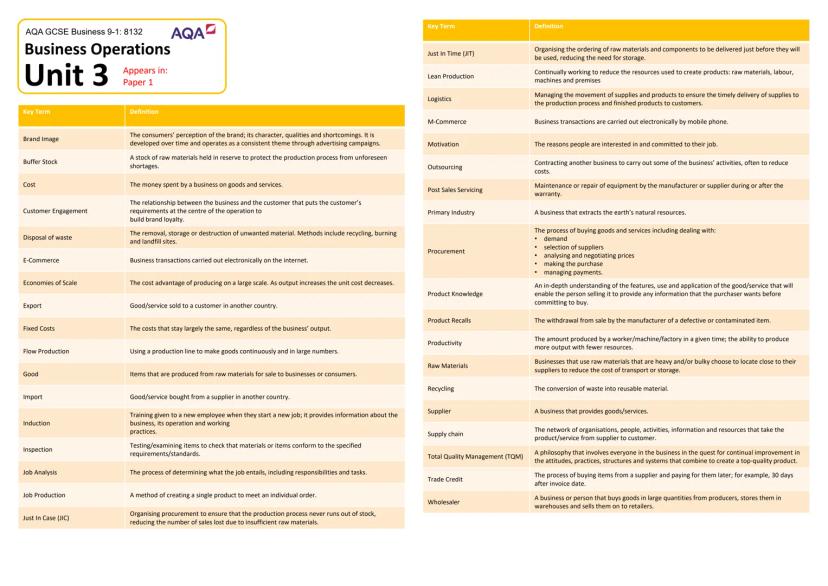
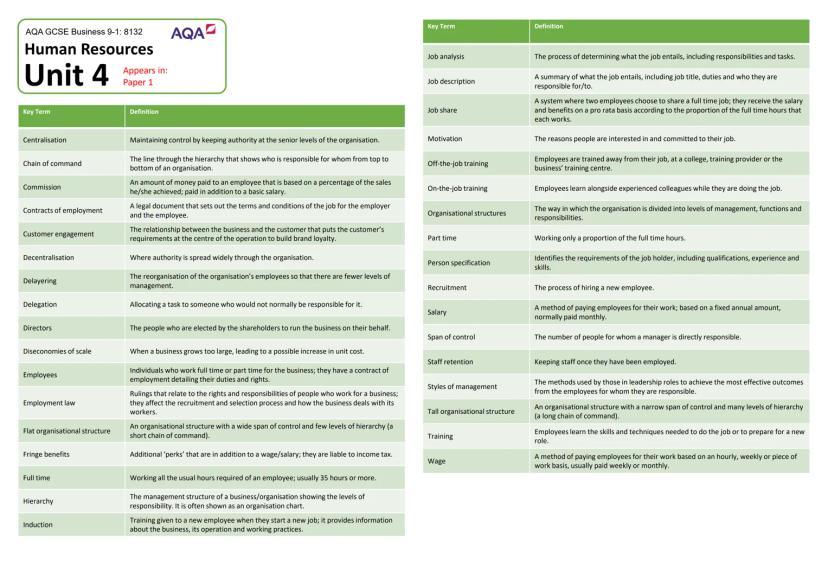
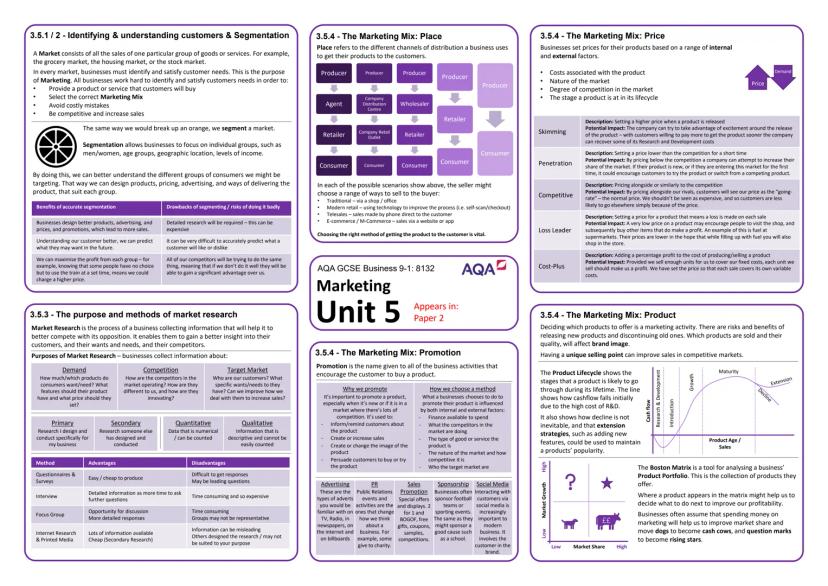
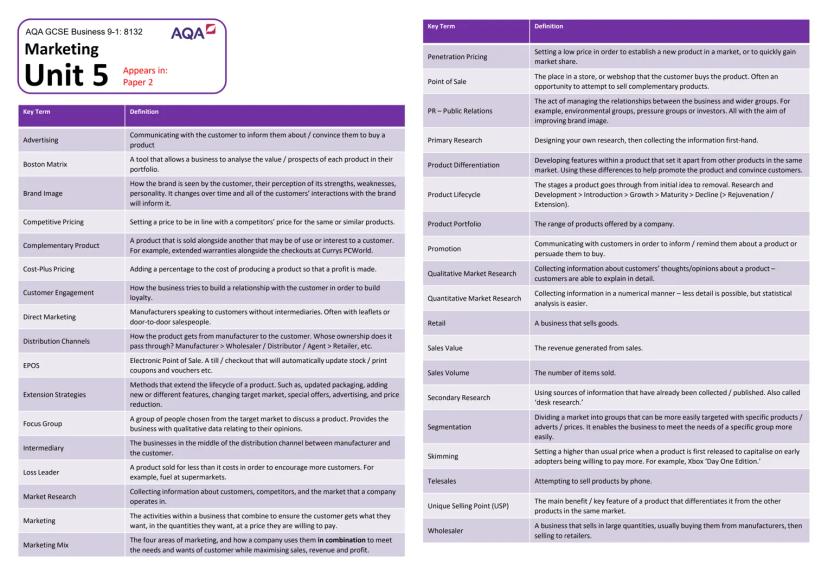
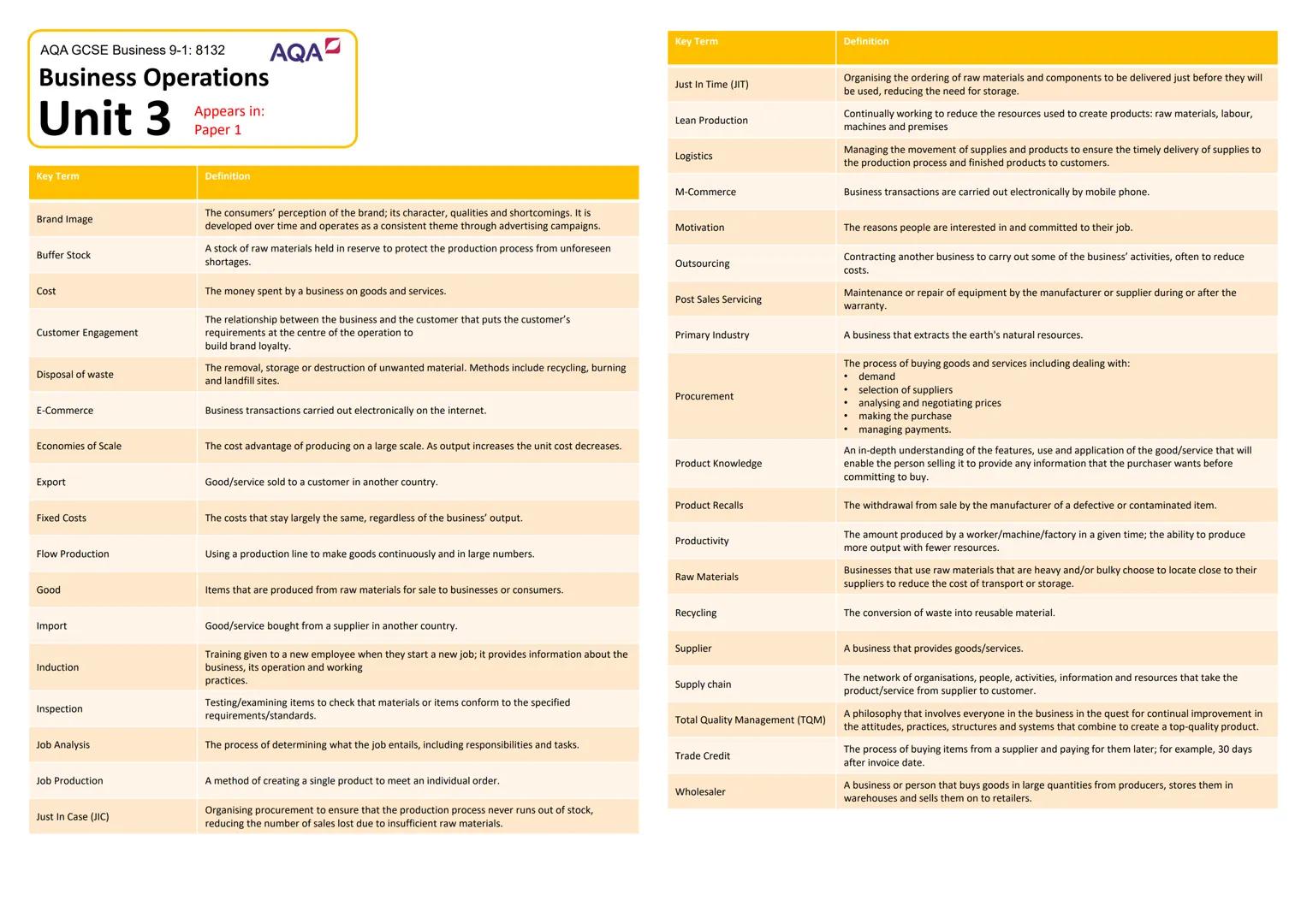
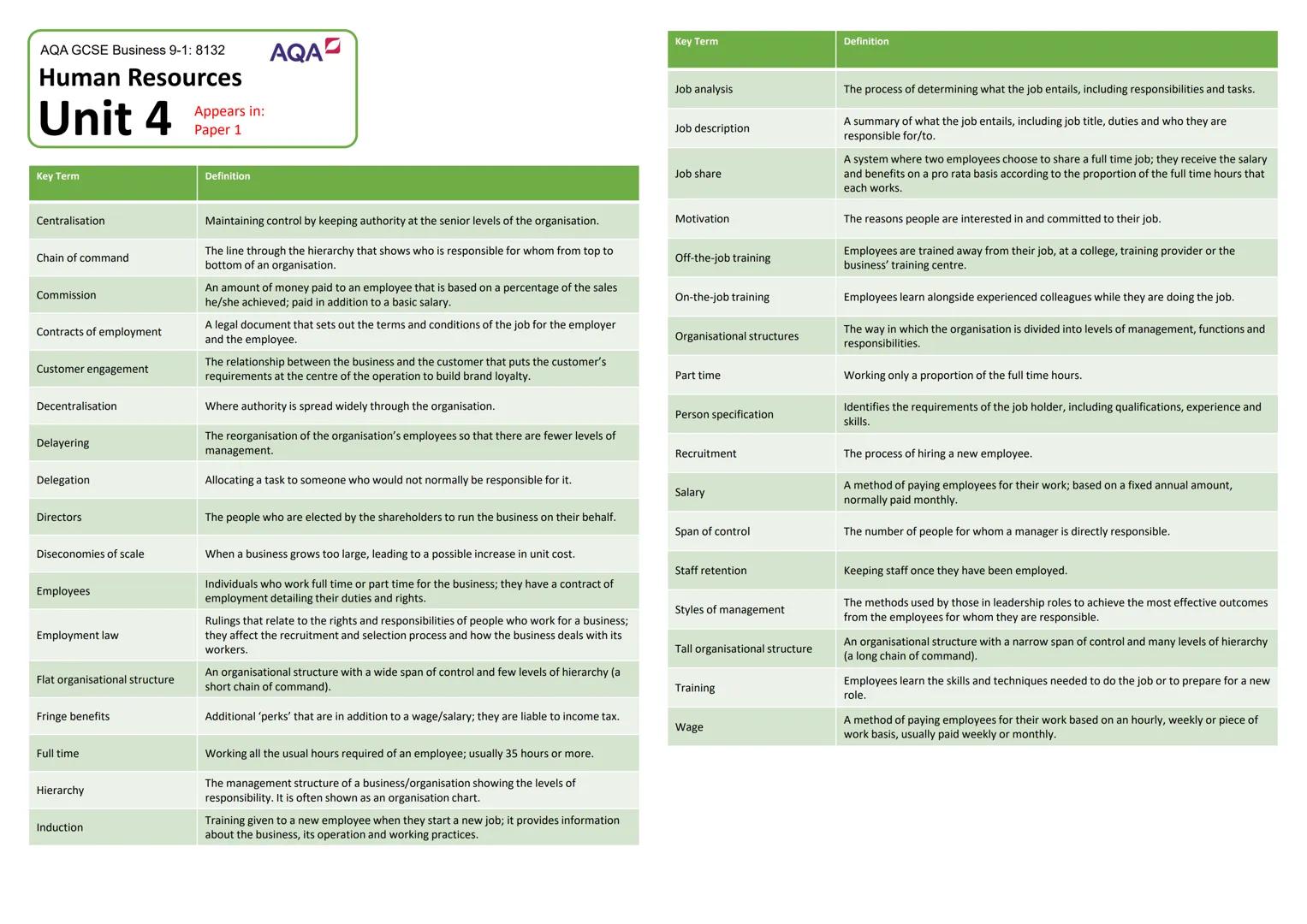
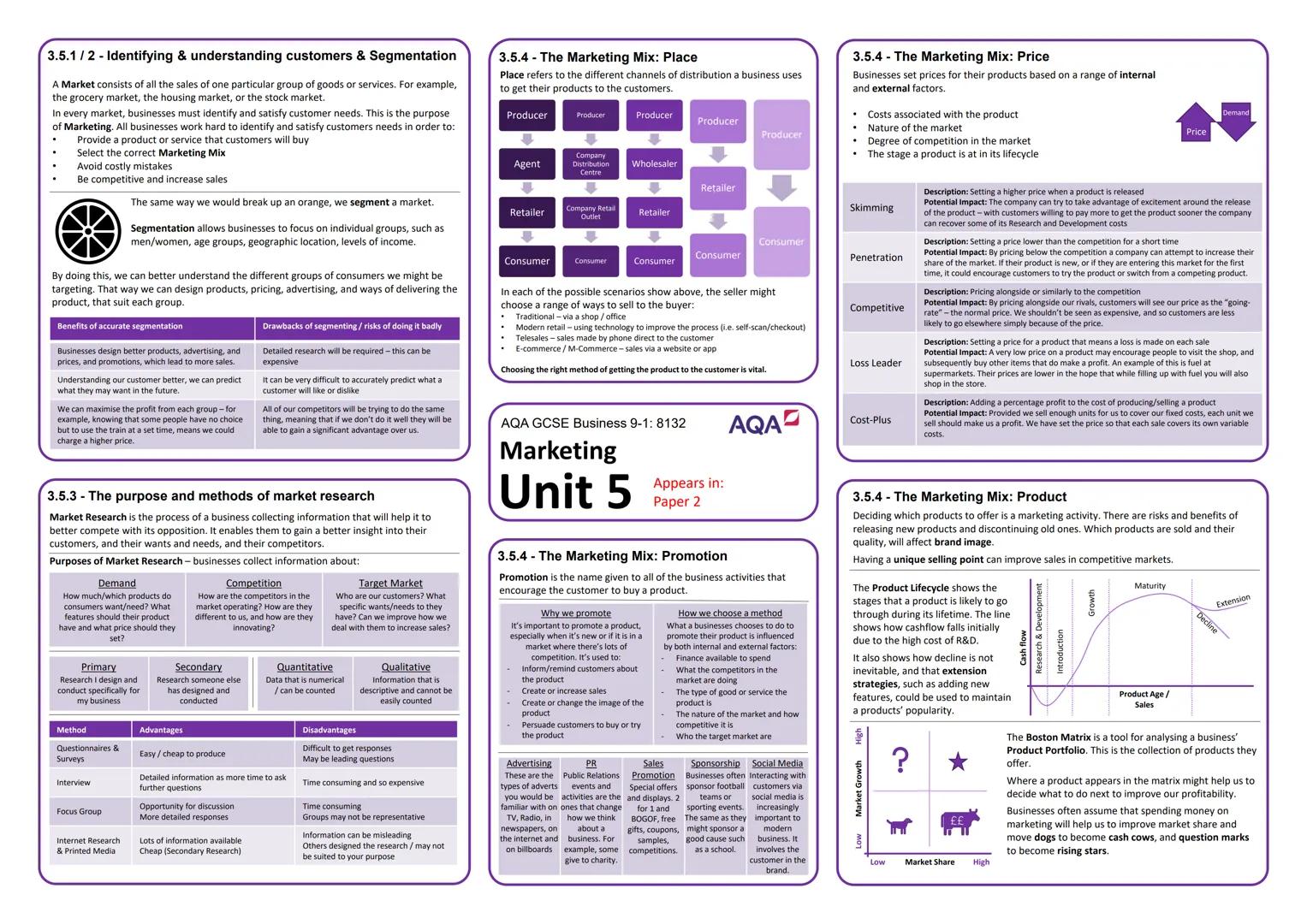
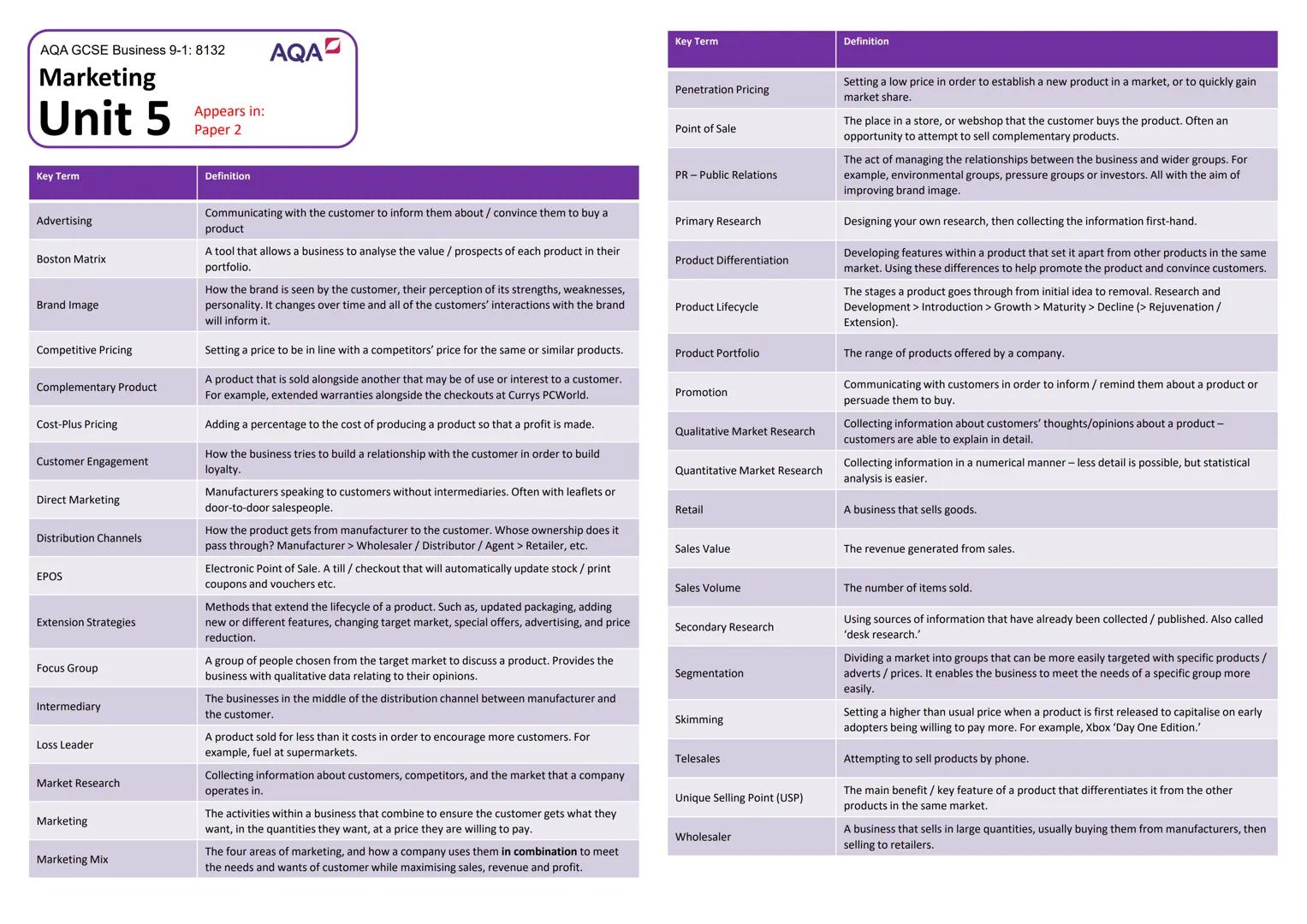
Technology's Impact on Modern Business
Technology has completely transformed how businesses operate, and it's happening faster than ever. E-commerce has revolutionised retail, allowing companies to reach global markets 24/7, whilst m-commerce (mobile commerce) enables shopping anywhere through smartphones and tablets.
Social media marketing lets businesses target specific individuals based on their interests and behaviours, putting personalised adverts in front of potential customers at exactly the right moment. This precision targeting was impossible with traditional advertising methods.
Digital communication has replaced much business travel with video conferencing apps like FaceTime and Skype. Companies can now collaborate globally whilst saving time, money, and reducing environmental impact - it's a win-win situation.
Callout: Apps like PayPal, Uber, and Office 365 haven't just changed individual businesses - they've created entirely new ways of working and living!
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Modern consumers expect businesses to operate ethically - meaning fairly and honestly whilst minimising environmental damage. This includes reducing single-use plastics, avoiding palm oil (linked to deforestation), and cutting air pollution from operations.
Sustainability aims to avoid unnecessary resource consumption and environmental damage. Whilst this approach can increase short-term costs, it improves company reputation and ensures long-term viability by protecting the resources businesses depend on.
Companies must balance ethics with profitability - there's often a trade-off between doing what's cheapest and doing what's right. Smart businesses find creative solutions that achieve both goals simultaneously.
Callout: Ethical business practices aren't just about doing good - they're increasingly essential for attracting customers and top talent in competitive markets!
The Economic Climate and Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing and reward for saving - they're set by the Bank of England to control economic activity. Higher rates make borrowing expensive, reducing spending and cooling an overheated economy.
When people spend money, it becomes someone else's income - creating a self-reinforcing cycle. If unemployment rises and people have less money, reduced spending leads to further job losses and economic decline.
Inflation occurs when prices rise too quickly due to excessive demand, whilst deflation happens when falling demand causes widespread price reductions. Both extremes can damage economic stability and business confidence.
Callout: Understanding this economic cycle helps explain why businesses struggle during recessions and thrive during periods of economic growth!
Globalisation and Currency Exchange
Globalisation has made the world feel smaller, with businesses operating internationally and goods moving freely across borders. This creates opportunities for growth but also increases competition from overseas companies.
Exchange rates dramatically affect international trade. The acronym SPICED (Strong Pound, Imports Cheaper, Exports Decline) explains how currency strength impacts business - whilst WPIDEC (Weak Pound, Imports Decline, Exports Cheaper) shows the opposite effect.
Imports and exports depend heavily on exchange rates and transportation costs. Companies must constantly balance the benefits of global operations against currency risks and logistical challenges.
Callout: When the pound strengthens, your foreign holiday becomes cheaper, but UK exporters struggle to compete internationally!
Legislation and Legal Compliance
Legal changes force businesses to adapt their operations, often requiring significant time and money investments. Even small regulatory changes can create large administrative costs and operational disruptions.
The National Minimum Wage sets hourly pay floors based on age, directly affecting business costs and potentially forcing workforce reductions. However, it improves living standards for low-paid workers and increases consumer spending power.
The Equality Act (2010) protects against discrimination based on characteristics like age, gender, race, and religion. The Health and Safety at Work Act (1974) ensures safe working environments, whilst the Trade Descriptions Act (1968) prevents misleading advertising.
Callout: Good legal compliance isn't just about avoiding penalties - it creates better workplaces and builds customer trust in your brand!
Competition and Market Dynamics
Competitive markets benefit consumers through lower prices and innovation, whilst monopolies can dictate terms due to their dominant position 25. Understanding market structure helps predict business behaviour and opportunities.
Businesses compete through various methods: price (competitive or promotional pricing), quality (superior materials or craftsmanship), location (convenience for customers), and unique selling points (features no competitor offers).
After-sales service, delivery options, and branding also differentiate companies in crowded markets. Apple's success demonstrates how strong branding can command premium prices and fierce customer loyalty.
Callout: In highly competitive markets, businesses must constantly innovate and improve to maintain their market position - standing still means falling behind!