Your body is like a sophisticated communication network that never... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
185
•
15 Feb 2026
•
Busola Oworu
@busolaoworu_ojhx
Your body is like a sophisticated communication network that never... Show more






Ever wondered how your body coordinates millions of cells to work together perfectly? Cell signalling is the answer - it's like having a massive group chat where cells send chemical messages to each other. Some signals travel short distances (like neurotransmitters jumping between brain cells), whilst others journey across your entire body (like hormones from your pituitary gland telling your kidneys to conserve water).
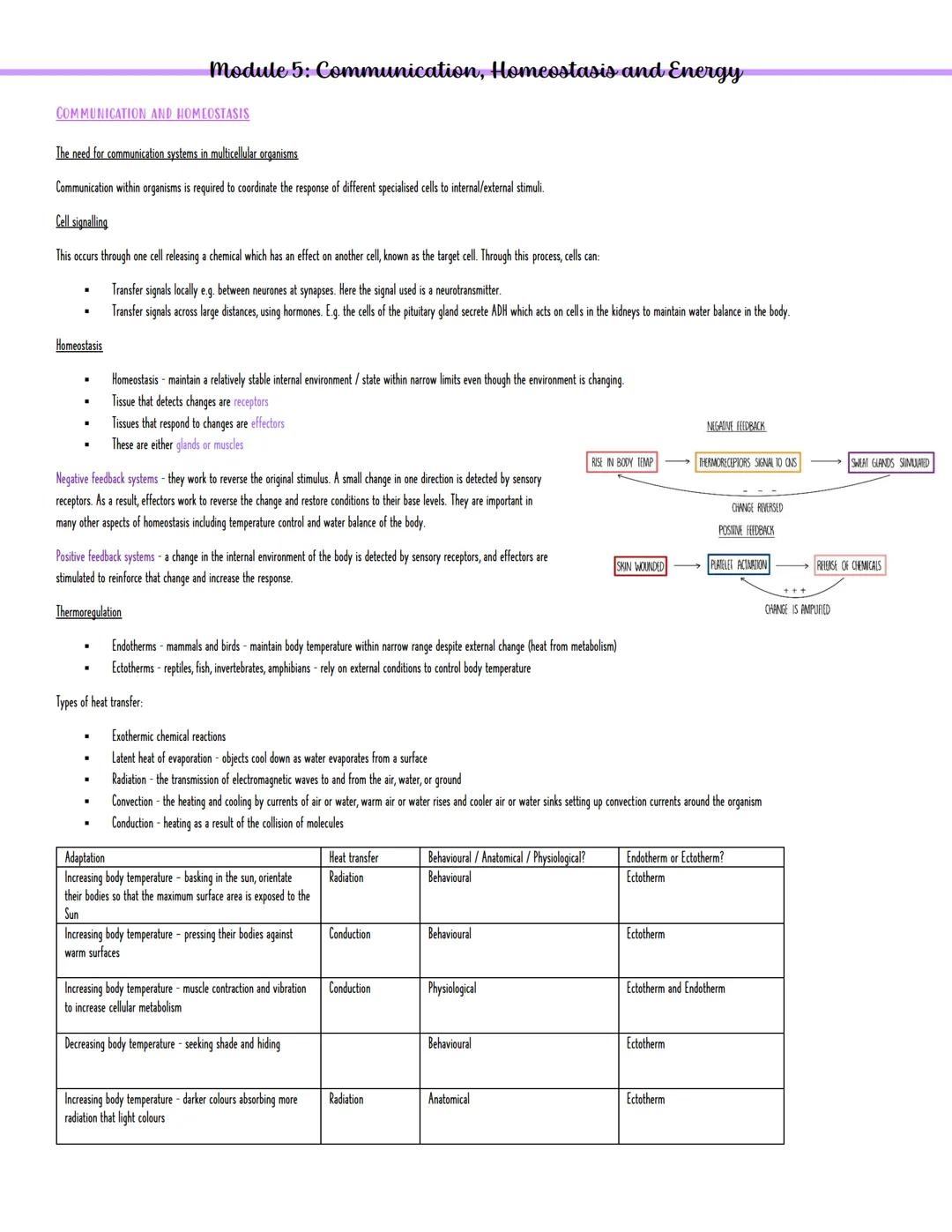
Homeostasis keeps your internal environment stable even when everything around you changes. Think of it as your body's autopilot system. Receptors detect changes, then effectors (muscles or glands) respond to fix any problems. Most of the time, your body uses negative feedback - like a thermostat that switches heating off when it gets too warm.
Positive feedback is rarer but powerful - it amplifies changes rather than reversing them. You'll see this during labour contractions, where each contraction triggers stronger ones.
Key Point: Negative feedback maintains stability, whilst positive feedback amplifies responses when your body needs rapid change.
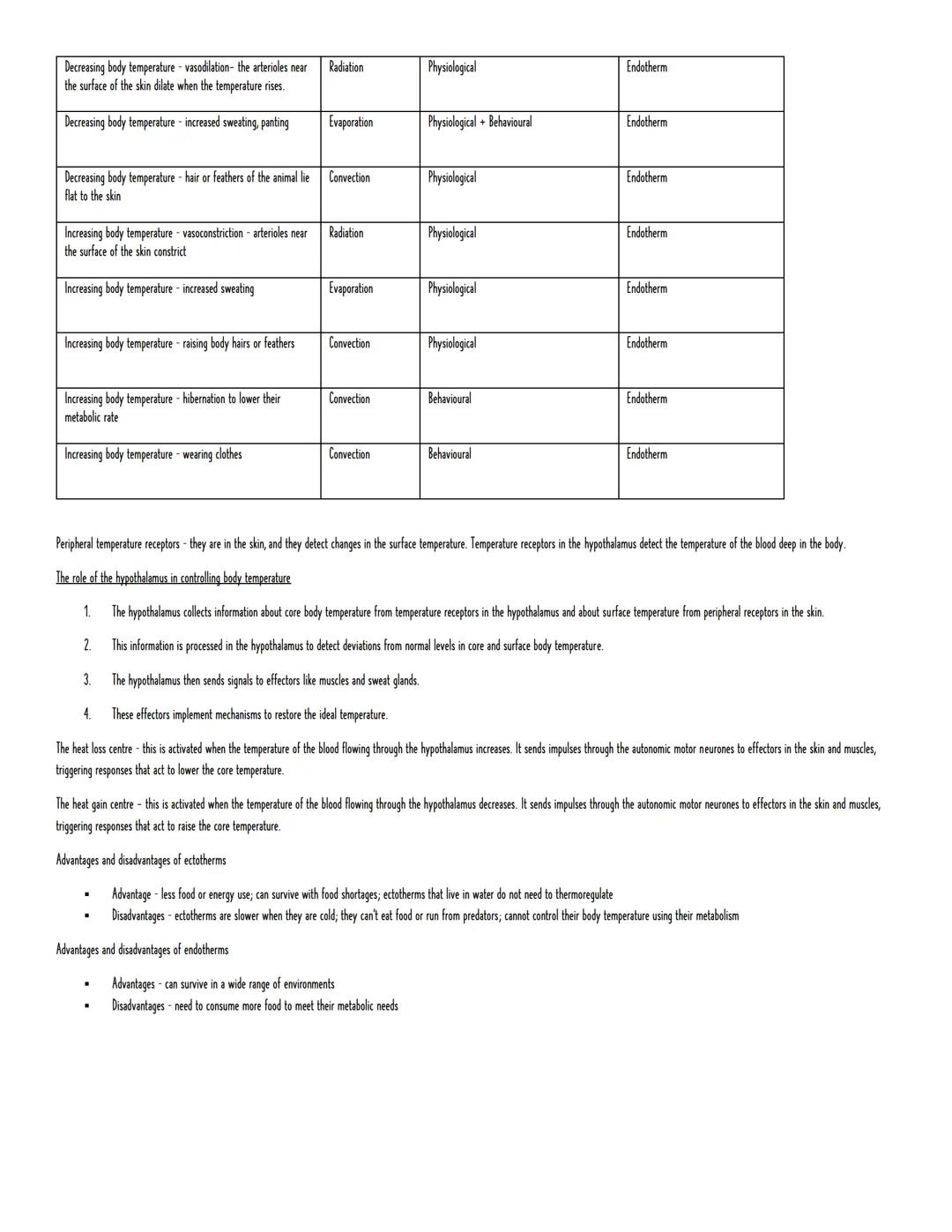
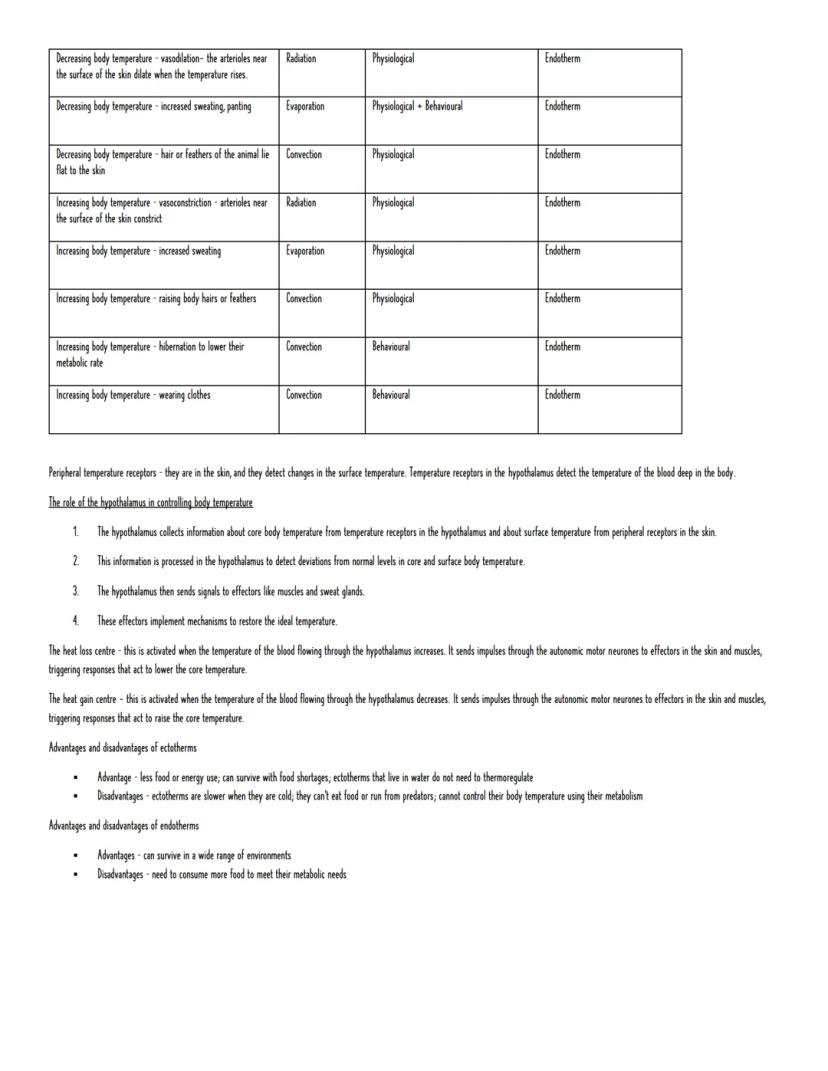
Your ability to maintain body temperature depends on whether you're an endotherm (like mammals and birds) or an ectotherm (like reptiles and fish). Endotherms generate heat internally through metabolism, whilst ectotherms rely on environmental heat sources.
Heat moves through your body via radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation. Ectotherms cleverly exploit these - basking in sunlight (radiation), pressing against warm rocks (conduction), or seeking shade when overheated. Some even change colour to absorb or reflect more heat.
Endotherms have more sophisticated responses. When you're hot, blood vessels near your skin dilate (vasodilation), you sweat more, and body hairs lie flat. When cold, the opposite happens - vasoconstriction, reduced sweating, and raised hairs create insulation.
Your hypothalamus acts as mission control, collecting temperature data from skin receptors and blood sensors. It then activates either the heat loss centre (when you're too warm) or heat gain centre (when you're too cold). The trade-off? Endotherms need loads more food to fuel this system, but can survive in almost any environment.
Remember: Ectotherms are energy-efficient but temperature-dependent; endotherms are energy-expensive but environmentally flexible.
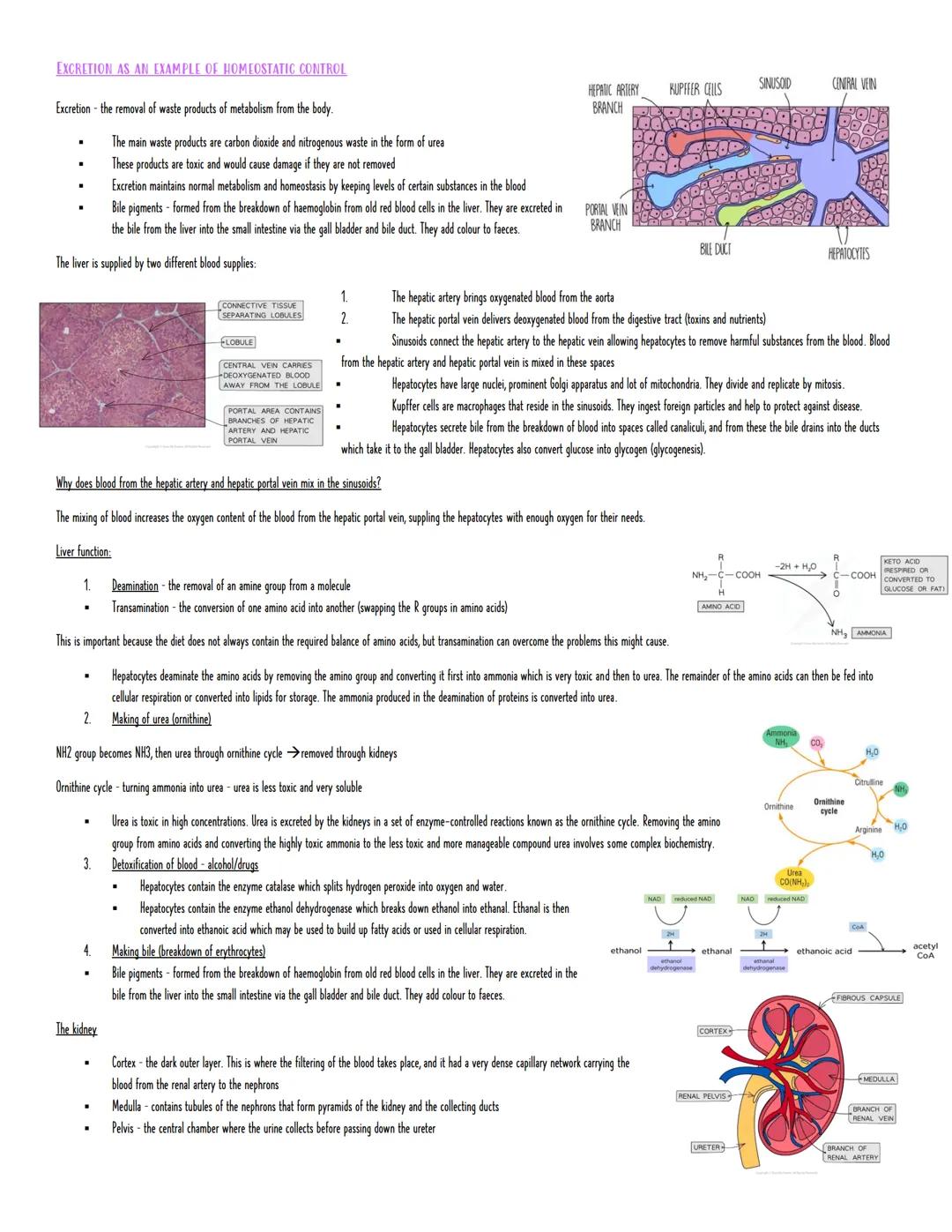
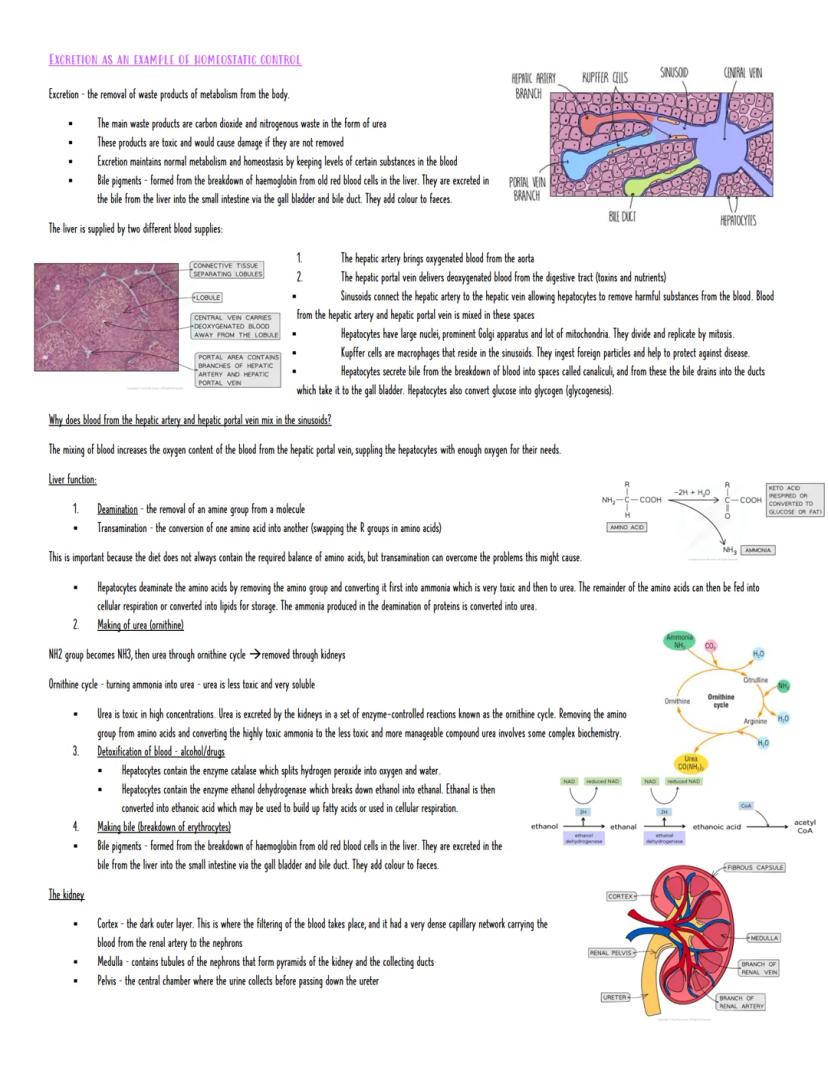
Your liver is basically a chemical processing plant that never stops working. It receives blood from two sources - oxygenated blood from the hepatic artery and nutrient-rich blood from the hepatic portal vein. These mix in spaces called sinusoids, where hepatocytes (liver cells) get to work removing toxins and processing nutrients.
Deamination is one of the liver's crucial jobs - removing amino groups from excess amino acids. This produces toxic ammonia, which gets converted to less harmful urea through the ornithine cycle. It's like having a recycling centre that breaks down unwanted proteins and safely packages the waste for disposal.
The liver also detoxifies alcohol using ethanol dehydrogenase, breaks down hydrogen peroxide with catalase, and creates bile from old red blood cells. Bile pigments give your faeces their characteristic colour - definitely more interesting than you thought!
Clinical Connection: Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests often indicate liver damage, showing how important these processes are for health.
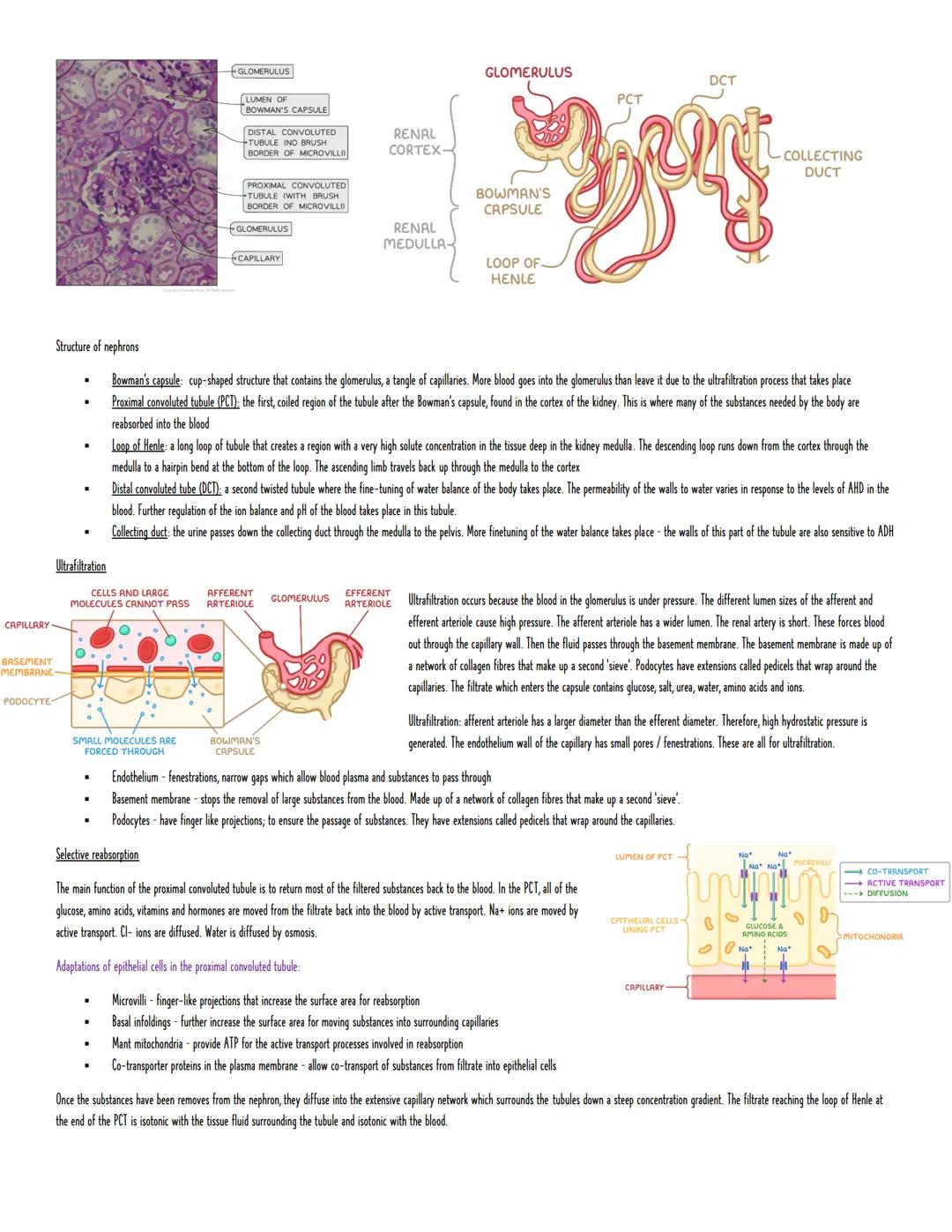
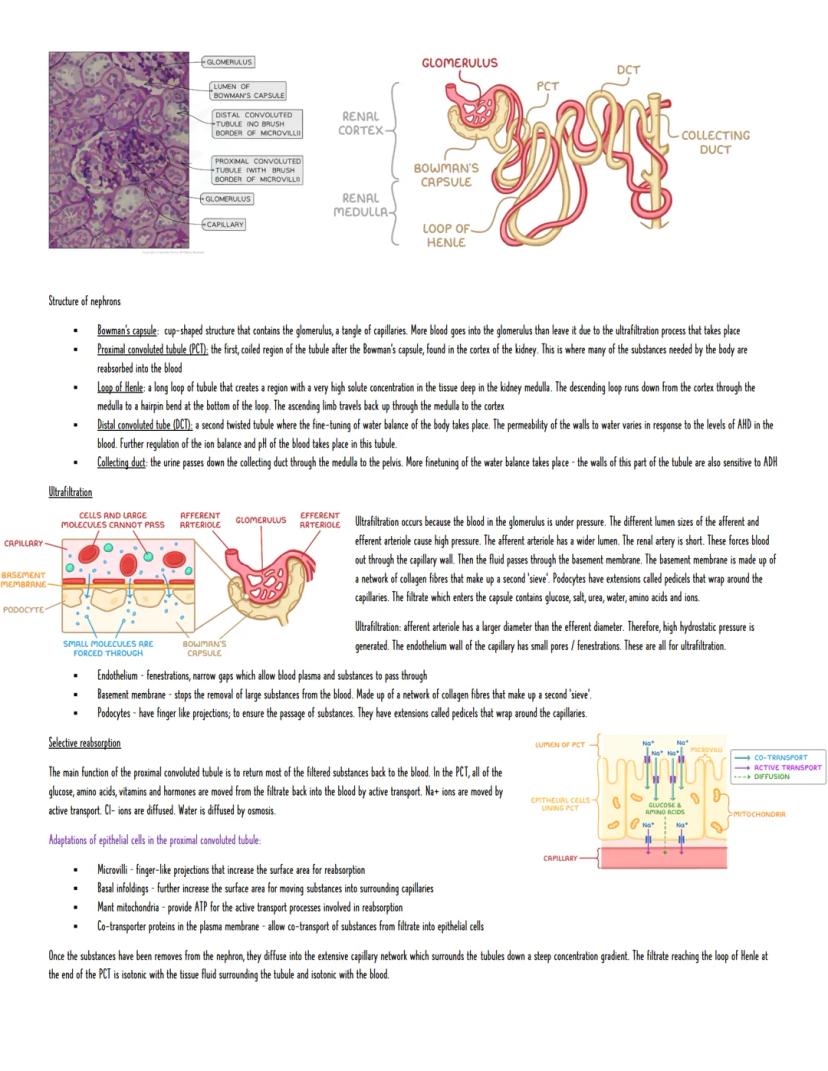
Each kidney contains about a million tiny filters called nephrons. The filtering starts in Bowman's capsule, which surrounds a knot of capillaries called the glomerulus. Here's where the magic happens - ultrafiltration forces everything small enough through a three-layer barrier.
The afferent arteriole (bringing blood in) is wider than the efferent arteriole (taking blood out), creating high pressure that pushes fluid through. The filtering system has three parts: fenestrations (tiny holes) in capillary walls, a basement membrane that blocks large molecules, and podocytes with finger-like projections that complete the sieve.
What gets through? Water, glucose, salts, urea, amino acids, and ions - basically everything except blood cells and large proteins. In the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), your body reclaims the good stuff through selective reabsorption. Glucose and amino acids are actively transported back into the blood, with sodium following and water tagging along through osmosis.
The PCT cells are perfectly adapted for this job - they've got microvilli for extra surface area, loads of mitochondria for energy, and co-transporter proteins that can move multiple substances at once.
Efficiency Check: Your kidneys filter about 180 litres of fluid daily but only produce 1-2 litres of urine - that's 99% reabsorption!

The loop of Henle creates a concentration gradient that's essential for water conservation. As filtrate travels down the descending limb, water leaves by osmosis, concentrating the remaining fluid. The ascending limb pumps out sodium and chloride ions but won't let water follow, diluting what's left.
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is your body's water-saving hormone. Made in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary, it targets the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct. When ADH levels rise, aquaporins (water channels) get inserted into cell membranes, making them permeable to water.
Here's how it works: ADH binds to receptors, triggering cAMP formation inside cells. This causes vesicles containing aquaporins to fuse with the cell membrane, creating water channels. More ADH means more channels and greater water reabsorption. When ADH levels drop, the channels get removed and stored away again.
Osmoreceptors in your hypothalamus constantly monitor blood concentration. Dehydrated? They detect the concentrated blood and trigger ADH release. Over-hydrated? ADH release stops, and you produce lots of dilute urine.
Practical Tip: Understanding ADH explains why you produce less urine when dehydrated and more when you've drunk lots of water.

Urine analysis reveals loads about health. Glucose in urine often indicates diabetes, proteins suggest kidney damage, and elevated creatinine points to muscle or kidney problems. Monoclonal antibodies make these tests incredibly specific and accurate.
Pregnancy tests use these antibodies to detect hCG hormone. The process involves injecting mice with hCG, harvesting the antibodies, and fusing them with rapidly-dividing cancer cells to create hybridomas. These produce identical antibodies that can detect tiny amounts of hCG in urine.
Drug tests work similarly, using immunoassays followed by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry for confirmation. This combination provides both quick screening and definitive identification of substances like anabolic steroids or recreational drugs.
Kidney failure disrupts everything - electrolyte balance gets thrown off, toxic urea builds up, blood pressure soars, and anaemia develops. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measures kidney function, with low values indicating problems.
Medical Reality: Kidney disease affects millions worldwide, making understanding these processes crucial for recognising symptoms early.

When kidneys fail, dialysis becomes a lifeline. Haemodialysis works like an artificial kidney - blood flows past a semi-permeable membrane with dialysis fluid on the other side. The fluid contains normal levels of glucose and ions but no urea, so waste diffuses out whilst essential substances stay balanced.
The process is clever: urea (high in blood, absent in dialysis fluid) moves out by diffusion. Excess ions also leave until blood levels normalise. Large molecules like proteins and blood cells can't cross the membrane, so they stay put. It's like having a selective molecular bouncer.
Kidney transplants offer freedom from dialysis but come with trade-offs. Benefits include better quality of life, no dietary restrictions, and preventing long-term damage from waste build-up. However, there's always organ rejection risk, requiring lifelong immunosuppressive drugs, plus the usual surgical risks.
The shortage of donor organs means many patients wait years for transplants. Meanwhile, dialysis keeps them alive but requires multiple weekly sessions and strict monitoring of diet and fluid intake.
Life Choice: Patients must weigh transplant risks against the limitations of lifelong dialysis - there's no perfect solution.

Your sensory receptors are incredibly sophisticated detectors, each specialised for specific stimuli. Mechanoreceptors detect pressure, chemoreceptors respond to chemicals, thermoreceptors sense temperature changes, and photoreceptors capture light. They all work as transducers, converting energy from stimuli into electrical nerve impulses.
Pacinian corpuscles in your skin detect pressure brilliantly. When pressed, the membrane stretches, opening sodium channels and allowing sodium ions to rush in. This creates a generator potential that triggers an action potential if strong enough.
Neurons come in three main types. Sensory neurons carry information from receptors toward the CNS, with cell bodies positioned along the pathway. Motor neurons transmit signals from CNS to muscles, with cell bodies at one end. Relay neurons connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS, featuring many short projections.
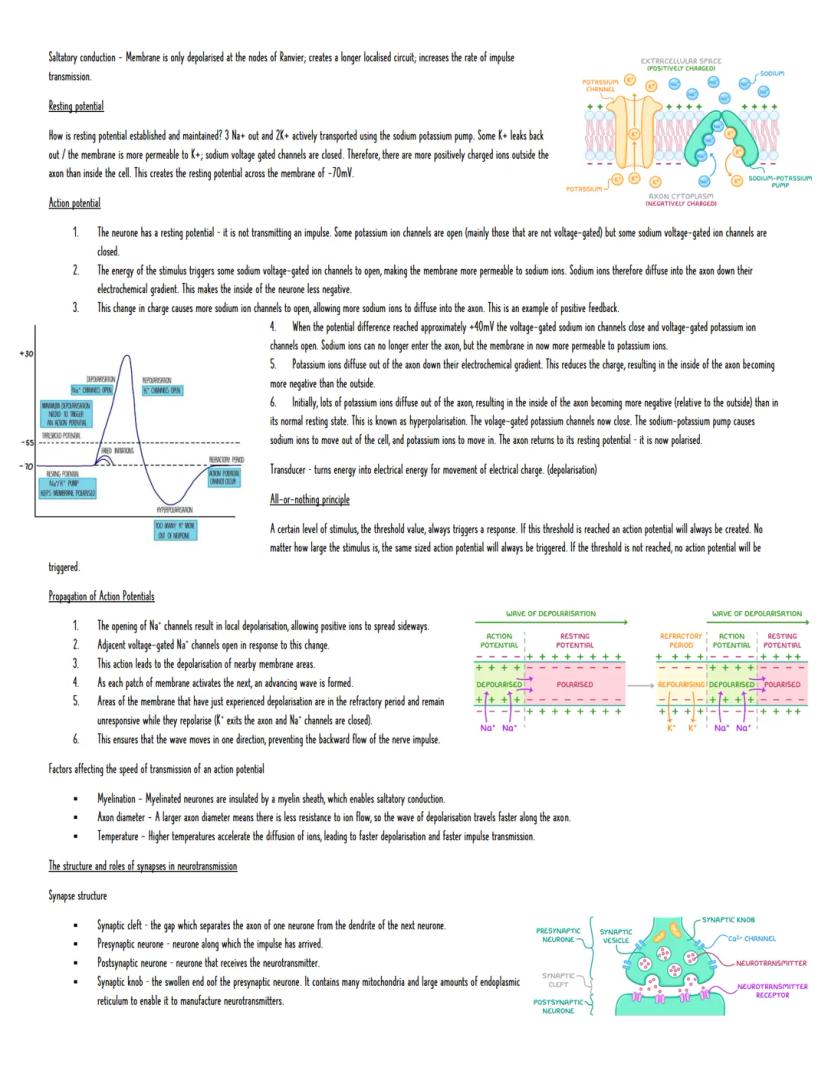
Myelination dramatically speeds up signal transmission. Schwann cells wrap around axons multiple times, creating insulating layers of myelin sheath. This enables saltatory conduction, where electrical impulses jump between gaps (nodes of Ranvier) rather than travelling continuously.
Speed Boost: Myelinated neurons can transmit signals at 120 m/s compared to just 2 m/s in unmyelinated ones.

Resting potential is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump, which moves 3 sodium ions out for every 2 potassium ions in. The membrane is more permeable to potassium, so some leaks back out, creating the negative charge inside.
Action potentials follow a predictable sequence. A stimulus opens voltage-gated sodium channels, causing depolarisation as sodium floods in. This triggers more channels to open (positive feedback) until the potential reaches +40mV. Then sodium channels close, potassium channels open, and the membrane repolarises. Brief hyperpolarisation occurs before normal conditions restore.
The all-or-nothing principle means stimuli either trigger a full action potential or nothing at all. There's no half-measures - once threshold is reached, you get maximum response regardless of stimulus strength.
Synapses are gaps between neurons where chemical communication occurs. When an action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal, calcium channels open, causing synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
Summation allows weak signals to combine and trigger responses. Temporal summation occurs when one neuron fires repeatedly, whilst spatial summation involves multiple neurons contributing simultaneously.
One-Way Traffic: Synapses ensure signals only travel in one direction because neurotransmitter vesicles only exist in presynaptic terminals.

Neurotransmitters come in two main types that have opposite effects. Excitatory neurotransmitters like acetylcholine cause depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane, potentially triggering action potentials. Inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA cause hyperpolarisation, making action potentials less likely.
Cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine and are found throughout the nervous system, especially at neuromuscular junctions. After acetylcholine binds to receptors and triggers a response, acetylcholinesterase breaks it down into choline and ethanoic acid. These components get recycled back into the presynaptic neuron to make more neurotransmitter.
This breakdown and recycling process is crucial - without it, neurotransmitter would keep stimulating the postsynaptic cell continuously. The synapse would become jammed "on," preventing normal function.
Synapses do much more than just pass signals along. They filter out weak stimuli, prevent overstimulation, allow decision-making by integrating multiple inputs, and enable learning and memory formation. The combination of excitatory and inhibitory inputs creates incredibly sophisticated information processing.
Summation allows the nervous system to amplify important signals whilst ignoring background noise. Multiple weak inputs can combine to create strong outputs, giving your brain remarkable flexibility in processing information.
Brain Power: Your brain contains trillions of synapses, each capable of this sophisticated signal processing - no wonder you can think, learn, and remember!
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Busola Oworu
@busolaoworu_ojhx
Your body is like a sophisticated communication network that never switches off. From maintaining your core temperature to filtering waste from your blood, countless processes work together to keep you alive and functioning - and it's all controlled by intricate... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Ever wondered how your body coordinates millions of cells to work together perfectly? Cell signalling is the answer - it's like having a massive group chat where cells send chemical messages to each other. Some signals travel short distances (like neurotransmitters jumping between brain cells), whilst others journey across your entire body (like hormones from your pituitary gland telling your kidneys to conserve water).
Homeostasis keeps your internal environment stable even when everything around you changes. Think of it as your body's autopilot system. Receptors detect changes, then effectors (muscles or glands) respond to fix any problems. Most of the time, your body uses negative feedback - like a thermostat that switches heating off when it gets too warm.
Positive feedback is rarer but powerful - it amplifies changes rather than reversing them. You'll see this during labour contractions, where each contraction triggers stronger ones.
Key Point: Negative feedback maintains stability, whilst positive feedback amplifies responses when your body needs rapid change.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your ability to maintain body temperature depends on whether you're an endotherm (like mammals and birds) or an ectotherm (like reptiles and fish). Endotherms generate heat internally through metabolism, whilst ectotherms rely on environmental heat sources.
Heat moves through your body via radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation. Ectotherms cleverly exploit these - basking in sunlight (radiation), pressing against warm rocks (conduction), or seeking shade when overheated. Some even change colour to absorb or reflect more heat.
Endotherms have more sophisticated responses. When you're hot, blood vessels near your skin dilate (vasodilation), you sweat more, and body hairs lie flat. When cold, the opposite happens - vasoconstriction, reduced sweating, and raised hairs create insulation.
Your hypothalamus acts as mission control, collecting temperature data from skin receptors and blood sensors. It then activates either the heat loss centre (when you're too warm) or heat gain centre (when you're too cold). The trade-off? Endotherms need loads more food to fuel this system, but can survive in almost any environment.
Remember: Ectotherms are energy-efficient but temperature-dependent; endotherms are energy-expensive but environmentally flexible.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your liver is basically a chemical processing plant that never stops working. It receives blood from two sources - oxygenated blood from the hepatic artery and nutrient-rich blood from the hepatic portal vein. These mix in spaces called sinusoids, where hepatocytes (liver cells) get to work removing toxins and processing nutrients.
Deamination is one of the liver's crucial jobs - removing amino groups from excess amino acids. This produces toxic ammonia, which gets converted to less harmful urea through the ornithine cycle. It's like having a recycling centre that breaks down unwanted proteins and safely packages the waste for disposal.
The liver also detoxifies alcohol using ethanol dehydrogenase, breaks down hydrogen peroxide with catalase, and creates bile from old red blood cells. Bile pigments give your faeces their characteristic colour - definitely more interesting than you thought!
Clinical Connection: Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests often indicate liver damage, showing how important these processes are for health.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Each kidney contains about a million tiny filters called nephrons. The filtering starts in Bowman's capsule, which surrounds a knot of capillaries called the glomerulus. Here's where the magic happens - ultrafiltration forces everything small enough through a three-layer barrier.
The afferent arteriole (bringing blood in) is wider than the efferent arteriole (taking blood out), creating high pressure that pushes fluid through. The filtering system has three parts: fenestrations (tiny holes) in capillary walls, a basement membrane that blocks large molecules, and podocytes with finger-like projections that complete the sieve.
What gets through? Water, glucose, salts, urea, amino acids, and ions - basically everything except blood cells and large proteins. In the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), your body reclaims the good stuff through selective reabsorption. Glucose and amino acids are actively transported back into the blood, with sodium following and water tagging along through osmosis.
The PCT cells are perfectly adapted for this job - they've got microvilli for extra surface area, loads of mitochondria for energy, and co-transporter proteins that can move multiple substances at once.
Efficiency Check: Your kidneys filter about 180 litres of fluid daily but only produce 1-2 litres of urine - that's 99% reabsorption!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The loop of Henle creates a concentration gradient that's essential for water conservation. As filtrate travels down the descending limb, water leaves by osmosis, concentrating the remaining fluid. The ascending limb pumps out sodium and chloride ions but won't let water follow, diluting what's left.
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is your body's water-saving hormone. Made in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary, it targets the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct. When ADH levels rise, aquaporins (water channels) get inserted into cell membranes, making them permeable to water.
Here's how it works: ADH binds to receptors, triggering cAMP formation inside cells. This causes vesicles containing aquaporins to fuse with the cell membrane, creating water channels. More ADH means more channels and greater water reabsorption. When ADH levels drop, the channels get removed and stored away again.
Osmoreceptors in your hypothalamus constantly monitor blood concentration. Dehydrated? They detect the concentrated blood and trigger ADH release. Over-hydrated? ADH release stops, and you produce lots of dilute urine.
Practical Tip: Understanding ADH explains why you produce less urine when dehydrated and more when you've drunk lots of water.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Urine analysis reveals loads about health. Glucose in urine often indicates diabetes, proteins suggest kidney damage, and elevated creatinine points to muscle or kidney problems. Monoclonal antibodies make these tests incredibly specific and accurate.
Pregnancy tests use these antibodies to detect hCG hormone. The process involves injecting mice with hCG, harvesting the antibodies, and fusing them with rapidly-dividing cancer cells to create hybridomas. These produce identical antibodies that can detect tiny amounts of hCG in urine.
Drug tests work similarly, using immunoassays followed by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry for confirmation. This combination provides both quick screening and definitive identification of substances like anabolic steroids or recreational drugs.
Kidney failure disrupts everything - electrolyte balance gets thrown off, toxic urea builds up, blood pressure soars, and anaemia develops. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measures kidney function, with low values indicating problems.
Medical Reality: Kidney disease affects millions worldwide, making understanding these processes crucial for recognising symptoms early.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
When kidneys fail, dialysis becomes a lifeline. Haemodialysis works like an artificial kidney - blood flows past a semi-permeable membrane with dialysis fluid on the other side. The fluid contains normal levels of glucose and ions but no urea, so waste diffuses out whilst essential substances stay balanced.
The process is clever: urea (high in blood, absent in dialysis fluid) moves out by diffusion. Excess ions also leave until blood levels normalise. Large molecules like proteins and blood cells can't cross the membrane, so they stay put. It's like having a selective molecular bouncer.
Kidney transplants offer freedom from dialysis but come with trade-offs. Benefits include better quality of life, no dietary restrictions, and preventing long-term damage from waste build-up. However, there's always organ rejection risk, requiring lifelong immunosuppressive drugs, plus the usual surgical risks.
The shortage of donor organs means many patients wait years for transplants. Meanwhile, dialysis keeps them alive but requires multiple weekly sessions and strict monitoring of diet and fluid intake.
Life Choice: Patients must weigh transplant risks against the limitations of lifelong dialysis - there's no perfect solution.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your sensory receptors are incredibly sophisticated detectors, each specialised for specific stimuli. Mechanoreceptors detect pressure, chemoreceptors respond to chemicals, thermoreceptors sense temperature changes, and photoreceptors capture light. They all work as transducers, converting energy from stimuli into electrical nerve impulses.
Pacinian corpuscles in your skin detect pressure brilliantly. When pressed, the membrane stretches, opening sodium channels and allowing sodium ions to rush in. This creates a generator potential that triggers an action potential if strong enough.
Neurons come in three main types. Sensory neurons carry information from receptors toward the CNS, with cell bodies positioned along the pathway. Motor neurons transmit signals from CNS to muscles, with cell bodies at one end. Relay neurons connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS, featuring many short projections.
Myelination dramatically speeds up signal transmission. Schwann cells wrap around axons multiple times, creating insulating layers of myelin sheath. This enables saltatory conduction, where electrical impulses jump between gaps (nodes of Ranvier) rather than travelling continuously.
Speed Boost: Myelinated neurons can transmit signals at 120 m/s compared to just 2 m/s in unmyelinated ones.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Resting potential is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump, which moves 3 sodium ions out for every 2 potassium ions in. The membrane is more permeable to potassium, so some leaks back out, creating the negative charge inside.
Action potentials follow a predictable sequence. A stimulus opens voltage-gated sodium channels, causing depolarisation as sodium floods in. This triggers more channels to open (positive feedback) until the potential reaches +40mV. Then sodium channels close, potassium channels open, and the membrane repolarises. Brief hyperpolarisation occurs before normal conditions restore.
The all-or-nothing principle means stimuli either trigger a full action potential or nothing at all. There's no half-measures - once threshold is reached, you get maximum response regardless of stimulus strength.
Synapses are gaps between neurons where chemical communication occurs. When an action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal, calcium channels open, causing synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
Summation allows weak signals to combine and trigger responses. Temporal summation occurs when one neuron fires repeatedly, whilst spatial summation involves multiple neurons contributing simultaneously.
One-Way Traffic: Synapses ensure signals only travel in one direction because neurotransmitter vesicles only exist in presynaptic terminals.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Neurotransmitters come in two main types that have opposite effects. Excitatory neurotransmitters like acetylcholine cause depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane, potentially triggering action potentials. Inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA cause hyperpolarisation, making action potentials less likely.
Cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine and are found throughout the nervous system, especially at neuromuscular junctions. After acetylcholine binds to receptors and triggers a response, acetylcholinesterase breaks it down into choline and ethanoic acid. These components get recycled back into the presynaptic neuron to make more neurotransmitter.
This breakdown and recycling process is crucial - without it, neurotransmitter would keep stimulating the postsynaptic cell continuously. The synapse would become jammed "on," preventing normal function.
Synapses do much more than just pass signals along. They filter out weak stimuli, prevent overstimulation, allow decision-making by integrating multiple inputs, and enable learning and memory formation. The combination of excitatory and inhibitory inputs creates incredibly sophisticated information processing.
Summation allows the nervous system to amplify important signals whilst ignoring background noise. Multiple weak inputs can combine to create strong outputs, giving your brain remarkable flexibility in processing information.
Brain Power: Your brain contains trillions of synapses, each capable of this sophisticated signal processing - no wonder you can think, learn, and remember!
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
6
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user