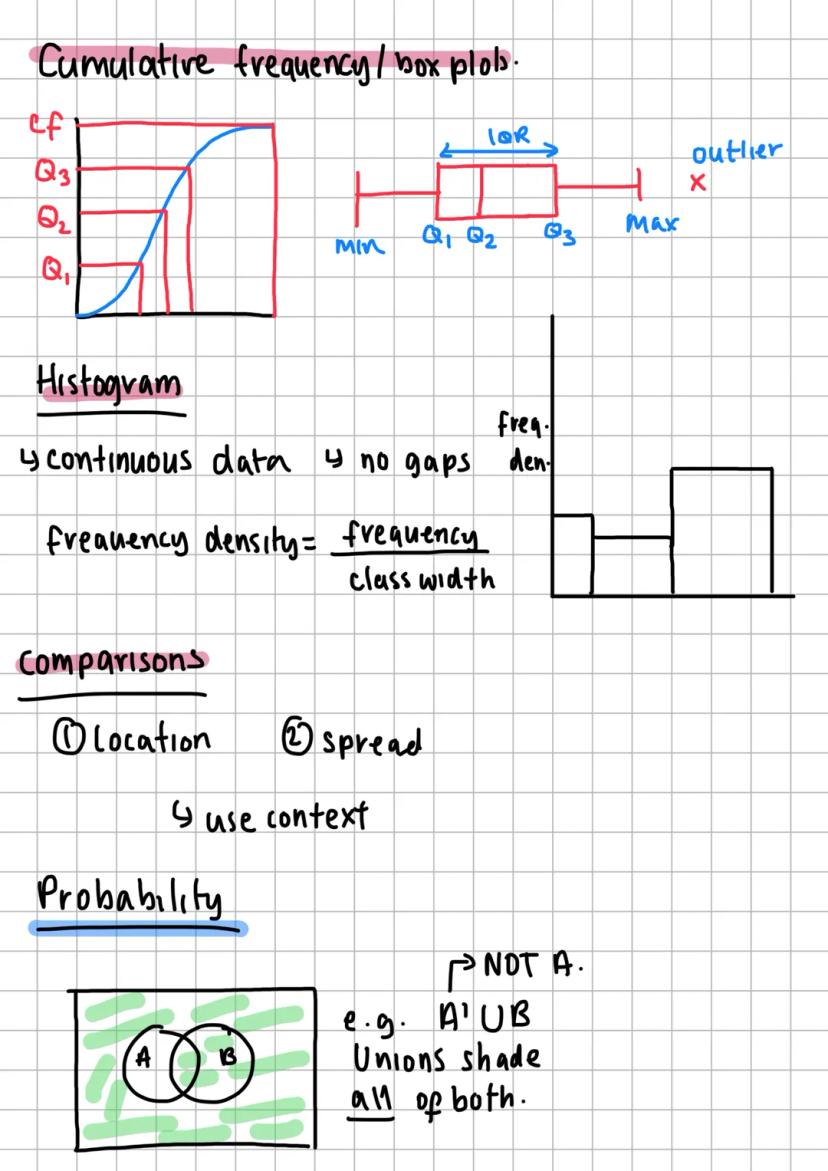
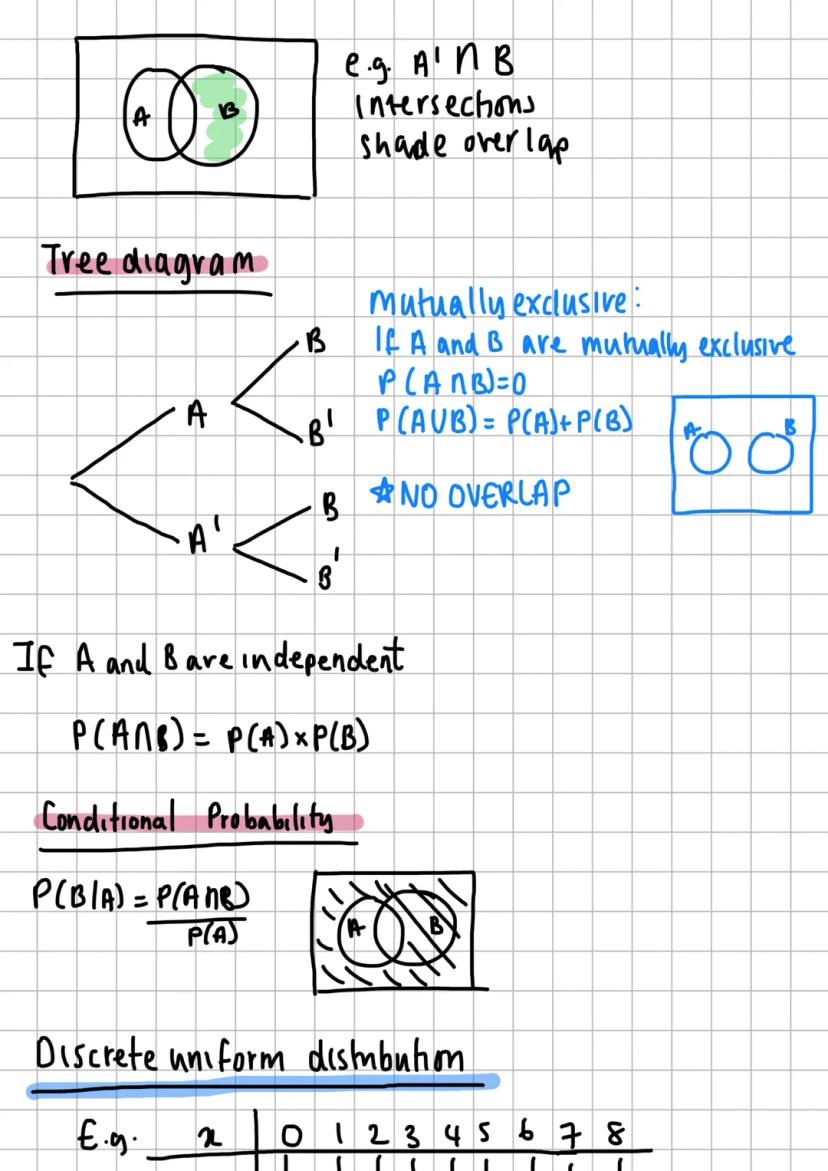
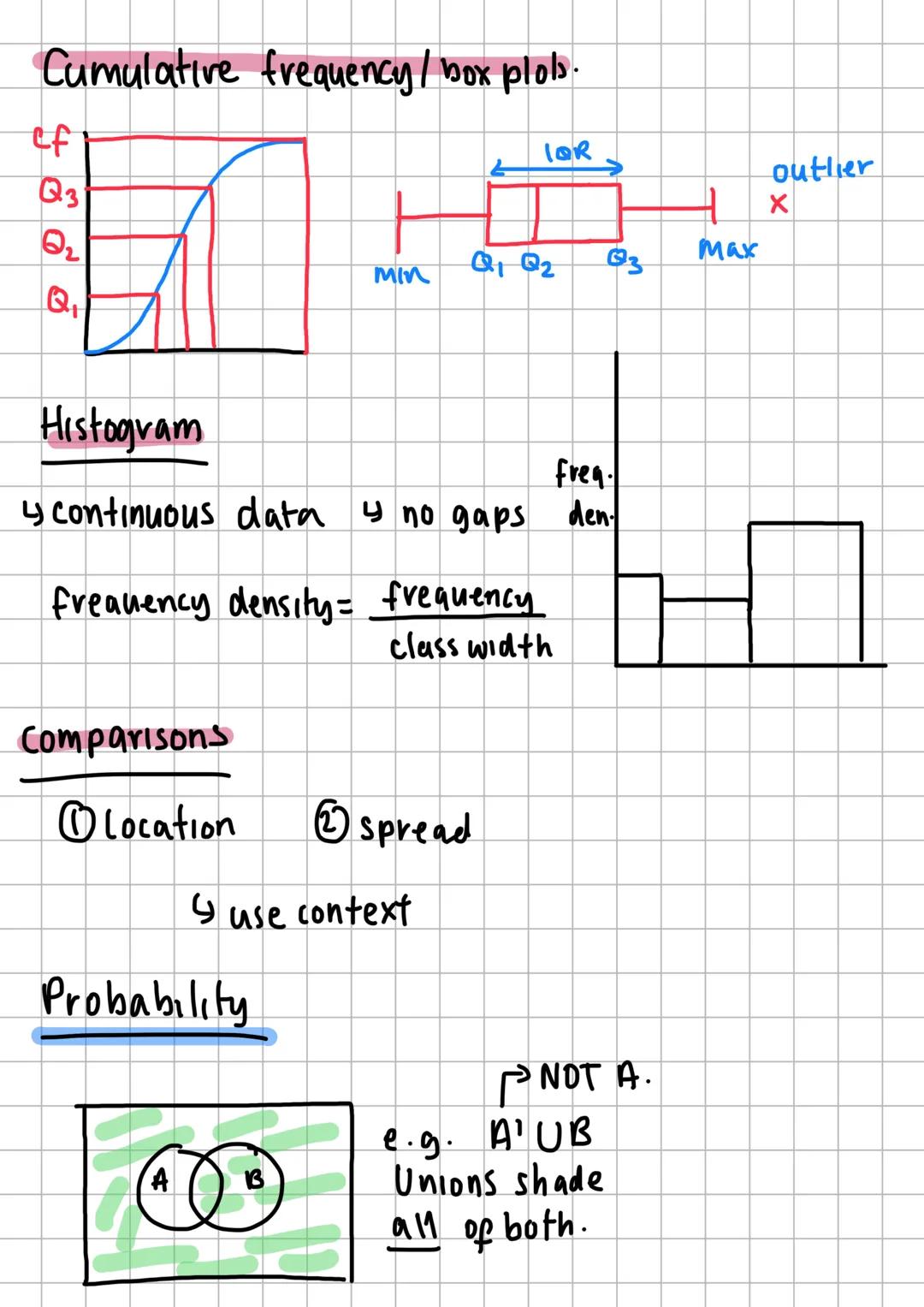
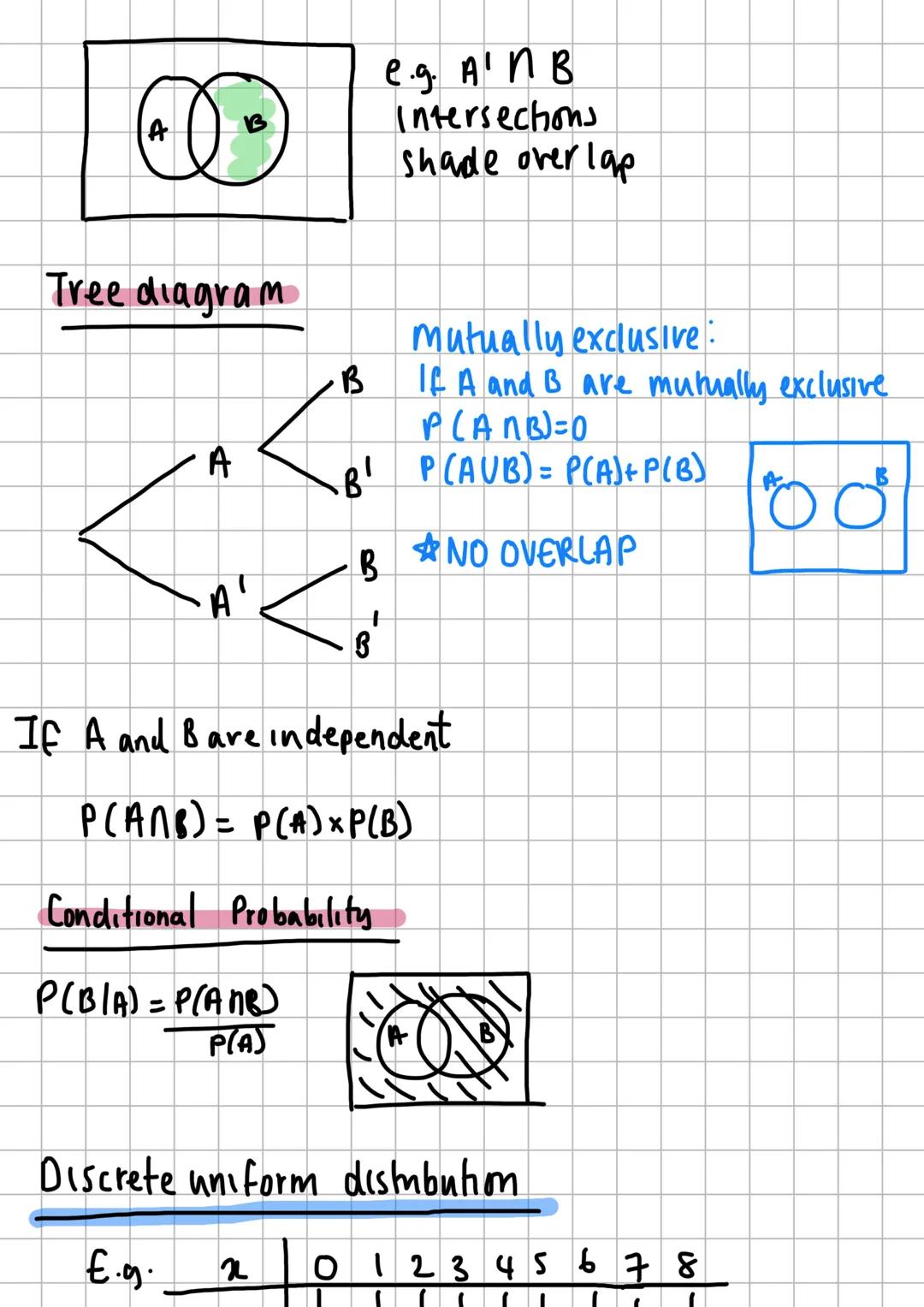
Statistical Testing and Correlation
Binomial hypothesis testing uses your observed number of successes as the test statistic. Assume H₀ is true, find P(X≥ or ≤ observed value), then compare with your significance level. If P < significance level, reject H₀. If P > significance level, there's insufficient evidence to reject H₀.
Correlation vs causation - just because two variables move together doesn't mean one causes the other. Ice cream sales and drowning incidents both increase in summer, but ice cream doesn't cause drowning. Always consider lurking variables that might explain apparent relationships.
Linear regression finds the line of best fit using y = a + bx. The least squares regression line minimises the sum of squared errors, giving you the most accurate predictions possible. The slope (b) tells you how much y changes for each unit increase in x.
Understanding what your regression equation means in context is crucial. If y = 20 + 3x represents exam marks vs revision hours, then 20 is the expected mark with zero revision, and each hour of revision adds 3 marks on average.
Exam success: Always interpret your regression coefficients in the context of the problem - don't just state the numbers without explaining what they mean in real terms.