Physics gets much more interesting when you see how forces... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
72
•
Updated 25 Feb 2026
•
Sara
@osaraii
Physics gets much more interesting when you see how forces... Show more






$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_1.webp&w=2048&q=75)
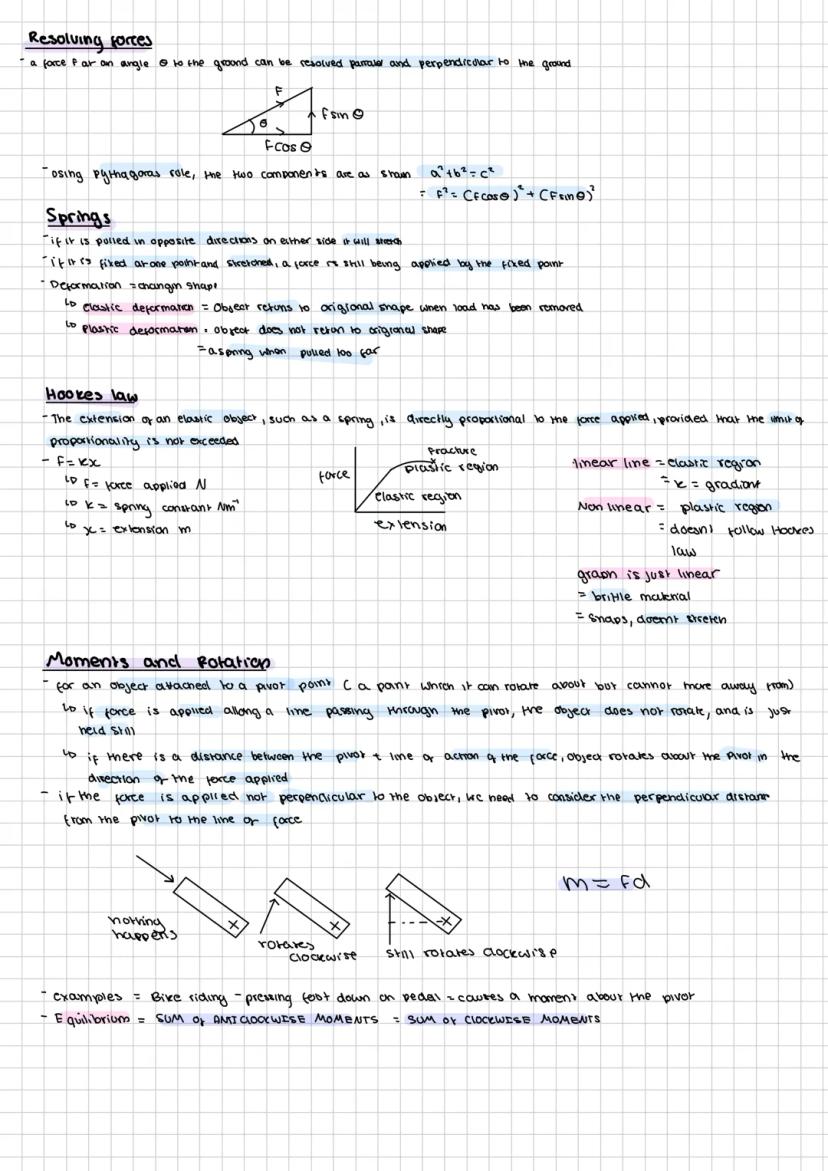
Ever wondered how engineers calculate forces acting at angles? Resolving forces breaks any angled force into two parts: one parallel to the ground (F cos θ) and one perpendicular (F sin θ). Think of pushing a heavy box up a ramp - you're working against both gravity and friction.
Springs are brilliant for understanding deformation. When you stretch a spring, it shows elastic deformation - it snaps back to its original shape. Pull too hard though, and you get plastic deformation where it stays stretched permanently. Eventually, it'll snap completely.
Hooke's Law is your best friend here: F = kx. This means the force needed to stretch a spring is directly proportional to how far you stretch it. The spring constant (k) tells you how stiff the spring is - a higher k means a stiffer spring that's harder to stretch.
Quick tip: On force-extension graphs, the straight line shows the elastic region where Hooke's law works. Once it curves, you're in the plastic region where things get permanently damaged.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_2.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Moments explain why spanners have long handles and why you can't open a door by pushing near the hinges. The moment equation is simple: M = Fd (force × perpendicular distance from the pivot). Want more turning effect? Apply the force further from the pivot.
Gears are brilliant for changing speed and force through rotation. Connect a big gear to a small one, and the small gear spins faster but with less force. It's like having a mechanical advantage - perfect for bikes where you need different power outputs for hills versus flat roads.
Pressure in fluids creates some fascinating effects. Objects float when their weight is less than the weight of water they displace - that's why massive ships don't sink. Upthrust acts upward on submerged objects because water pressure increases with depth, creating more force on the bottom than the top.
Real-world connection: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude because there's less air above you. That's why your ears pop when climbing mountains or taking off in planes.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_3.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Here's where physics gets properly exciting. Speed is just how fast you're going, but velocity includes direction too. This means an object moving in a circle at constant speed is actually accelerating because its direction keeps changing - mind-bending but true!
Distance-time graphs have gradient equal to velocity, while velocity-time graphs have gradient equal to acceleration. The area under a velocity-time graph gives you distance travelled - dead useful for exam questions.
Newton's three laws govern everything that moves. First law: objects keep doing what they're doing unless a force acts. Second law: F = ma (force equals mass times acceleration). Third law: every action has an equal and opposite reaction - like rockets pushing gases down to lift themselves up.
Terminal velocity happens when falling objects reach maximum speed. Initially they accelerate due to gravity, but air resistance increases until it balances weight perfectly. No net force means no more acceleration.
Exam success: Master these graphs and Newton's laws - they appear in virtually every mechanics question and form the foundation for understanding all motion.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_4.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Stopping distances could literally save your life. Total stopping distance equals thinking distance plus braking distance. Your reaction time affects thinking distance (tiredness, distractions, alcohol all make it worse), while speed, road conditions, and tyre quality affect braking distance.
When brakes work, they convert the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat through friction. Go faster and you need much more braking force to stop in the same distance - which is why speed limits exist and why brakes can overheat.
Momentum is always conserved in collisions and explosions . This principle helps crash investigators work out what happened and engineers design safer vehicles.
Safety features work by increasing the time taken to stop, which reduces the force experienced. Seatbelts stretch slightly, airbags inflate to cushion impact, and crumple zones deform - all designed to reduce the rate of momentum change and keep forces survivable.
Life skill alert: Understanding stopping distances isn't just for exams - it's crucial knowledge for when you start driving. Speed kills because braking distance increases dramatically with velocity.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_5.webp&w=2048&q=75)

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_6.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Sara
@osaraii
Physics gets much more interesting when you see how forces actually work in real life. This section covers everything from why springs bounce back to how your car's brakes keep you safe - plus the fundamental laws that govern all... Show more

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_1.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Ever wondered how engineers calculate forces acting at angles? Resolving forces breaks any angled force into two parts: one parallel to the ground (F cos θ) and one perpendicular (F sin θ). Think of pushing a heavy box up a ramp - you're working against both gravity and friction.
Springs are brilliant for understanding deformation. When you stretch a spring, it shows elastic deformation - it snaps back to its original shape. Pull too hard though, and you get plastic deformation where it stays stretched permanently. Eventually, it'll snap completely.
Hooke's Law is your best friend here: F = kx. This means the force needed to stretch a spring is directly proportional to how far you stretch it. The spring constant (k) tells you how stiff the spring is - a higher k means a stiffer spring that's harder to stretch.
Quick tip: On force-extension graphs, the straight line shows the elastic region where Hooke's law works. Once it curves, you're in the plastic region where things get permanently damaged.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_2.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Moments explain why spanners have long handles and why you can't open a door by pushing near the hinges. The moment equation is simple: M = Fd (force × perpendicular distance from the pivot). Want more turning effect? Apply the force further from the pivot.
Gears are brilliant for changing speed and force through rotation. Connect a big gear to a small one, and the small gear spins faster but with less force. It's like having a mechanical advantage - perfect for bikes where you need different power outputs for hills versus flat roads.
Pressure in fluids creates some fascinating effects. Objects float when their weight is less than the weight of water they displace - that's why massive ships don't sink. Upthrust acts upward on submerged objects because water pressure increases with depth, creating more force on the bottom than the top.
Real-world connection: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude because there's less air above you. That's why your ears pop when climbing mountains or taking off in planes.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_3.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Here's where physics gets properly exciting. Speed is just how fast you're going, but velocity includes direction too. This means an object moving in a circle at constant speed is actually accelerating because its direction keeps changing - mind-bending but true!
Distance-time graphs have gradient equal to velocity, while velocity-time graphs have gradient equal to acceleration. The area under a velocity-time graph gives you distance travelled - dead useful for exam questions.
Newton's three laws govern everything that moves. First law: objects keep doing what they're doing unless a force acts. Second law: F = ma (force equals mass times acceleration). Third law: every action has an equal and opposite reaction - like rockets pushing gases down to lift themselves up.
Terminal velocity happens when falling objects reach maximum speed. Initially they accelerate due to gravity, but air resistance increases until it balances weight perfectly. No net force means no more acceleration.
Exam success: Master these graphs and Newton's laws - they appear in virtually every mechanics question and form the foundation for understanding all motion.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_4.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Stopping distances could literally save your life. Total stopping distance equals thinking distance plus braking distance. Your reaction time affects thinking distance (tiredness, distractions, alcohol all make it worse), while speed, road conditions, and tyre quality affect braking distance.
When brakes work, they convert the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat through friction. Go faster and you need much more braking force to stop in the same distance - which is why speed limits exist and why brakes can overheat.
Momentum is always conserved in collisions and explosions . This principle helps crash investigators work out what happened and engineers design safer vehicles.
Safety features work by increasing the time taken to stop, which reduces the force experienced. Seatbelts stretch slightly, airbags inflate to cushion impact, and crumple zones deform - all designed to reduce the rate of momentum change and keep forces survivable.
Life skill alert: Understanding stopping distances isn't just for exams - it's crucial knowledge for when you start driving. Speed kills because braking distance increases dramatically with velocity.

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_5.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

$fsi](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F01953955-a0ec-7037-a230-81ffeebf78a6_image_page_6.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
4
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user