Probability Fundamentals
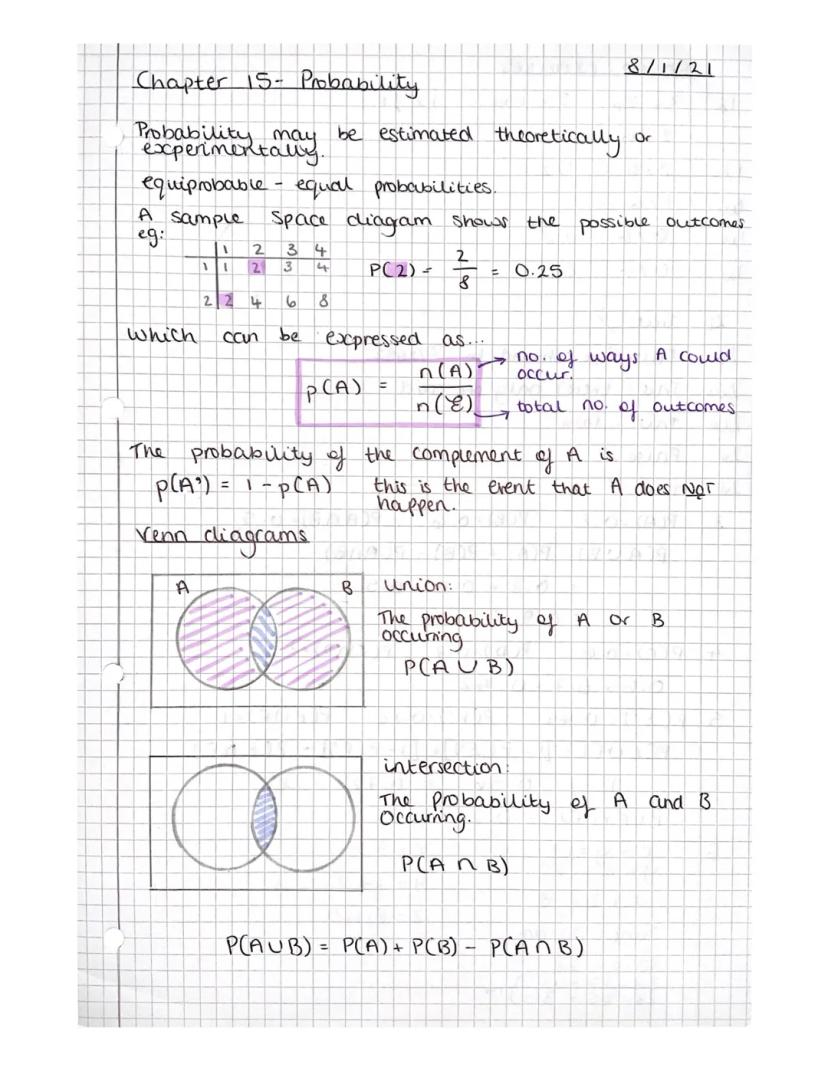
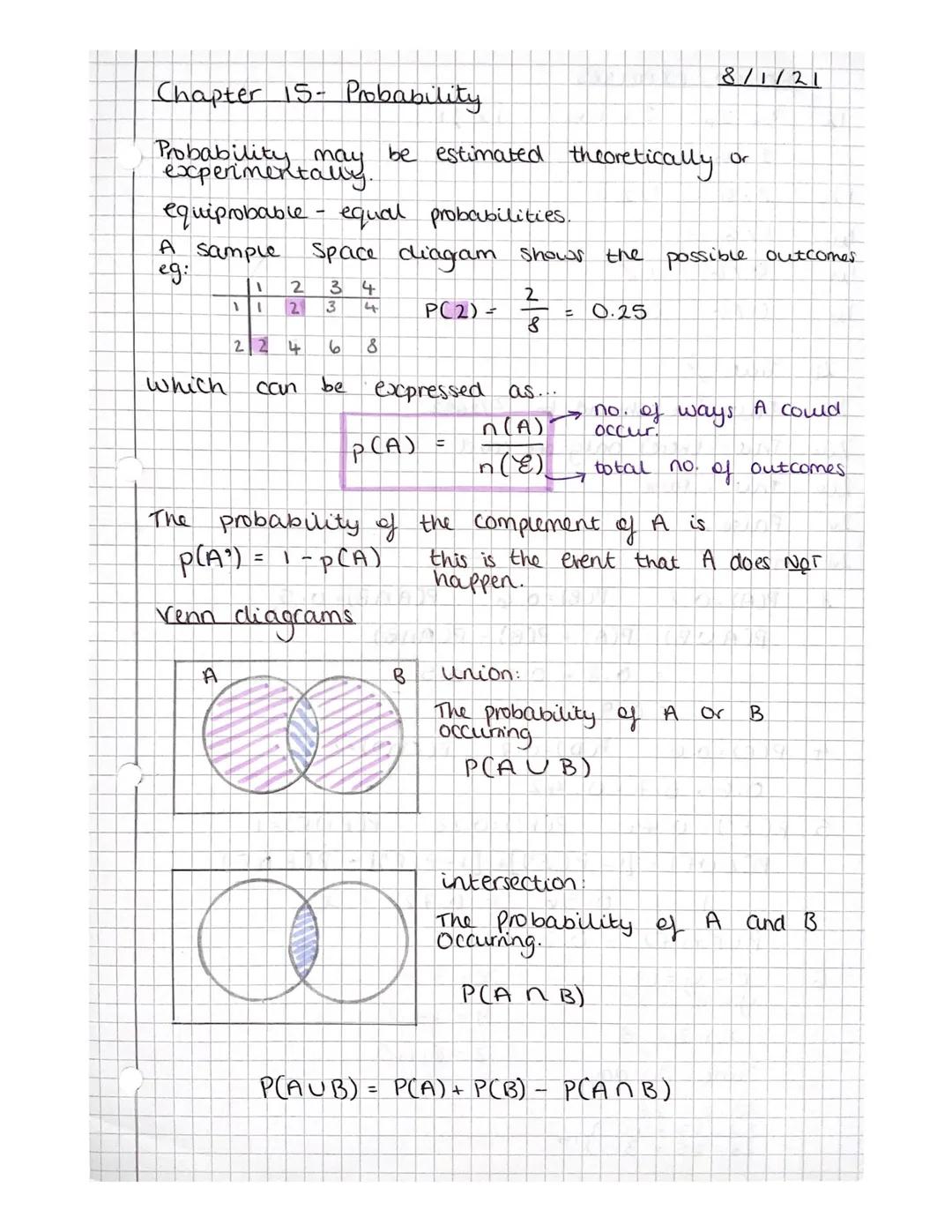
Ever wondered how to calculate the odds of rolling a specific number on a dice? Probability gives you the tools to work this out mathematically. When outcomes have equal chances of happening, we call them equiprobable.
Sample space diagrams are brilliant for visualising all possible outcomes. Think of flipping two coins - you can map out every combination heads−heads,heads−tails,etc.. The basic probability formula is P(A) = n(A)/n(ξ), where n(A) is the number of ways event A can occur, and n(ξ) is the total number of possible outcomes.
The complement of an event (written as A') represents everything that isn't A. If there's a 0.3 chance of rain, there's a 0.7 chance it won't rain. This gives us P(A') = 1 - P(A).
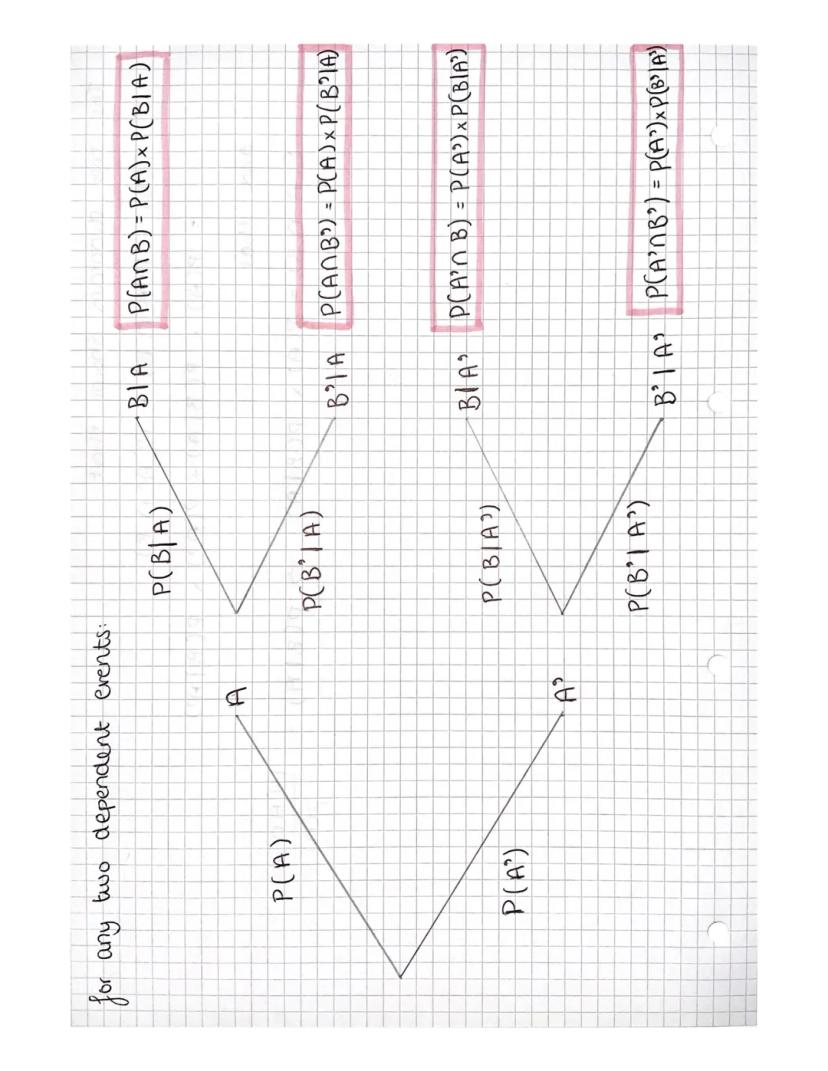
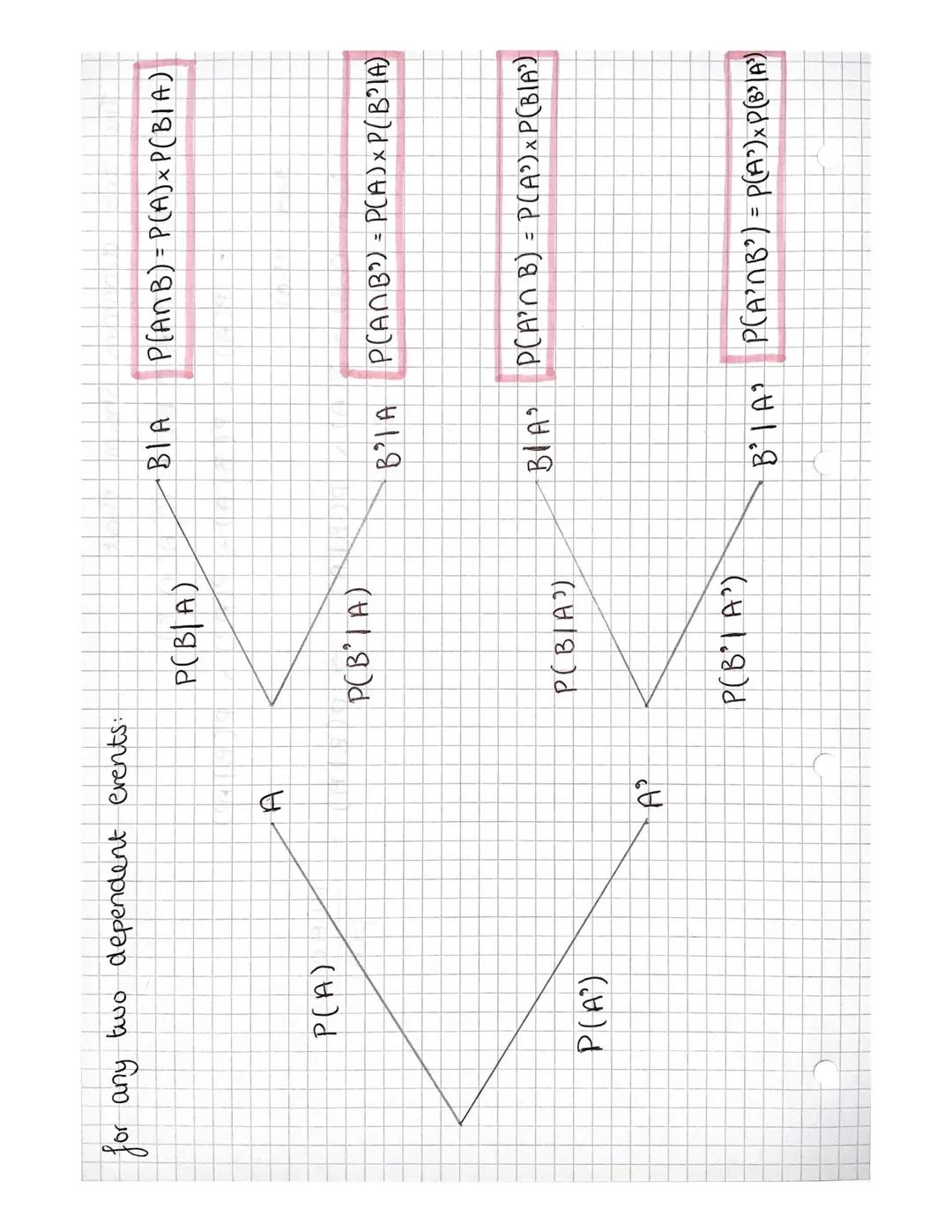
Quick Tip: Venn diagrams help visualise probability problems. The union (A ∪ B) means "A or B happening", whilst the intersection (A ∩ B) means "both A and B happening".