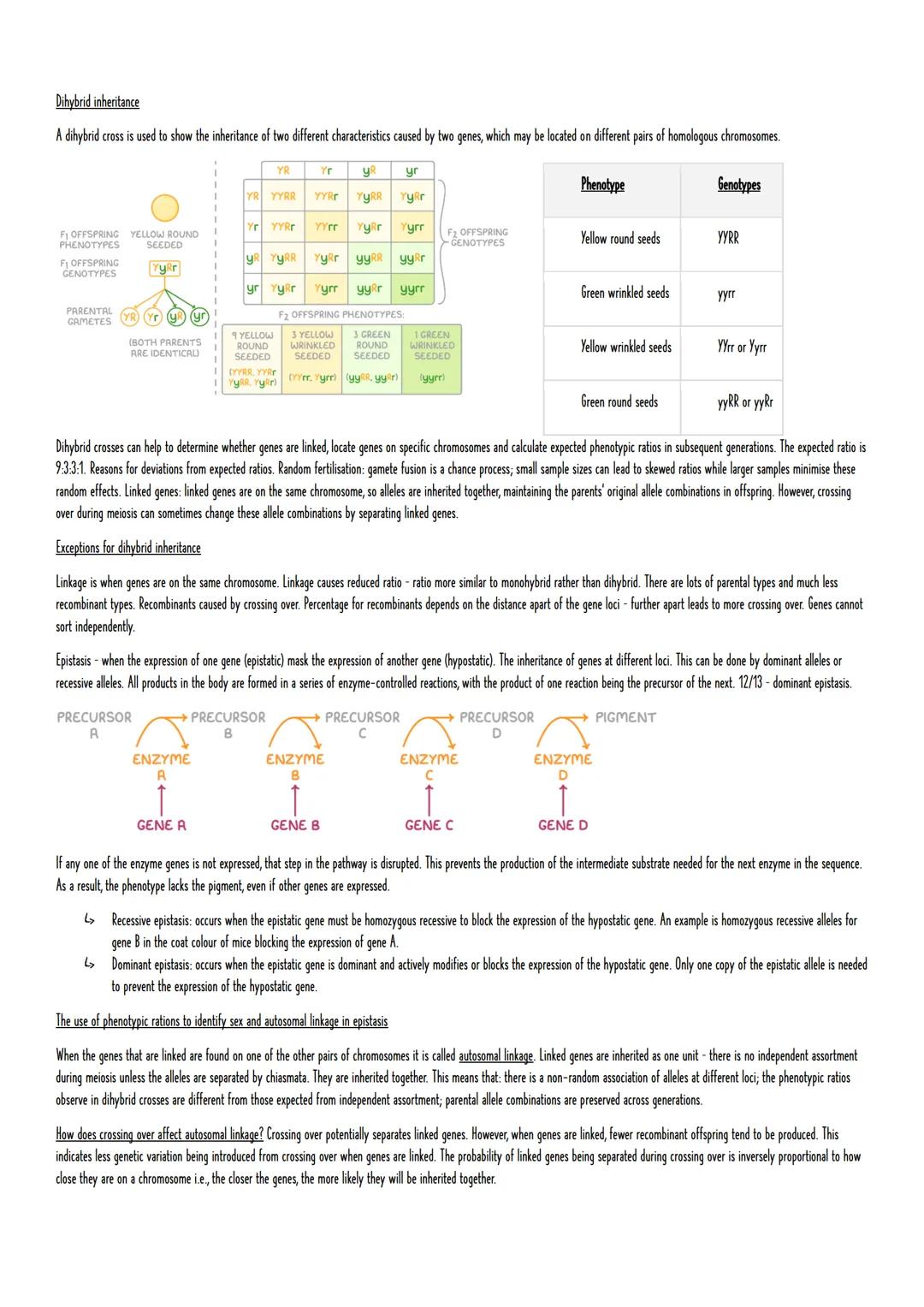
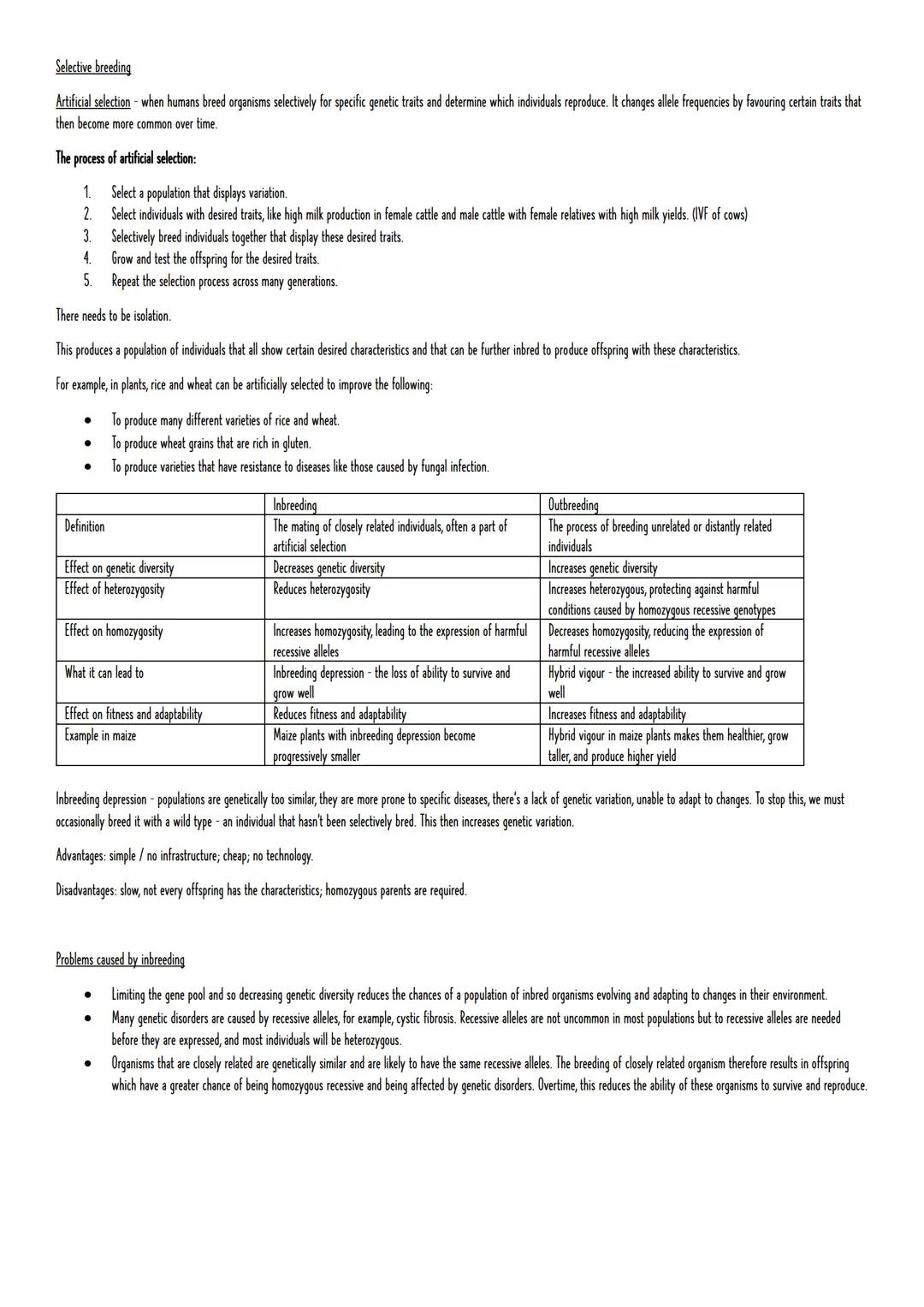
Selective Breeding and Artificial Selection
Humans have been shaping evolution for thousands of years through selective breeding. This process demonstrates evolution in action by deliberately changing allele frequencies to produce desired traits.
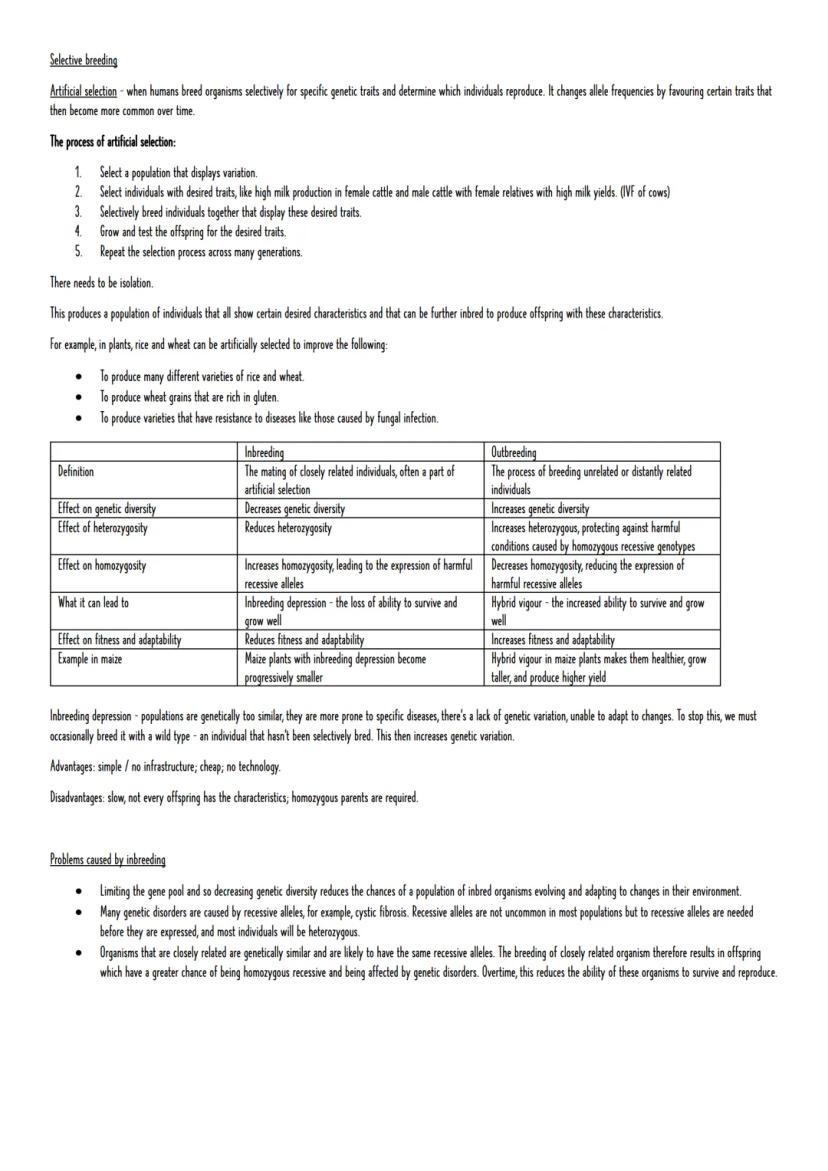
Artificial selection follows a simple process: identify variation in a population, select individuals with desired traits, breed them together, test their offspring, and repeat for many generations. This has produced everything from high-yielding crop varieties to specialised dog breeds.
Inbreeding occurs when closely related individuals mate, often as part of selective breeding programmes. While this can fix desired traits quickly, it reduces genetic diversity and increases homozygosity. This leads to inbreeding depression - reduced fitness, fertility, and survival rates.
Outbreeding involves mating unrelated individuals, which increases genetic diversity and heterozygosity. This often produces hybrid vigour - offspring that are healthier, larger, and more productive than either parent. Maize is a perfect example, where hybrid varieties dramatically outperform inbred lines.
The challenge in selective breeding is balancing the desire for specific traits with the need to maintain genetic health. Occasional outcrossing with wild-type individuals helps restore genetic diversity and prevents the accumulation of harmful recessive alleles.
Key Point: Inbreeding fixes desired traits but reduces genetic diversity, while outbreeding increases diversity and often produces hybrid vigour in offspring.