Ever wonder how scientists classify millions of species on Earth... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
104
•
13 Feb 2026
•
Busola Oworu
@busolaoworu_ojhx
Ever wonder how scientists classify millions of species on Earth... Show more









Think about how chaotic biology would be if every scientist called the same organism by different names! The binomial system solves this by giving every species a universal two-part name (like Homo sapiens for humans) that's recognised worldwide.
Taxonomy organises life into eight hierarchical groups: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. The species concept is simple yet powerful - two individuals that can breed together to produce fertile offspring belong to the same species.
Organisms are also classified by how they obtain nutrition. Autotrophs make their own food through photosynthesis, heterotrophs digest other organisms, and saprotrophs absorb nutrients from dead matter. These feeding strategies help scientists understand evolutionary relationships.
Quick Tip: Remember the taxonomy hierarchy with "Daft King Philip Came Over For Good Soup" - Domain to Species!

Traditional classification divided life into five kingdoms based on observable features. Prokaryotes (bacteria) lack membrane-bound organelles and have peptidoglycan cell walls. Protoctista include algae with varying cell wall components. Fungi possess chitin cell walls and reproduce via spores, whilst plants have cellulose walls and photosynthesise. Animals lack cell walls entirely.
However, modern DNA sequencing and biochemical analysis have revolutionised classification. Scientists now compare DNA base sequences and protein structures like cytochrome C to determine evolutionary relationships more accurately than physical features alone.
The three-domain system (Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya) better reflects evolutionary history than the five kingdoms. This system recognises fundamental differences in RNA polymerase and protein synthesis between bacteria and archaea, despite both being prokaryotes.
Remember: Modern classification reflects phylogeny - actual evolutionary relationships rather than just superficial similarities.

Evolution is simply the fact that populations change over time, whilst natural selection is the process driving these changes. Darwin's brilliant insights came from four key observations: variation exists, organisms resemble their parents, huge numbers of offspring are produced, yet population sizes remain stable.
Natural selection works through genetic variation from random mutations. When selection pressures occur, individuals with advantageous characteristics survive and reproduce more successfully. Over many generations, beneficial alleles become more common in the population.
Fossil evidence strongly supports evolution. Older fossils in deeper rock layers are simpler than younger, more complex ones found above. Archaeopteryx beautifully demonstrates transitional forms between dinosaurs and birds. Importantly, no fossil has ever been found "out of sequence" - exactly what evolution predicts.
Comparative biochemistry provides additional evidence. The fewer differences in DNA or protein sequences between species, the more recently they shared a common ancestor.
Key Point: Natural selection isn't random - whilst mutations are random, survival and reproduction of beneficial traits is definitely not!

Understanding variation is crucial for grasping evolution. Continuous variation (like height) shows no distinct categories and results from multiple genes plus environmental factors. Discontinuous variation (like blood groups) creates distinct categories from single genes, unaffected by environment.
Genetic variation arises from mutation, meiosis, sexual reproduction, and chance fertilisation. This variation provides the raw material for natural selection to work upon.
Adaptations come in three forms: anatomical (structural features like bacterial flagella), physiological (functional processes like yeast switching between aerobic and anaerobic respiration), and behavioural (actions like earthworms showing thigmotaxis).
Understanding homologous versus analogous structures helps distinguish evolutionary relationships. Homologous structures (like bat wings and human arms) share common ancestry despite different functions. Analogous structures (like bird and insect wings) serve similar functions but evolved independently through convergent evolution.
Exam Tip: You'll be given the t-test and Spearman's rank formulas - focus on understanding when to use each statistical test rather than memorising equations!

Statistical tests help determine whether observed differences are real or just due to chance. The t-test compares means between two groups - if your calculated value exceeds the critical value, the difference is significant. Remember to calculate degrees of freedom correctly!
Spearman's rank correlation measures whether relationships between variables are significant. Values range from -1 (perfect negative correlation) through 0 (no correlation) to +1 (perfect positive correlation).
These statistical tools are essential for analysing biological data objectively. Whether comparing leaf lengths between different trees or correlating environmental factors with species distribution, statistics transform observations into reliable scientific evidence.
Standard deviation measures data spread around the mean - smaller values indicate data points cluster closely together, whilst larger values show greater variability.
Remember: Statistical significance doesn't always mean biological importance - a statistically significant difference might still be too small to matter in real ecosystems!

Biodiversity encompasses three levels: species diversity (number and evenness of different species), habitat diversity (range of different ecosystems), and genetic diversity (variety within species populations). Species richness counts different species, whilst species evenness measures how equally distributed they are.
Human activities pose the greatest threats to biodiversity. Population growth drives habitat destruction for agriculture, whilst climate change alters ecosystems faster than species can adapt. Monoculture farming replaces diverse ecosystems with single-species crops.
Maintaining biodiversity matters for multiple reasons. Ecological reasons include maintaining food webs and preventing soil depletion. Economic benefits include ecotourism and potential medical discoveries. Aesthetic value ensures future generations can experience natural beauty.
Keystone species play disproportionately important roles in ecosystem function - remove them and entire ecosystems collapse. This interconnectedness means protecting biodiversity requires understanding complex ecological relationships.
Think About It: Every ecosystem lost is like burning down a library - we lose potential medicines, foods, and scientific knowledge forever.

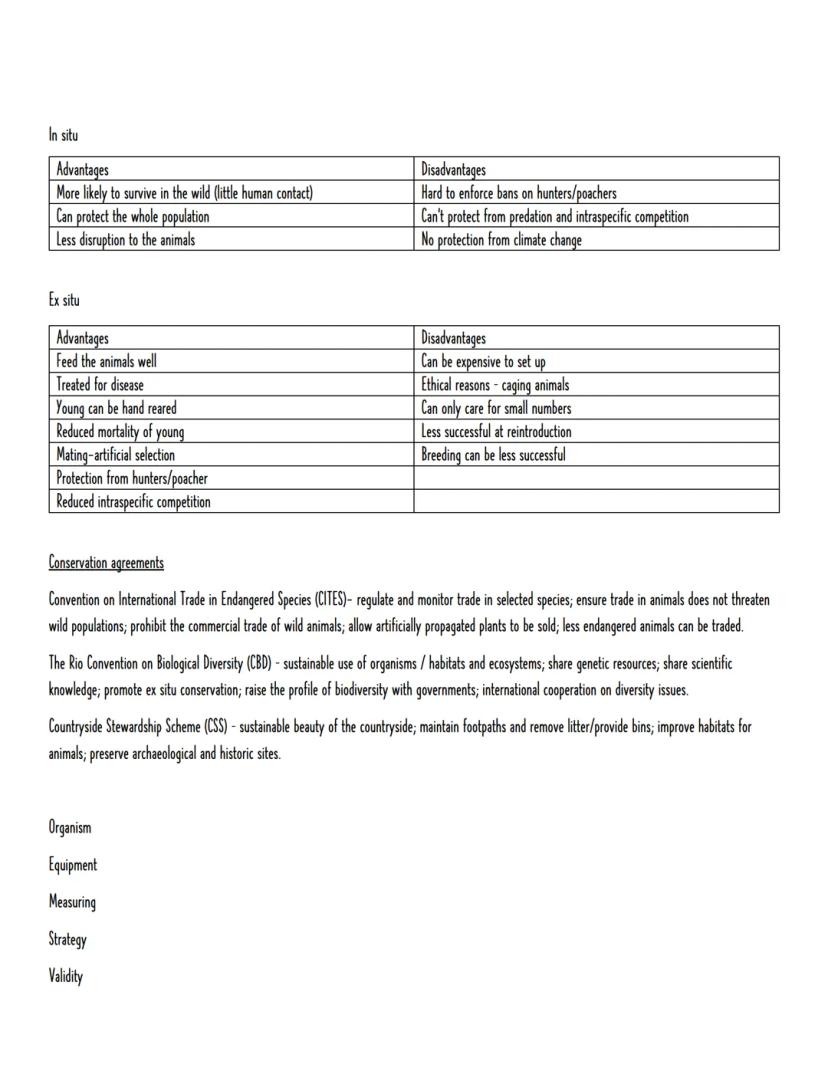
Conservation takes two main approaches: in situ (protecting species in natural habitats) and ex situ (protecting them away from natural environments). In situ methods include national parks and hunting bans, allowing whole populations to thrive with minimal human interference.
Ex situ conservation includes zoos and seed banks. Storing seeds proves particularly effective because they're produced in excess, require little space, remain viable long-term, and represent enormous genetic diversity. Seeds can be collected without damaging parent plants and transported cheaply.
International agreements coordinate global conservation efforts. CITES regulates trade in endangered species, whilst the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity promotes sustainable use and international cooperation. Local schemes like the Countryside Stewardship Scheme maintain habitats and archaeological sites.
Both approaches have trade-offs. In situ conservation protects entire ecosystems but can't prevent all threats. Ex situ conservation ensures survival but may reduce animals' ability to survive when reintroduced to the wild.
Key Insight: Successful conservation requires both approaches working together - protecting wild habitats whilst maintaining backup populations in captivity.

Accurately measuring biodiversity requires careful experimental design. Random sampling avoids bias and gives general biodiversity estimates, whilst systematic sampling identifies patterns along environmental gradients. Stratified sampling ensures different habitats are proportionally represented.
Quadrats measure plant communities effectively. Place them using random coordinates generated by computers or GPS systems. Count species consistently using the "half in, half out" rule and identify species using keys.
Improving validity requires standardising methodology - use the same quadrat size, counting methods, and identification keys throughout. Repeat sampling at different times of day and year to account for temporal variation.
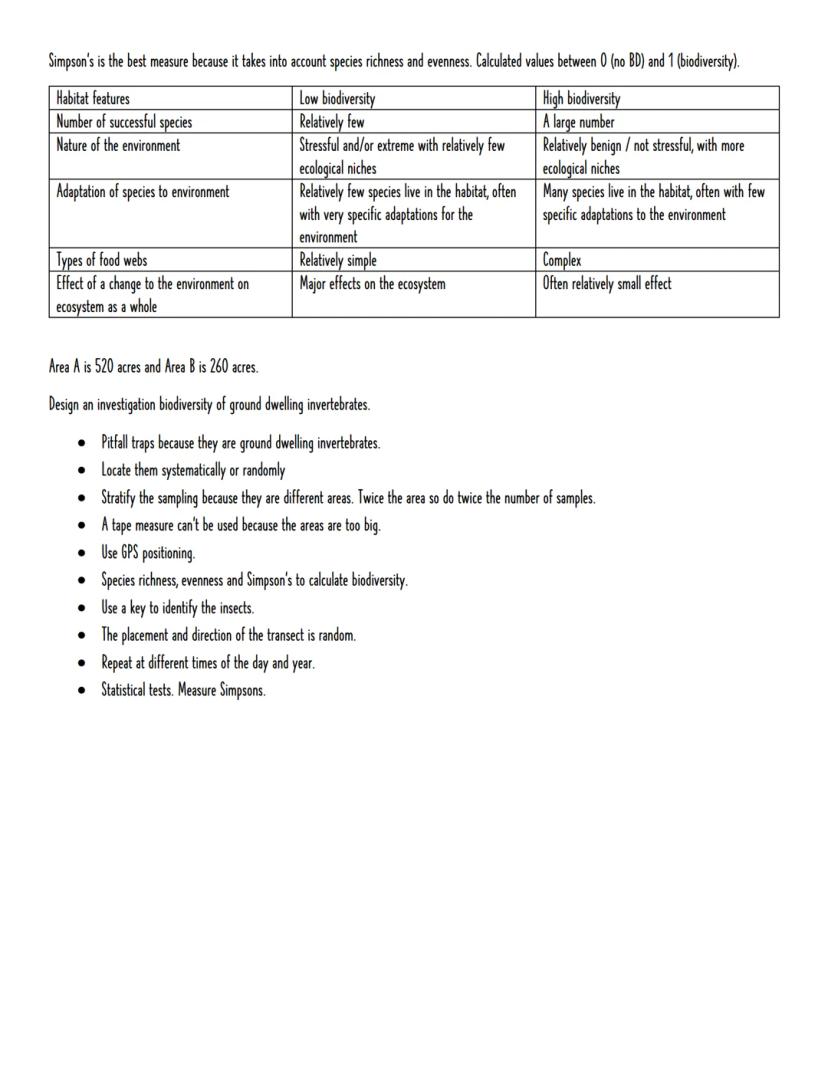
Simpson's Index provides the best biodiversity measure because it considers both species richness and evenness. Values range from 0 (no biodiversity) to 1 (maximum biodiversity), making comparisons between sites straightforward.
Practical Tip: More quadrats always improve reliability, but trial runs help determine the minimum number needed for statistically valid results.

High biodiversity ecosystems contain many species with few specific adaptations, complex food webs, and multiple ecological niches. They're relatively stable because changes affect only small portions of the community. Low biodiversity systems have fewer species with very specific adaptations, simple food webs, and extreme environments where changes can cause ecosystem collapse.
When designing biodiversity investigations for different areas, scale matters enormously. Large areas require GPS positioning rather than tape measures, with sampling intensity proportional to area size. Pitfall traps work brilliantly for ground-dwelling invertebrates, whilst stratified sampling ensures fair comparison between different habitat types.
Statistical analysis using Simpson's Index allows objective comparison between sites. Remember to repeat measurements across different seasons and times to account for natural variation in species activity and abundance.
Communicable diseases begin our next major topic. Understanding the difference between health and disease (impaired normal functioning) provides the foundation for studying how pathogens affect organisms.
Connection: Biodiversity and disease are intimately linked - diverse ecosystems often have fewer disease outbreaks because pathogens can't spread as easily through varied host populations.

Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms that have evolved sophisticated strategies for survival and reproduction. Parasites live on or in hosts, gaining nutrition whilst harming their host - they need hosts for food, warmth, protection, and transmission to new hosts.
Bacteria reproduce rapidly and cause disease through direct cell damage or toxin production. Tuberculosis devastates human lungs, whilst ring rot destroys potato crops. Fungi irritate tissues when reproductive hyphae grow to surfaces and release spores, causing conditions like athlete's foot.
Viruses hijack cellular machinery to reproduce, eventually bursting cells and releasing new viral particles. They cause diseases ranging from common colds to HIV/AIDS. Protoctista like malaria parasites feed on host cell contents, particularly targeting red blood cells.
Plant diseases demonstrate diverse transmission methods. Ring rot spreads through soil and insects, tobacco mosaic virus transmits through direct plant contact, and black sigatoka disperses via wind and water. Understanding transmission routes is crucial for developing effective control strategies.
Health Connection: Many human diseases have vectors like mosquitoes - controlling vector populations often proves more effective than treating individual patients.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Busola Oworu
@busolaoworu_ojhx
Ever wonder how scientists classify millions of species on Earth or why some areas have incredible biodiversity whilst others don't? This module covers everything from how we group organisms using DNA evidence to understanding evolution, natural selection, and the vital... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Think about how chaotic biology would be if every scientist called the same organism by different names! The binomial system solves this by giving every species a universal two-part name (like Homo sapiens for humans) that's recognised worldwide.
Taxonomy organises life into eight hierarchical groups: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. The species concept is simple yet powerful - two individuals that can breed together to produce fertile offspring belong to the same species.
Organisms are also classified by how they obtain nutrition. Autotrophs make their own food through photosynthesis, heterotrophs digest other organisms, and saprotrophs absorb nutrients from dead matter. These feeding strategies help scientists understand evolutionary relationships.
Quick Tip: Remember the taxonomy hierarchy with "Daft King Philip Came Over For Good Soup" - Domain to Species!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Traditional classification divided life into five kingdoms based on observable features. Prokaryotes (bacteria) lack membrane-bound organelles and have peptidoglycan cell walls. Protoctista include algae with varying cell wall components. Fungi possess chitin cell walls and reproduce via spores, whilst plants have cellulose walls and photosynthesise. Animals lack cell walls entirely.
However, modern DNA sequencing and biochemical analysis have revolutionised classification. Scientists now compare DNA base sequences and protein structures like cytochrome C to determine evolutionary relationships more accurately than physical features alone.
The three-domain system (Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya) better reflects evolutionary history than the five kingdoms. This system recognises fundamental differences in RNA polymerase and protein synthesis between bacteria and archaea, despite both being prokaryotes.
Remember: Modern classification reflects phylogeny - actual evolutionary relationships rather than just superficial similarities.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Evolution is simply the fact that populations change over time, whilst natural selection is the process driving these changes. Darwin's brilliant insights came from four key observations: variation exists, organisms resemble their parents, huge numbers of offspring are produced, yet population sizes remain stable.
Natural selection works through genetic variation from random mutations. When selection pressures occur, individuals with advantageous characteristics survive and reproduce more successfully. Over many generations, beneficial alleles become more common in the population.
Fossil evidence strongly supports evolution. Older fossils in deeper rock layers are simpler than younger, more complex ones found above. Archaeopteryx beautifully demonstrates transitional forms between dinosaurs and birds. Importantly, no fossil has ever been found "out of sequence" - exactly what evolution predicts.
Comparative biochemistry provides additional evidence. The fewer differences in DNA or protein sequences between species, the more recently they shared a common ancestor.
Key Point: Natural selection isn't random - whilst mutations are random, survival and reproduction of beneficial traits is definitely not!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Understanding variation is crucial for grasping evolution. Continuous variation (like height) shows no distinct categories and results from multiple genes plus environmental factors. Discontinuous variation (like blood groups) creates distinct categories from single genes, unaffected by environment.
Genetic variation arises from mutation, meiosis, sexual reproduction, and chance fertilisation. This variation provides the raw material for natural selection to work upon.
Adaptations come in three forms: anatomical (structural features like bacterial flagella), physiological (functional processes like yeast switching between aerobic and anaerobic respiration), and behavioural (actions like earthworms showing thigmotaxis).
Understanding homologous versus analogous structures helps distinguish evolutionary relationships. Homologous structures (like bat wings and human arms) share common ancestry despite different functions. Analogous structures (like bird and insect wings) serve similar functions but evolved independently through convergent evolution.
Exam Tip: You'll be given the t-test and Spearman's rank formulas - focus on understanding when to use each statistical test rather than memorising equations!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Statistical tests help determine whether observed differences are real or just due to chance. The t-test compares means between two groups - if your calculated value exceeds the critical value, the difference is significant. Remember to calculate degrees of freedom correctly!
Spearman's rank correlation measures whether relationships between variables are significant. Values range from -1 (perfect negative correlation) through 0 (no correlation) to +1 (perfect positive correlation).
These statistical tools are essential for analysing biological data objectively. Whether comparing leaf lengths between different trees or correlating environmental factors with species distribution, statistics transform observations into reliable scientific evidence.
Standard deviation measures data spread around the mean - smaller values indicate data points cluster closely together, whilst larger values show greater variability.
Remember: Statistical significance doesn't always mean biological importance - a statistically significant difference might still be too small to matter in real ecosystems!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Biodiversity encompasses three levels: species diversity (number and evenness of different species), habitat diversity (range of different ecosystems), and genetic diversity (variety within species populations). Species richness counts different species, whilst species evenness measures how equally distributed they are.
Human activities pose the greatest threats to biodiversity. Population growth drives habitat destruction for agriculture, whilst climate change alters ecosystems faster than species can adapt. Monoculture farming replaces diverse ecosystems with single-species crops.
Maintaining biodiversity matters for multiple reasons. Ecological reasons include maintaining food webs and preventing soil depletion. Economic benefits include ecotourism and potential medical discoveries. Aesthetic value ensures future generations can experience natural beauty.
Keystone species play disproportionately important roles in ecosystem function - remove them and entire ecosystems collapse. This interconnectedness means protecting biodiversity requires understanding complex ecological relationships.
Think About It: Every ecosystem lost is like burning down a library - we lose potential medicines, foods, and scientific knowledge forever.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Conservation takes two main approaches: in situ (protecting species in natural habitats) and ex situ (protecting them away from natural environments). In situ methods include national parks and hunting bans, allowing whole populations to thrive with minimal human interference.
Ex situ conservation includes zoos and seed banks. Storing seeds proves particularly effective because they're produced in excess, require little space, remain viable long-term, and represent enormous genetic diversity. Seeds can be collected without damaging parent plants and transported cheaply.
International agreements coordinate global conservation efforts. CITES regulates trade in endangered species, whilst the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity promotes sustainable use and international cooperation. Local schemes like the Countryside Stewardship Scheme maintain habitats and archaeological sites.
Both approaches have trade-offs. In situ conservation protects entire ecosystems but can't prevent all threats. Ex situ conservation ensures survival but may reduce animals' ability to survive when reintroduced to the wild.
Key Insight: Successful conservation requires both approaches working together - protecting wild habitats whilst maintaining backup populations in captivity.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Accurately measuring biodiversity requires careful experimental design. Random sampling avoids bias and gives general biodiversity estimates, whilst systematic sampling identifies patterns along environmental gradients. Stratified sampling ensures different habitats are proportionally represented.
Quadrats measure plant communities effectively. Place them using random coordinates generated by computers or GPS systems. Count species consistently using the "half in, half out" rule and identify species using keys.
Improving validity requires standardising methodology - use the same quadrat size, counting methods, and identification keys throughout. Repeat sampling at different times of day and year to account for temporal variation.
Simpson's Index provides the best biodiversity measure because it considers both species richness and evenness. Values range from 0 (no biodiversity) to 1 (maximum biodiversity), making comparisons between sites straightforward.
Practical Tip: More quadrats always improve reliability, but trial runs help determine the minimum number needed for statistically valid results.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
High biodiversity ecosystems contain many species with few specific adaptations, complex food webs, and multiple ecological niches. They're relatively stable because changes affect only small portions of the community. Low biodiversity systems have fewer species with very specific adaptations, simple food webs, and extreme environments where changes can cause ecosystem collapse.
When designing biodiversity investigations for different areas, scale matters enormously. Large areas require GPS positioning rather than tape measures, with sampling intensity proportional to area size. Pitfall traps work brilliantly for ground-dwelling invertebrates, whilst stratified sampling ensures fair comparison between different habitat types.
Statistical analysis using Simpson's Index allows objective comparison between sites. Remember to repeat measurements across different seasons and times to account for natural variation in species activity and abundance.
Communicable diseases begin our next major topic. Understanding the difference between health and disease (impaired normal functioning) provides the foundation for studying how pathogens affect organisms.
Connection: Biodiversity and disease are intimately linked - diverse ecosystems often have fewer disease outbreaks because pathogens can't spread as easily through varied host populations.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms that have evolved sophisticated strategies for survival and reproduction. Parasites live on or in hosts, gaining nutrition whilst harming their host - they need hosts for food, warmth, protection, and transmission to new hosts.
Bacteria reproduce rapidly and cause disease through direct cell damage or toxin production. Tuberculosis devastates human lungs, whilst ring rot destroys potato crops. Fungi irritate tissues when reproductive hyphae grow to surfaces and release spores, causing conditions like athlete's foot.
Viruses hijack cellular machinery to reproduce, eventually bursting cells and releasing new viral particles. They cause diseases ranging from common colds to HIV/AIDS. Protoctista like malaria parasites feed on host cell contents, particularly targeting red blood cells.
Plant diseases demonstrate diverse transmission methods. Ring rot spreads through soil and insects, tobacco mosaic virus transmits through direct plant contact, and black sigatoka disperses via wind and water. Understanding transmission routes is crucial for developing effective control strategies.
Health Connection: Many human diseases have vectors like mosquitoes - controlling vector populations often proves more effective than treating individual patients.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
2
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user