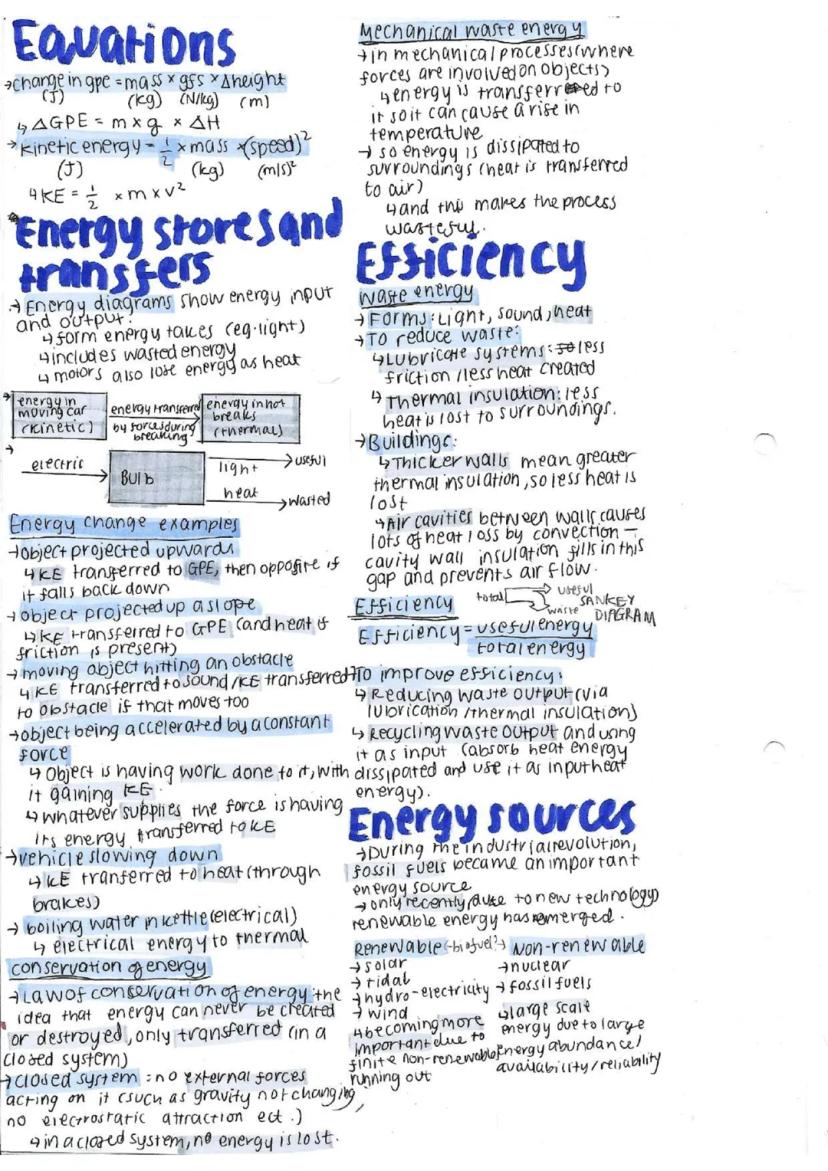
Energy makes everything happen, but it never disappears - it just changes form.
Energy comes in different forms (or "stores") like kinetic energy (movement), gravitational potential energy (height), and thermal energy (heat). The formulas to calculate these are:
Energy transfer diagrams show how energy flows from one form to another, including any wasted energy. For example, in an electric bulb, electrical energy transfers to light (useful) and heat (usually wasted).
Fascinating fact: The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, only transferred from one form to another.
Common energy transfers include:
Efficiency measures how much useful energy we get compared to the total energy input. To improve efficiency, we can reduce waste output through lubrication or thermal insulation, or recycle waste energy (like using waste heat as an input elsewhere).
Energy sources come in renewable types (solar, wind, tidal, hydroelectric) and non-renewable types (nuclear, fossil fuels). Renewable sources are becoming more important as non-renewable sources are finite and running out.

Waves are all around us, transferring energy and information without moving matter.
There are two main types of waves. Transverse waves have vibrations perpendicular to the direction of travel . Longitudinal waves have vibrations parallel to the direction of travel .
Key wave characteristics include:
The wave equation links these properties: Wave speed = frequency (Hz) × wavelength (m).
Did you know? To measure the speed of waves, scientists use techniques like recording time differences between two microphones for sound waves, or using a stroboscope for water waves.
When waves move from one medium to another, several things can happen:

Sound waves help us communicate and explore the world in fascinating ways.
The human ear is a remarkable detector of sound waves. Sound enters the ear canal and makes the eardrum vibrate. These vibrations pass through tiny bones that amplify them, then into the fluid-filled cochlea where tiny hairs detect different frequencies and create electrical signals that travel to the brain. Most people can hear frequencies between 20Hz and 20,000Hz.
Cool fact: Different parts of the cochlea detect different frequencies - high frequencies at the base and low frequencies at the apex.
Ultrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies above 20,000Hz, which humans can't hear. It has many practical applications:
Infrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies below 20Hz. Seismic P-waves (longitudinal) and S-waves (transverse) are examples of infrasound. P-waves can pass through both solids and liquids, while S-waves only pass through solids. By studying which waves reach different parts of Earth during earthquakes, scientists have determined that Earth's outer core is likely liquid, as it creates an S-wave "shadow zone."
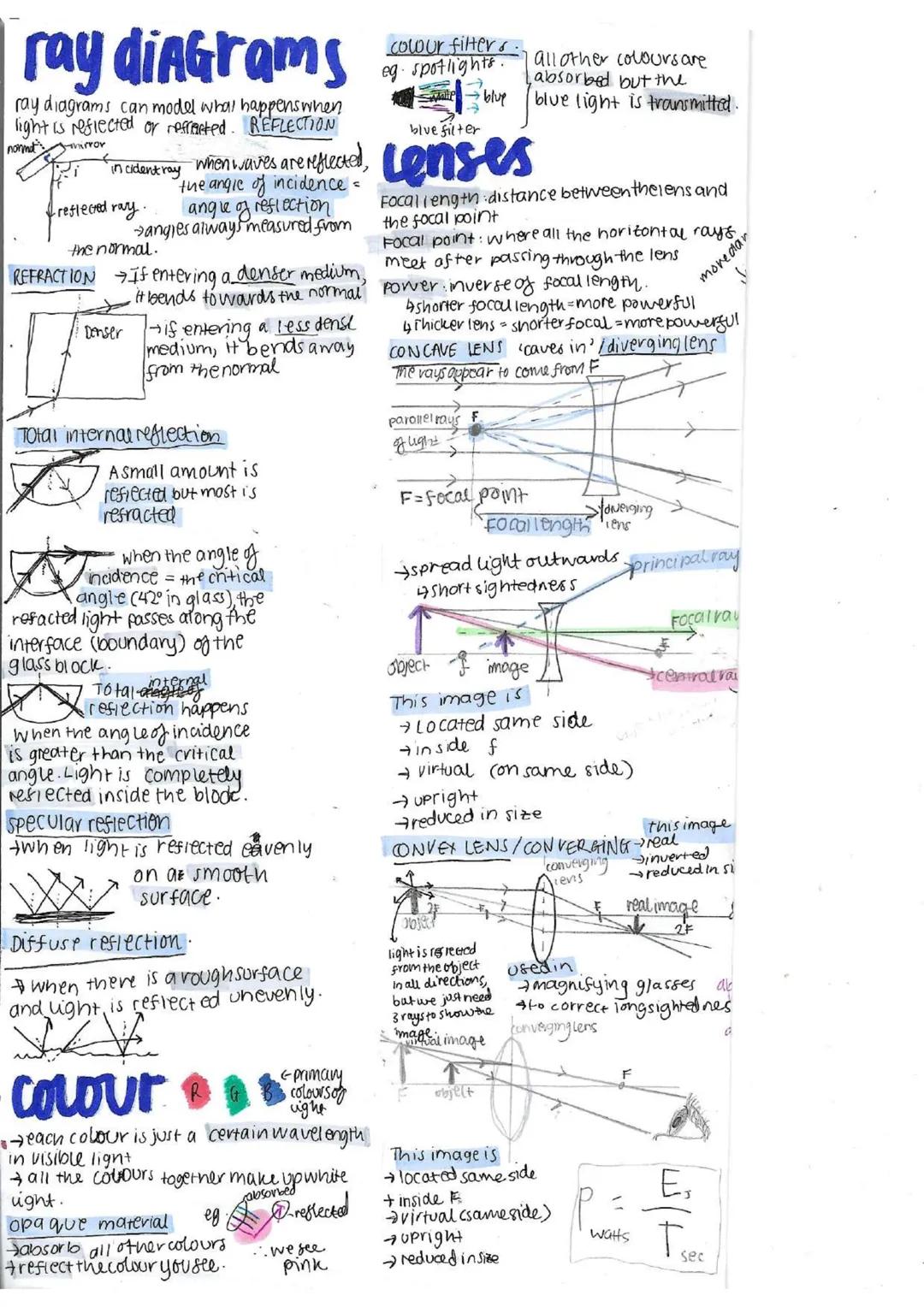
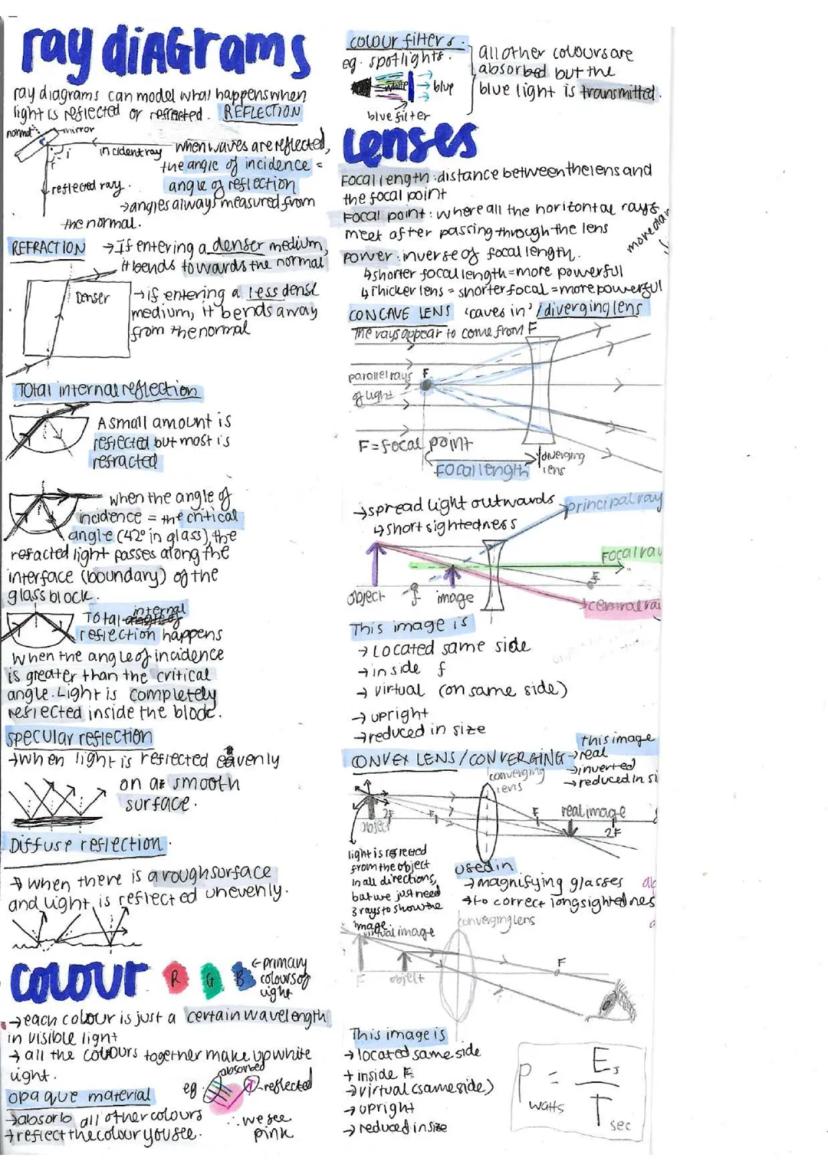
Light behaves in predictable ways that help us see and create amazing optical devices.
When light hits a boundary, it can be reflected or refracted. In reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Smooth surfaces create specular (clear) reflections, while rough surfaces create diffuse reflections.
Refraction occurs when light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. When entering a denser medium (like air to glass), light bends towards the normal line. Total internal reflection happens when light tries to exit a denser medium at an angle greater than the critical angle - it's completely reflected back inside.
Fascinating fact: Fiber optic cables use total internal reflection to send information via light pulses that bounce along the inside of the cable without escaping.
Lenses focus or spread light depending on their shape. Concave lenses (thinner in the middle) diverge light and produce virtual, upright, reduced images. They're used to correct short-sightedness. Convex lenses (thicker in the middle) converge light and can produce different types of images depending on the object's position. They're used in magnifying glasses and to correct long-sightedness.
Colour is just different wavelengths of light. When white light hits an opaque object, some wavelengths are absorbed and others reflected - we see the reflected colours. Colour filters work by transmitting only certain wavelengths and absorbing others.

The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a huge range of waves with different properties and applications.
All electromagnetic (EM) waves are transverse waves that travel at the same speed in a vacuum . They transfer energy from a source to an observer but differ in wavelength and frequency. The EM spectrum, from longest to shortest wavelength, includes: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Each type has specific sources and uses:
Health alert: Many EM waves pose health hazards! Gamma and X-rays can mutate DNA and cause cancer, UV can cause sunburn and skin cancer, and microwaves can heat body tissues.
Radio communication works because oscillations (variations in current and voltage) in a transmitting aerial create radio waves that cause similar oscillations in a receiving aerial. Some radio waves are reflected by the ionosphere (a region of charged particles in the atmosphere), allowing them to travel beyond the horizon.

Electromagnetic waves connect us to the world while radioactive emissions reveal the secrets of atoms.
Different EM waves have different uses and hazards:
The atom has evolved in scientific understanding over time. Today we know it consists of a positively charged nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is incredibly small (about 10⁻¹⁴m) compared to the atom (about 10⁻¹⁰m), with most of the mass concentrated in the nucleus.
Historical insight: Rutherford's alpha scattering experiment revolutionised our understanding of atomic structure. When alpha particles were fired at gold foil, most passed straight through but some bounced back - proving atoms were mostly empty space with a dense nucleus.
Electrons exist in orbits or energy levels around the nucleus. When electrons absorb energy, they move to a higher orbit (away from the nucleus). When they emit energy (often as visible light), they move to a lower orbit. Each element has a unique emission/absorption spectrum based on these electron transitions.
Ionisation occurs when enough energy is provided for electrons to completely escape from the atom, creating ions (charged particles). This is a key process in radiation detection and has implications for safety with radioactive materials.

Radioactive materials emit particles that can be both dangerous and incredibly useful.
There are three main types of radiation:
Safety first: Background radiation is all around us from sources like radon gas (50%), medical procedures (13%), food (11%), buildings, and cosmic rays. It's measured using Geiger-Müller tubes or photographic film.
Radioactive decay happens when unstable isotopes release particles to become more stable. In alpha decay, an atom loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons, decreasing its mass number by 4 and atomic number by 2. In beta decay (β⁻), a neutron changes into a proton and an electron, increasing the atomic number by 1 while the mass number stays the same.
The half-life is the time taken for half the unstable nuclei in a sample to decay. It's a measure of how quickly radioactivity decreases, and each isotope has a specific half-life ranging from fractions of a second to billions of years.
Radiation has many practical applications including smoke alarms (alpha), food irradiation (gamma), medical tracers (gamma), thickness gauging (beta), and pipe leak detection (gamma).

Radiation offers powerful tools for medicine and energy, but requires careful handling.
In medicine, radiation is used in several ways:
Energy debate: Nuclear energy has prevented 1.8 million deaths by reducing air pollution from fossil fuels and has prevented 64 gigatons of CO₂ emissions. However, nuclear accidents can contaminate large areas, and waste disposal remains challenging.
Nuclear fission occurs when large nuclei split into smaller nuclei, releasing energy. This powers nuclear reactors, which contain:
Nuclear fusion combines small nuclei to form larger ones, releasing energy. It powers the sun but requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to overcome the repulsion between positively charged nuclei. Fusion has advantages over fission (no radioactive waste, unlimited fuel) but hasn't yet been achieved on a practical scale due to the technical challenges.
When handling radioactive materials, proper precautions are essential. These include wearing protective gear, storing materials safely, monitoring exposure with badges, limiting dose to patients, and having clear emergency procedures for containment.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
olivia
@oliviarx
Physics is a subject that explains how our universe works, from the smallest particles to the vastness of space. This study note covers key physics concepts including forces and motion, energy, waves, radiation, and the universe. These fundamental principles help... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Ever wondered why objects move or stay still? It all comes down to forces and Newton's laws.
Scalars have only magnitude (size) and no direction. Examples include speed, distance, time, mass and energy. Vectors have both magnitude and direction and can be negative. Examples include velocity, displacement, acceleration and force.
Velocity is speed in a certain direction, making it a vector quantity. To calculate speed: Speed = distance (m) ÷ time (s).
Remember: Newton's first law states that an object maintains constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force. No resultant force means no acceleration!
Newton's second law tells us that Force (N) = mass (kg) × acceleration , or F = ma. This helps us calculate how objects accelerate when forces act on them. Meanwhile, Newton's third law states that every action force has an equal and opposite reaction force .
Momentum (mass × velocity) is always conserved in collisions when there are no external forces. This conservation principle is crucial for understanding everything from car crashes to billiard ball collisions.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
When a vehicle needs to stop, physics explains exactly why it can't do so instantly.
The stopping distance consists of two parts: thinking distance (how far you travel during reaction time) and braking distance (how far you travel while braking). Together, these determine how much space you need to stop safely.
Several factors affect stopping distances. Thinking distance increases with higher speed, poor concentration, tiredness, distractions, or drugs/alcohol. Braking distance increases with higher speed, poor road conditions, bald tyres, worn brake pads, or greater vehicle mass.
Road safety fact: At 70mph, the typical stopping distance is 96 metres – about the length of a football pitch!
The relationship between speed and braking distance is not linear. Doubling your speed quadruples your braking distance because braking distance is proportional to the square of initial velocity. This is because work done to stop = initial kinetic energy = ½mv².
Large decelerations during crashes are particularly dangerous. When a vehicle stops suddenly from high speed, there's a large change in momentum over a very short time, creating enormous forces that can cause serious injuries. That's why safety features like crumple zones and airbags are designed to extend the stopping time.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Energy makes everything happen, but it never disappears - it just changes form.
Energy comes in different forms (or "stores") like kinetic energy (movement), gravitational potential energy (height), and thermal energy (heat). The formulas to calculate these are:
Energy transfer diagrams show how energy flows from one form to another, including any wasted energy. For example, in an electric bulb, electrical energy transfers to light (useful) and heat (usually wasted).
Fascinating fact: The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, only transferred from one form to another.
Common energy transfers include:
Efficiency measures how much useful energy we get compared to the total energy input. To improve efficiency, we can reduce waste output through lubrication or thermal insulation, or recycle waste energy (like using waste heat as an input elsewhere).
Energy sources come in renewable types (solar, wind, tidal, hydroelectric) and non-renewable types (nuclear, fossil fuels). Renewable sources are becoming more important as non-renewable sources are finite and running out.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Waves are all around us, transferring energy and information without moving matter.
There are two main types of waves. Transverse waves have vibrations perpendicular to the direction of travel . Longitudinal waves have vibrations parallel to the direction of travel .
Key wave characteristics include:
The wave equation links these properties: Wave speed = frequency (Hz) × wavelength (m).
Did you know? To measure the speed of waves, scientists use techniques like recording time differences between two microphones for sound waves, or using a stroboscope for water waves.
When waves move from one medium to another, several things can happen:

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Sound waves help us communicate and explore the world in fascinating ways.
The human ear is a remarkable detector of sound waves. Sound enters the ear canal and makes the eardrum vibrate. These vibrations pass through tiny bones that amplify them, then into the fluid-filled cochlea where tiny hairs detect different frequencies and create electrical signals that travel to the brain. Most people can hear frequencies between 20Hz and 20,000Hz.
Cool fact: Different parts of the cochlea detect different frequencies - high frequencies at the base and low frequencies at the apex.
Ultrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies above 20,000Hz, which humans can't hear. It has many practical applications:
Infrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies below 20Hz. Seismic P-waves (longitudinal) and S-waves (transverse) are examples of infrasound. P-waves can pass through both solids and liquids, while S-waves only pass through solids. By studying which waves reach different parts of Earth during earthquakes, scientists have determined that Earth's outer core is likely liquid, as it creates an S-wave "shadow zone."

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Light behaves in predictable ways that help us see and create amazing optical devices.
When light hits a boundary, it can be reflected or refracted. In reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Smooth surfaces create specular (clear) reflections, while rough surfaces create diffuse reflections.
Refraction occurs when light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. When entering a denser medium (like air to glass), light bends towards the normal line. Total internal reflection happens when light tries to exit a denser medium at an angle greater than the critical angle - it's completely reflected back inside.
Fascinating fact: Fiber optic cables use total internal reflection to send information via light pulses that bounce along the inside of the cable without escaping.
Lenses focus or spread light depending on their shape. Concave lenses (thinner in the middle) diverge light and produce virtual, upright, reduced images. They're used to correct short-sightedness. Convex lenses (thicker in the middle) converge light and can produce different types of images depending on the object's position. They're used in magnifying glasses and to correct long-sightedness.
Colour is just different wavelengths of light. When white light hits an opaque object, some wavelengths are absorbed and others reflected - we see the reflected colours. Colour filters work by transmitting only certain wavelengths and absorbing others.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a huge range of waves with different properties and applications.
All electromagnetic (EM) waves are transverse waves that travel at the same speed in a vacuum . They transfer energy from a source to an observer but differ in wavelength and frequency. The EM spectrum, from longest to shortest wavelength, includes: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Each type has specific sources and uses:
Health alert: Many EM waves pose health hazards! Gamma and X-rays can mutate DNA and cause cancer, UV can cause sunburn and skin cancer, and microwaves can heat body tissues.
Radio communication works because oscillations (variations in current and voltage) in a transmitting aerial create radio waves that cause similar oscillations in a receiving aerial. Some radio waves are reflected by the ionosphere (a region of charged particles in the atmosphere), allowing them to travel beyond the horizon.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Electromagnetic waves connect us to the world while radioactive emissions reveal the secrets of atoms.
Different EM waves have different uses and hazards:
The atom has evolved in scientific understanding over time. Today we know it consists of a positively charged nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is incredibly small (about 10⁻¹⁴m) compared to the atom (about 10⁻¹⁰m), with most of the mass concentrated in the nucleus.
Historical insight: Rutherford's alpha scattering experiment revolutionised our understanding of atomic structure. When alpha particles were fired at gold foil, most passed straight through but some bounced back - proving atoms were mostly empty space with a dense nucleus.
Electrons exist in orbits or energy levels around the nucleus. When electrons absorb energy, they move to a higher orbit (away from the nucleus). When they emit energy (often as visible light), they move to a lower orbit. Each element has a unique emission/absorption spectrum based on these electron transitions.
Ionisation occurs when enough energy is provided for electrons to completely escape from the atom, creating ions (charged particles). This is a key process in radiation detection and has implications for safety with radioactive materials.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Radioactive materials emit particles that can be both dangerous and incredibly useful.
There are three main types of radiation:
Safety first: Background radiation is all around us from sources like radon gas (50%), medical procedures (13%), food (11%), buildings, and cosmic rays. It's measured using Geiger-Müller tubes or photographic film.
Radioactive decay happens when unstable isotopes release particles to become more stable. In alpha decay, an atom loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons, decreasing its mass number by 4 and atomic number by 2. In beta decay (β⁻), a neutron changes into a proton and an electron, increasing the atomic number by 1 while the mass number stays the same.
The half-life is the time taken for half the unstable nuclei in a sample to decay. It's a measure of how quickly radioactivity decreases, and each isotope has a specific half-life ranging from fractions of a second to billions of years.
Radiation has many practical applications including smoke alarms (alpha), food irradiation (gamma), medical tracers (gamma), thickness gauging (beta), and pipe leak detection (gamma).

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Radiation offers powerful tools for medicine and energy, but requires careful handling.
In medicine, radiation is used in several ways:
Energy debate: Nuclear energy has prevented 1.8 million deaths by reducing air pollution from fossil fuels and has prevented 64 gigatons of CO₂ emissions. However, nuclear accidents can contaminate large areas, and waste disposal remains challenging.
Nuclear fission occurs when large nuclei split into smaller nuclei, releasing energy. This powers nuclear reactors, which contain:
Nuclear fusion combines small nuclei to form larger ones, releasing energy. It powers the sun but requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to overcome the repulsion between positively charged nuclei. Fusion has advantages over fission (no radioactive waste, unlimited fuel) but hasn't yet been achieved on a practical scale due to the technical challenges.
When handling radioactive materials, proper precautions are essential. These include wearing protective gear, storing materials safely, monitoring exposure with badges, limiting dose to patients, and having clear emergency procedures for containment.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
10
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user