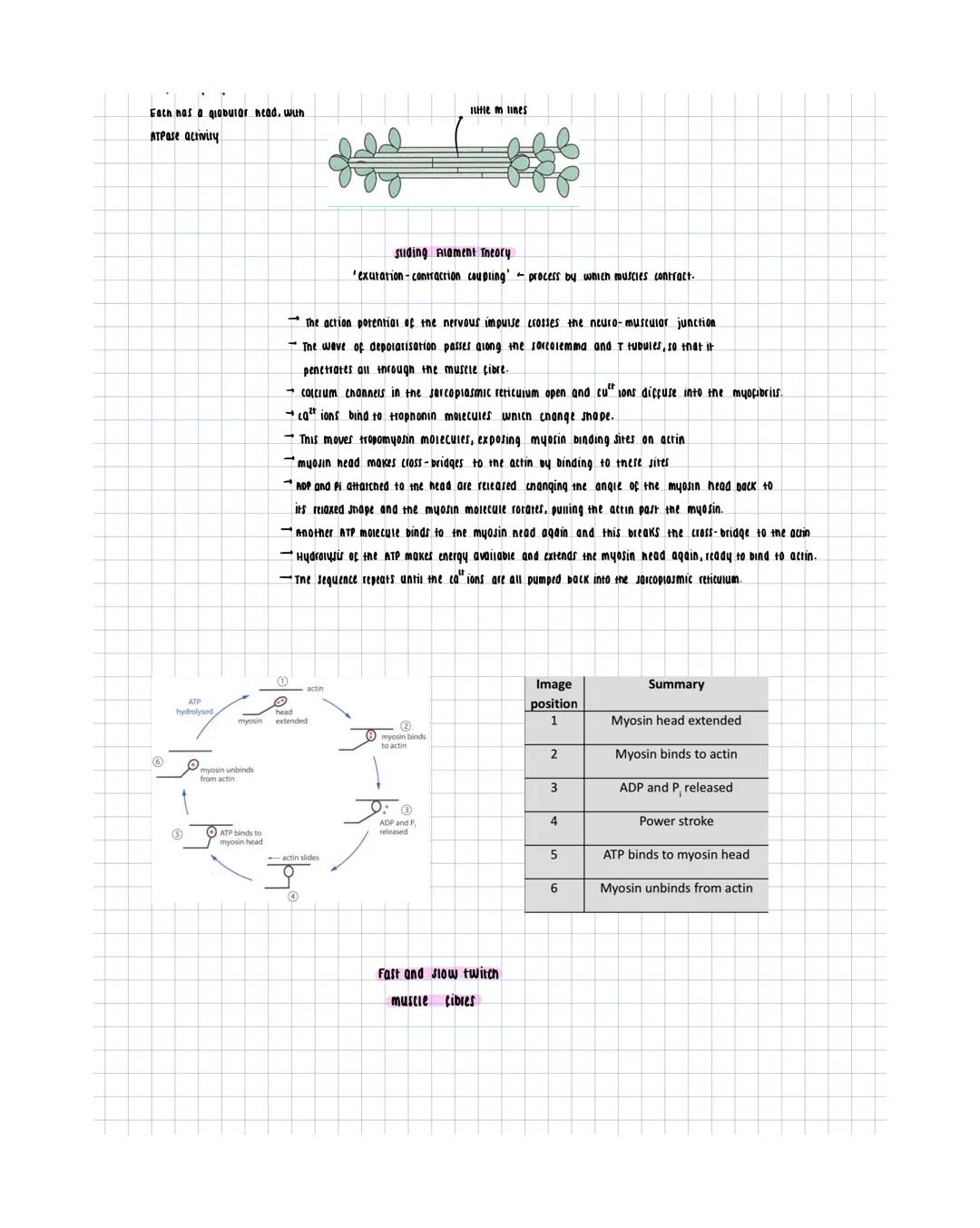
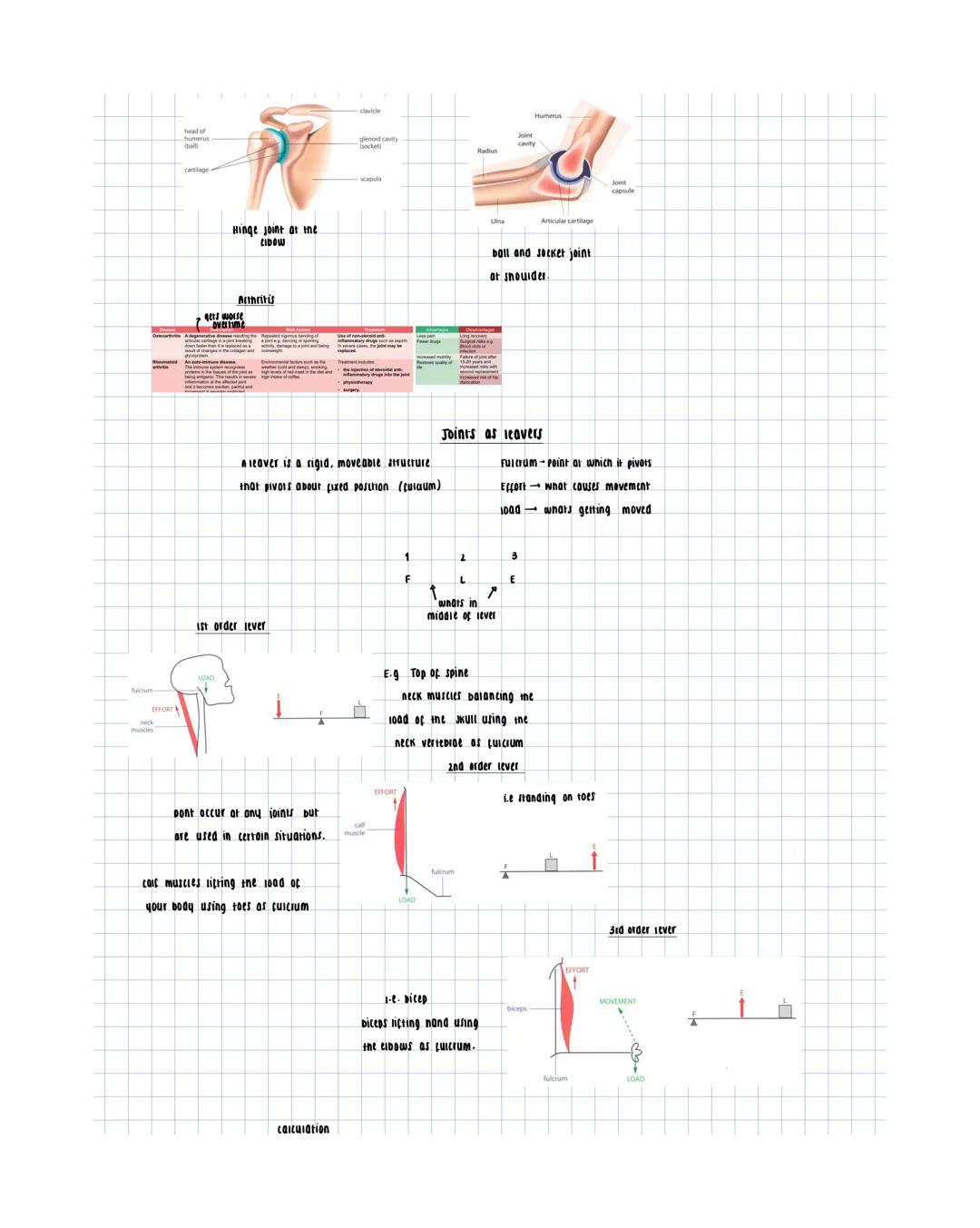
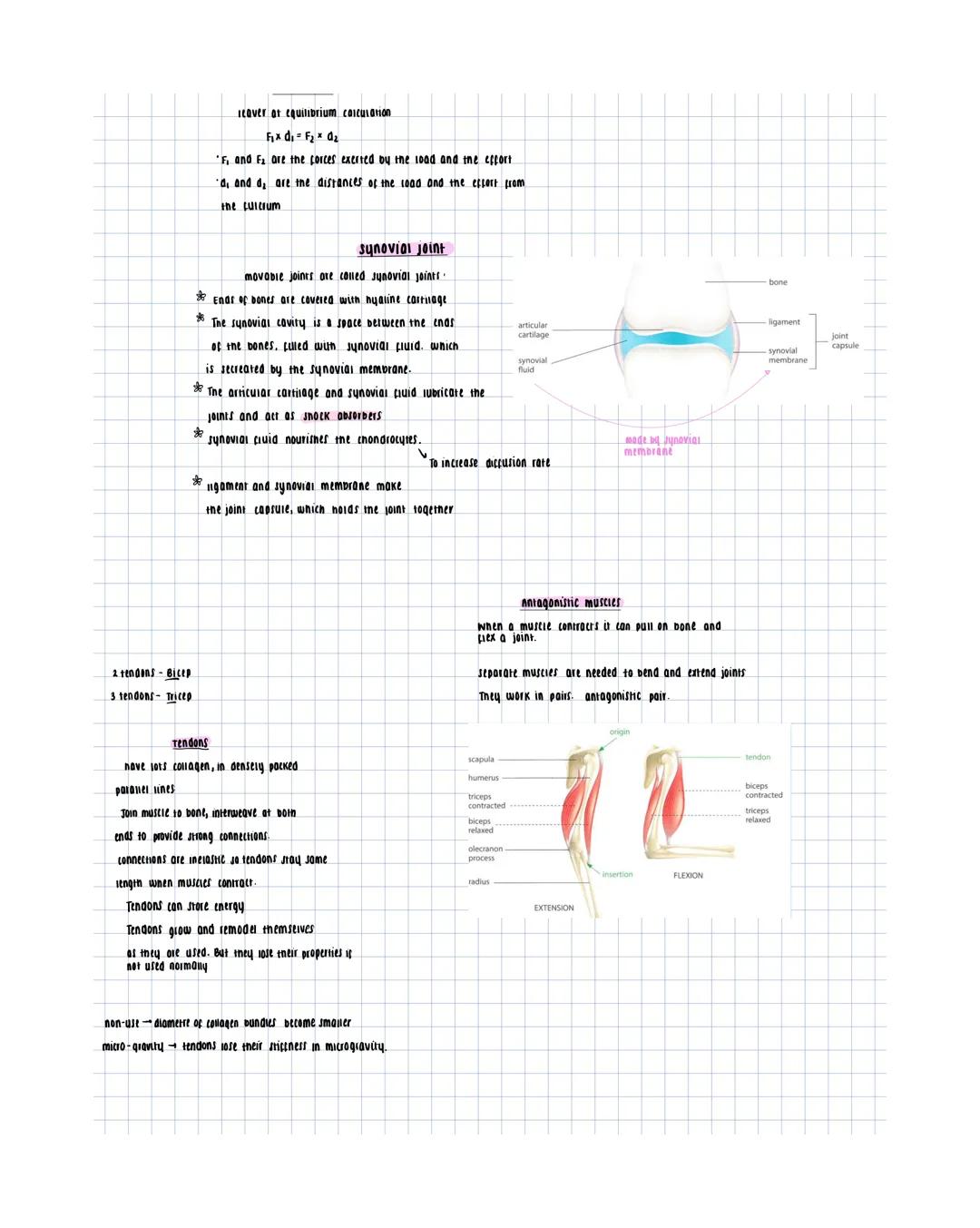
Skeletal Structure and Fractures
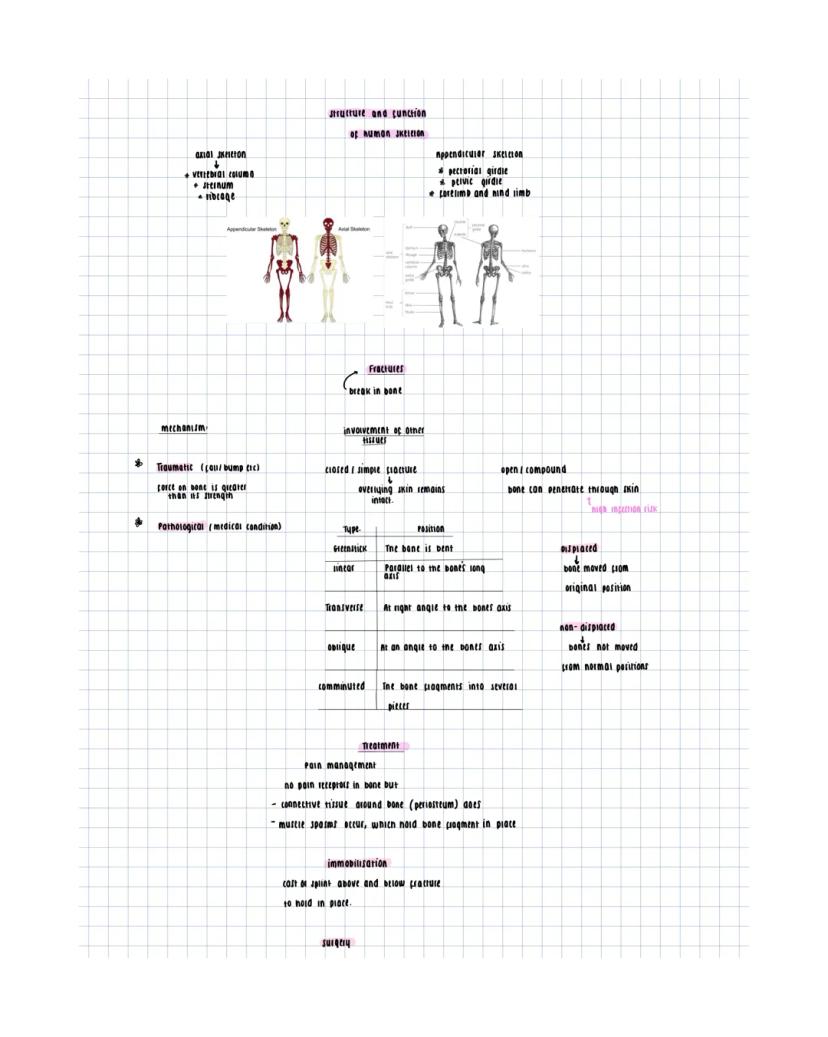
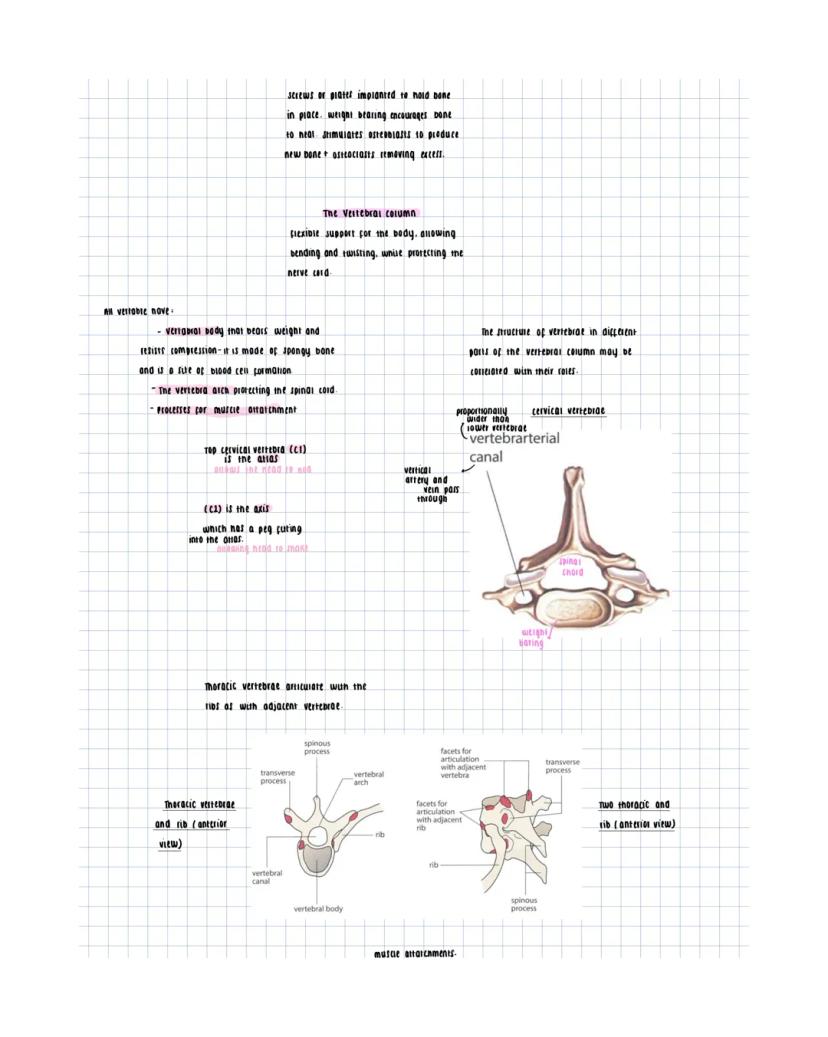
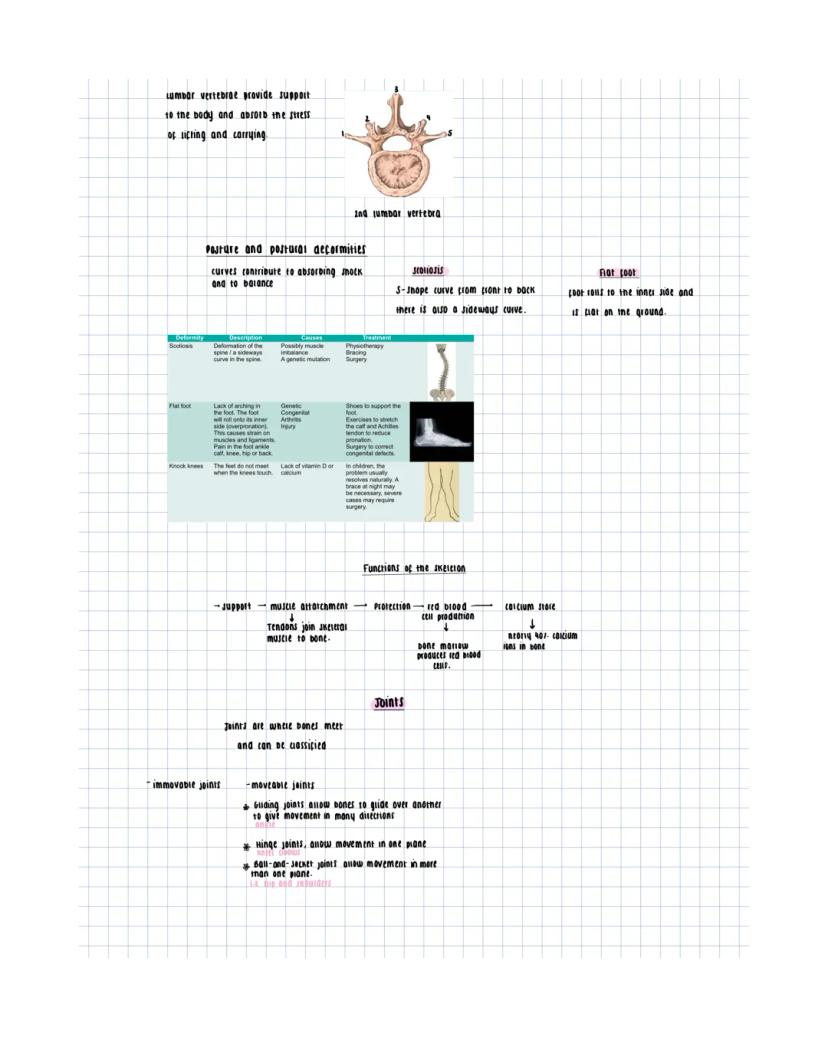
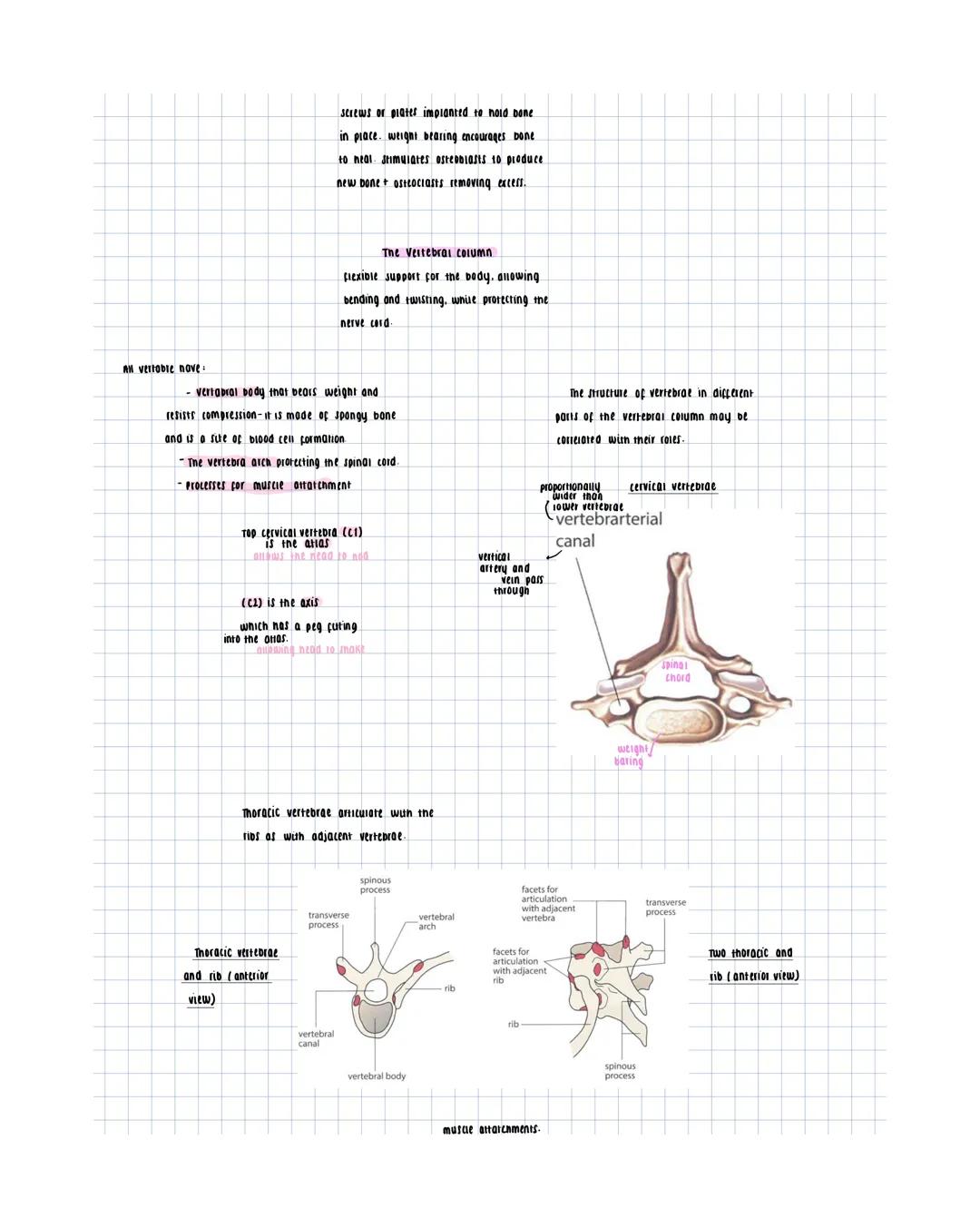
Your skeleton divides into two main parts: the axial skeleton (vertebral column, sternum, ribcage) and appendicular skeleton (limbs and girdles). This framework provides support, protection, and attachment points for muscles.
Fractures occur when force exceeds bone strength. Traumatic fractures result from accidents, whilst pathological fractures happen due to medical conditions. The main types include greenstick (bent), linear (parallel to bone), transverse (right angle), oblique (angled), and comminuted (multiple fragments).
Treatment involves pain management remember,boneitselfhasnopainreceptors−it′sthesurroundingperiosteumthathurts, immobilisation with casts, and sometimes surgery with screws or plates. Weight-bearing actually encourages healing by stimulating osteoblasts.
Important distinction: Closed fractures keep skin intact, whilst open fractures break through the skin with high infection risk.