The atomic bomb's devastating impact on Hiroshima and Nagasaki marked... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Responding to change (a2 only)
Infection and response
Homeostasis and response
Energy transfers (a2 only)
Cell biology
Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments (a-level only)
Biological molecules
Organisation
Substance exchange
Bioenergetics
Genetic information & variation
Inheritance, variation and evolution
Genetics & ecosystems (a2 only)
Ecology
Cells
Show all topics
Britain & the wider world: 1745 -1901
1l the quest for political stability: germany, 1871-1991
The cold war
Inter-war germany
Medieval period: 1066 -1509
2d religious conflict and the church in england, c1529-c1570
2o democracy and nazism: germany, 1918-1945
1f industrialisation and the people: britain, c1783-1885
1c the tudors: england, 1485-1603
2m wars and welfare: britain in transition, 1906-1957
World war two & the holocaust
2n revolution and dictatorship: russia, 1917-1953
2s the making of modern britain, 1951-2007
World war one
Britain: 1509 -1745
Show all topics

12
0
Jenny
22/12/2025
History
COLD WAR
284
•
22 Dec 2025
•
Jenny
@jennyy_bp
The atomic bomb's devastating impact on Hiroshima and Nagasaki marked... Show more










The post-war period saw a deepening ideological divide between the capitalist West and the communist East, exacerbated by the development of atomic weapons.
Ideological differences:
Definition: Buffer Zone - A region between two potentially hostile powers, intended to minimize the risk of conflict.
The atomic bomb and its consequences:
Highlight: The development of nuclear weapons led to the arms race, a key feature of the Cold War era.
Diplomatic tensions:
These communications deepened mistrust and contributed to the breakdown of the wartime Grand Alliance.

The Soviet Union's post-war expansion into Eastern Europe created a bloc of satellite states, which served as a buffer zone against potential Western aggression.
Soviet control methods:
Example: In Czechoslovakia, Stalin supported a communist coup in 1948, leading to a pro-Soviet government under Klement Gottwald.
Countries affected:
This expansion confirmed the division between East and West, with the US viewing it as a violation of the Yalta agreement for free elections.
Quote: Churchill's Iron Curtain Speech (March 1946) - "An iron curtain has descended across the continent."
This speech condemned Soviet expansion and highlighted the growing divide between the Eastern and Western blocs, setting the tone for the Cold War era.

The establishment of Soviet-aligned governments in Eastern Europe created a buffer zone for the USSR. Why did the Hungarian uprising happen can be traced to this period of Soviet control and the implementation of communist systems in previously independent nations.
Definition: Satellite States - countries formally independent but under heavy political and economic influence of another nation.
The process of establishing control varied by country:

In March 1946, Winston Churchill delivered his famous Iron Curtain speech, condemning Soviet expansion and warning of threats to world peace. This speech crystallized Western concerns about Soviet influence in Eastern Europe.
Quote: Churchill declared that an "Iron Curtain" had descended across Europe.
This speech marked a definitive moment in Cold War rhetoric and helped shape Western response to Soviet expansion.

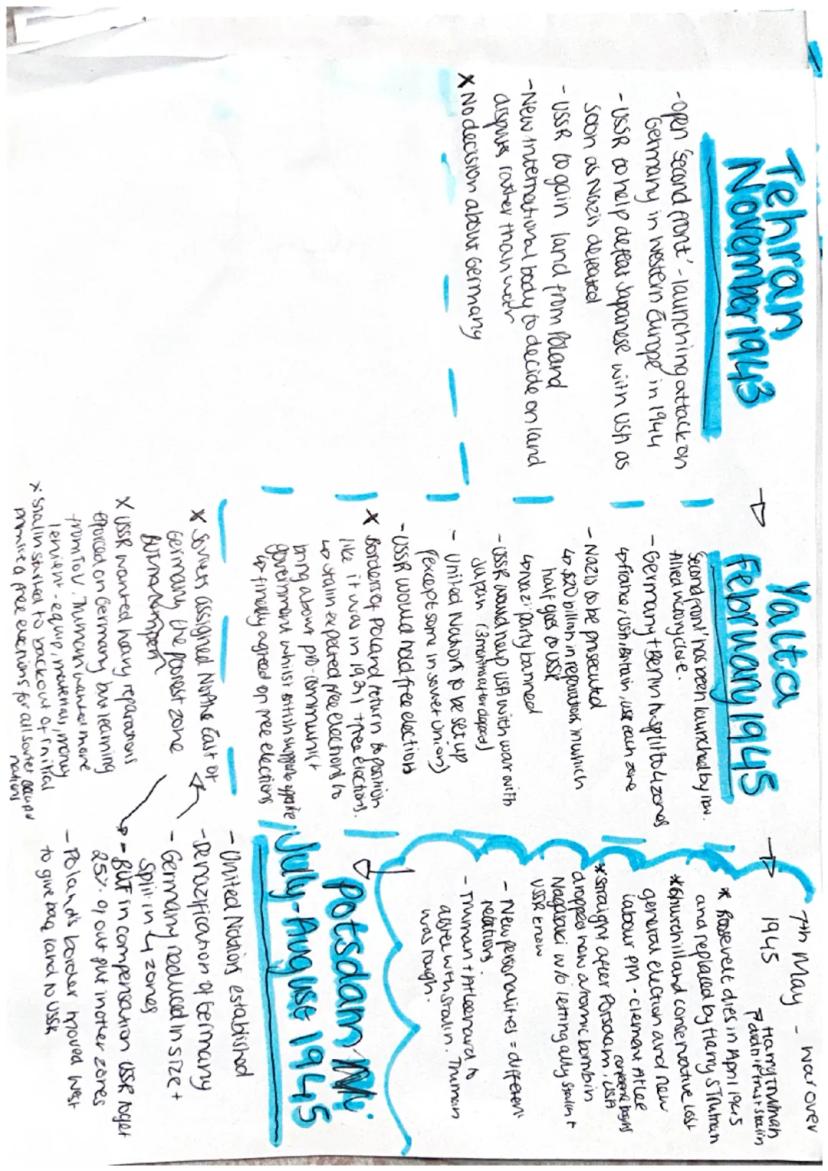
The Tehran, Yalta, and Potsdam conferences were crucial meetings between Allied leaders during and after World War II, setting the stage for post-war Europe and the emerging Cold War.
Highlight: These conferences laid the groundwork for the division of Germany, the establishment of the United Nations, and the future of Eastern Europe.
The Tehran Conference in November 1943 focused on:
The Yalta Conference in February 1945 made significant decisions:
Quote: "I finally agreed on free elections." - This statement reflects the complex negotiations and compromises made during these conferences.
The Potsdam Conference in July-August 1945 addressed:
Vocabulary: Denazification - The process of removing Nazi ideology and influence from post-war German society and institutions.





Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Jenny
@jennyy_bp
The atomic bomb's devastating impact on Hiroshima and Nagasaki marked a critical turning point in Cold War history, leading to heightened tensions and the start of the nuclear weapons and the escalation of the Cold War, 1945-1962. This period... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The post-war period saw a deepening ideological divide between the capitalist West and the communist East, exacerbated by the development of atomic weapons.
Ideological differences:
Definition: Buffer Zone - A region between two potentially hostile powers, intended to minimize the risk of conflict.
The atomic bomb and its consequences:
Highlight: The development of nuclear weapons led to the arms race, a key feature of the Cold War era.
Diplomatic tensions:
These communications deepened mistrust and contributed to the breakdown of the wartime Grand Alliance.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Soviet Union's post-war expansion into Eastern Europe created a bloc of satellite states, which served as a buffer zone against potential Western aggression.
Soviet control methods:
Example: In Czechoslovakia, Stalin supported a communist coup in 1948, leading to a pro-Soviet government under Klement Gottwald.
Countries affected:
This expansion confirmed the division between East and West, with the US viewing it as a violation of the Yalta agreement for free elections.
Quote: Churchill's Iron Curtain Speech (March 1946) - "An iron curtain has descended across the continent."
This speech condemned Soviet expansion and highlighted the growing divide between the Eastern and Western blocs, setting the tone for the Cold War era.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The establishment of Soviet-aligned governments in Eastern Europe created a buffer zone for the USSR. Why did the Hungarian uprising happen can be traced to this period of Soviet control and the implementation of communist systems in previously independent nations.
Definition: Satellite States - countries formally independent but under heavy political and economic influence of another nation.
The process of establishing control varied by country:

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
In March 1946, Winston Churchill delivered his famous Iron Curtain speech, condemning Soviet expansion and warning of threats to world peace. This speech crystallized Western concerns about Soviet influence in Eastern Europe.
Quote: Churchill declared that an "Iron Curtain" had descended across Europe.
This speech marked a definitive moment in Cold War rhetoric and helped shape Western response to Soviet expansion.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The Tehran, Yalta, and Potsdam conferences were crucial meetings between Allied leaders during and after World War II, setting the stage for post-war Europe and the emerging Cold War.
Highlight: These conferences laid the groundwork for the division of Germany, the establishment of the United Nations, and the future of Eastern Europe.
The Tehran Conference in November 1943 focused on:
The Yalta Conference in February 1945 made significant decisions:
Quote: "I finally agreed on free elections." - This statement reflects the complex negotiations and compromises made during these conferences.
The Potsdam Conference in July-August 1945 addressed:
Vocabulary: Denazification - The process of removing Nazi ideology and influence from post-war German society and institutions.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
12
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the key events and concepts of the Cold War, including the Arms Race, Space Race, and significant conflicts like the Korean and Vietnam Wars. This summary provides essential dates and insights into superpower relations, making it an ideal resource for students studying this pivotal era in history.
Explore the key events and consequences of the Berlin Crisis (1948-1949) in this concise summary. Understand the Berlin Blockade, the Berlin Airlift, and the formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact. This resource is essential for AQA GCSE History students studying the early Cold War and post-WWII Germany.
covers everything for edexcel GCSE history on cold war
Explore the key events and policies that shaped the Cold War, including the Yalta and Potsdam Conferences, the Berlin Blockade and Airlift, the formation of NATO, and the Arms Race. This comprehensive summary highlights the ideological conflict between capitalism and communism, the Truman Doctrine, and the impact of superpower relations on post-war Europe. Ideal for GCSE students seeking to understand the complexities of the Cold War era.
Explore the key events and concepts of the Cold War, including the Truman Doctrine, NATO, the Warsaw Pact, the Arms Race, and the Cuban Missile Crisis. This summary provides insights into superpower relations, the division of Germany, and the impact of Soviet control in Eastern Europe, including the invasion of Hungary and the Berlin Wall's significance. Ideal for students seeking a comprehensive understanding of Cold War dynamics.
Explore the pivotal events and key concepts of the Cold War, including the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, the formation of NATO, and the Cuban Missile Crisis. This summary provides insights into superpower relations, the arms race, and the impact of détente on global politics. Ideal for GCSE History students preparing for exams.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user