Your immune system is like a sophisticated security team protecting... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Classic Dramatic Literature
Modern Lyric Poetry
Influential English-Language Authors
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Romantic and Love Poetry
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Evidence Analysis and Integration
Author's Stylistic Elements
Figurative Language and Rhetoric
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Cellular Organization and Development
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Enzyme Structure and Regulation
Cellular Organization Types
Biological Homeostatic Processes
Cellular Membrane Structure
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Neural Communication Systems
Show all topics
Social Sciences Research & Practice
Social Structure and Mobility
Classic Social Influence Experiments
Social Systems Theories
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Memory Systems and Processes
Neural Bases of Behavior
Social Influence and Attraction
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
Human Agency and Responsibility
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Organic Functional Groups
Atomic Structure and Composition
Chromatographic Separation Principles
Chemical Compound Classifications
Electrochemical Cell Systems
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
Chemical Equation Conservation
Show all topics
Nazi Germany and Holocaust 1933-1945
World Wars and Peace Treaties
European Monarchs and Statesmen
Cold War Global Tensions
Medieval Institutions and Systems
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
Modern Global Environmental-Health Challenges
Modern Military Conflicts
Medieval Migration and Invasions
World Wars Era and Impact
Show all topics
48
•
9 Feb 2026
•
Nicole
@nicolelolll
Your immune system is like a sophisticated security team protecting... Show more






Your body has two main lines of defence working together to protect you from disease. Non-specific defences like your skin and stomach acid are always active, responding immediately to any threat with the same approach every time.
Specific defences take longer to kick in but are much more targeted. They involve T and B lymphocytes that remember past infections, making your immune response faster and stronger next time you encounter the same pathogen.
Antigens are essentially molecular name tags on cell surfaces that help your immune system distinguish between "self" and "foreign" cells. They're found on pathogens, cancer cells, transplanted organs, and even bacterial toxins.
Quick Tip: Think of antigens like enemy uniforms - they help your white blood cells spot the bad guys instantly!
Phagocytosis is your first line of cellular defence, where special white blood cells literally eat invading bacteria. The process involves recognition, engulfment, and destruction using powerful digestive enzymes.

T-lymphocytes are the commanders of your immune system, maturing in your thymus gland and coordinating attacks on infected cells. They're brilliant at spotting cells that have been hijacked by viruses or have turned cancerous.
The process starts when antigen-presenting cells display enemy proteins on their surface like wanted posters. Helper T cells with matching receptors bind to these antigens, triggering clonal selection - rapid cell division to create an army of identical defenders.
These cloned T cells become memory cells for future protection, stimulate other immune cells, and activate cytotoxic T cells. Cytotoxic T cells are the assassins of the immune world, using a protein called perforin to punch holes in infected cells, causing them to die.
Remember: Cytotoxic T cells are particularly effective against viruses because they destroy the host cells viruses need to reproduce!
This targeted destruction prevents viral replication whilst your body recovers from infection.
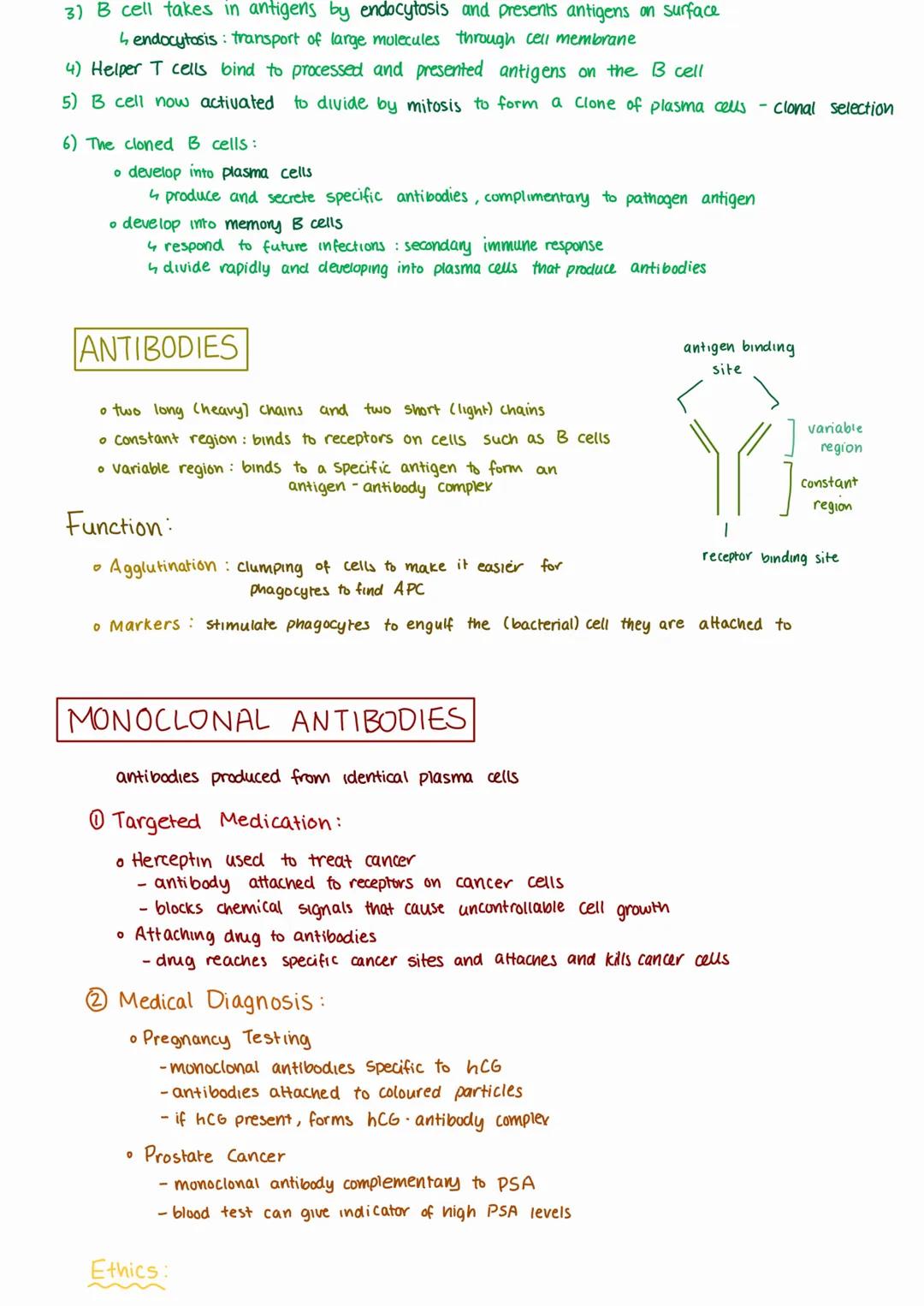
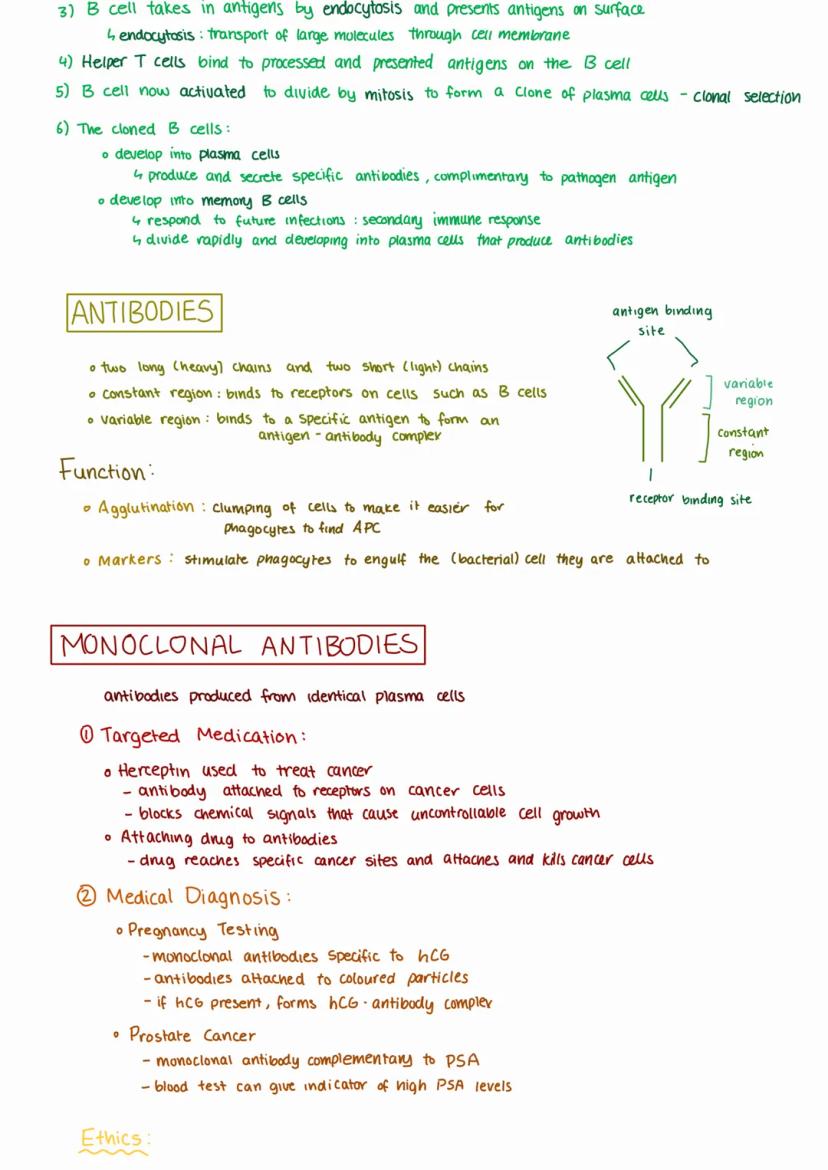
B-lymphocytes are your body's antibody factories, produced in your bone marrow and designed to tackle threats in your blood and body fluids. When they encounter matching antigens, they spring into action through a carefully orchestrated process.
The humoral response begins when B cells with complementary surface antibodies encounter their target antigen. After processing and presenting these antigens, helper T cells activate the B cells to divide rapidly, creating plasma cells and memory B cells.
Antibodies have a distinctive Y-shaped structure with heavy and light chains. Their variable regions bind specifically to antigens whilst their constant regions attach to immune cells. They work through agglutination (clumping cells together) and marking pathogens for destruction.
Monoclonal antibodies from identical plasma cells have revolutionised medicine. They're used in targeted cancer treatments like Herceptin, pregnancy tests detecting hCG, and prostate cancer screening through PSA detection.
Key Point: The specificity of antibodies makes them incredibly useful tools for both treatment and diagnosis!

The ELISA test is an incredibly sensitive diagnostic tool that can detect tiny amounts of specific molecules in samples. It uses a clever system of complementary antibodies and colour-changing enzymes to provide both qualitative and quantitative results.
Passive immunity gives you temporary protection through antibodies from external sources - like a baby receiving antibodies through breast milk or someone getting an antibody injection. It's quick but doesn't last because you don't develop memory cells.
Active immunity is the real deal - your immune system does the work itself. Natural active immunity comes from catching and recovering from diseases, whilst artificial active immunity comes from vaccination.
Think About It: Vaccination is like giving your immune system a practice run against weakened enemies!
Vaccines contain harmless versions of disease antigens that trigger memory cell production. When you encounter the real pathogen later, your immune system responds so quickly that you don't get ill.

Vaccination programmes require careful planning beyond just medical effectiveness. Success depends on economic availability, minimal side effects, proper storage and transportation, trained staff, and reaching the vast majority of the population.
Herd immunity occurs when enough people are vaccinated to make disease spread extremely difficult. This protects vulnerable individuals like babies, elderly people, and those with compromised immune systems who can't be vaccinated themselves.
However, vaccination programmes face several challenges. Some people don't develop immunity due to defective immune systems, whilst antigenic variability means pathogens can mutate and evade existing vaccines - that's why you need annual flu jabs.
Ethical considerations include research funding, animal testing, vaccine distribution priorities, and whether vaccinations should be compulsory. Religious, medical, and personal objections also complicate universal vaccination efforts.
Real World: The COVID-19 pandemic showed both the power of vaccines and the challenges of achieving global vaccination coverage!

HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) specifically targets your helper T cells, the very cells that coordinate your immune response. Its structure includes a lipid envelope, protein matrix, and RNA core containing reverse transcriptase - an enzyme that converts viral RNA into DNA.
HIV replication is particularly clever and destructive. After attaching to helper T cells, the virus fuses with the cell membrane and inserts its genetic material. The reverse transcriptase creates viral DNA that integrates into the host cell's nucleus, hijacking cellular machinery to produce new viruses.
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) develops when HIV has destroyed enough helper T cells that your immune system can't function properly. Without these crucial coordinators, B cells can't produce antibodies and cytotoxic T cells can't be activated effectively.
Important: Antibiotics don't work against HIV because viruses lack cell walls and hide inside host cells where antibiotics can't reach them!
This immunodeficiency leaves patients vulnerable to opportunistic infections and cancers that healthy immune systems would easily defeat, ultimately leading to death if untreated.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Nicole
@nicolelolll
Your immune system is like a sophisticated security team protecting your body 24/7. It uses both immediate defences and specialised responses to fight off infections and keep you healthy.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body has two main lines of defence working together to protect you from disease. Non-specific defences like your skin and stomach acid are always active, responding immediately to any threat with the same approach every time.
Specific defences take longer to kick in but are much more targeted. They involve T and B lymphocytes that remember past infections, making your immune response faster and stronger next time you encounter the same pathogen.
Antigens are essentially molecular name tags on cell surfaces that help your immune system distinguish between "self" and "foreign" cells. They're found on pathogens, cancer cells, transplanted organs, and even bacterial toxins.
Quick Tip: Think of antigens like enemy uniforms - they help your white blood cells spot the bad guys instantly!
Phagocytosis is your first line of cellular defence, where special white blood cells literally eat invading bacteria. The process involves recognition, engulfment, and destruction using powerful digestive enzymes.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
T-lymphocytes are the commanders of your immune system, maturing in your thymus gland and coordinating attacks on infected cells. They're brilliant at spotting cells that have been hijacked by viruses or have turned cancerous.
The process starts when antigen-presenting cells display enemy proteins on their surface like wanted posters. Helper T cells with matching receptors bind to these antigens, triggering clonal selection - rapid cell division to create an army of identical defenders.
These cloned T cells become memory cells for future protection, stimulate other immune cells, and activate cytotoxic T cells. Cytotoxic T cells are the assassins of the immune world, using a protein called perforin to punch holes in infected cells, causing them to die.
Remember: Cytotoxic T cells are particularly effective against viruses because they destroy the host cells viruses need to reproduce!
This targeted destruction prevents viral replication whilst your body recovers from infection.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
B-lymphocytes are your body's antibody factories, produced in your bone marrow and designed to tackle threats in your blood and body fluids. When they encounter matching antigens, they spring into action through a carefully orchestrated process.
The humoral response begins when B cells with complementary surface antibodies encounter their target antigen. After processing and presenting these antigens, helper T cells activate the B cells to divide rapidly, creating plasma cells and memory B cells.
Antibodies have a distinctive Y-shaped structure with heavy and light chains. Their variable regions bind specifically to antigens whilst their constant regions attach to immune cells. They work through agglutination (clumping cells together) and marking pathogens for destruction.
Monoclonal antibodies from identical plasma cells have revolutionised medicine. They're used in targeted cancer treatments like Herceptin, pregnancy tests detecting hCG, and prostate cancer screening through PSA detection.
Key Point: The specificity of antibodies makes them incredibly useful tools for both treatment and diagnosis!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The ELISA test is an incredibly sensitive diagnostic tool that can detect tiny amounts of specific molecules in samples. It uses a clever system of complementary antibodies and colour-changing enzymes to provide both qualitative and quantitative results.
Passive immunity gives you temporary protection through antibodies from external sources - like a baby receiving antibodies through breast milk or someone getting an antibody injection. It's quick but doesn't last because you don't develop memory cells.
Active immunity is the real deal - your immune system does the work itself. Natural active immunity comes from catching and recovering from diseases, whilst artificial active immunity comes from vaccination.
Think About It: Vaccination is like giving your immune system a practice run against weakened enemies!
Vaccines contain harmless versions of disease antigens that trigger memory cell production. When you encounter the real pathogen later, your immune system responds so quickly that you don't get ill.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Vaccination programmes require careful planning beyond just medical effectiveness. Success depends on economic availability, minimal side effects, proper storage and transportation, trained staff, and reaching the vast majority of the population.
Herd immunity occurs when enough people are vaccinated to make disease spread extremely difficult. This protects vulnerable individuals like babies, elderly people, and those with compromised immune systems who can't be vaccinated themselves.
However, vaccination programmes face several challenges. Some people don't develop immunity due to defective immune systems, whilst antigenic variability means pathogens can mutate and evade existing vaccines - that's why you need annual flu jabs.
Ethical considerations include research funding, animal testing, vaccine distribution priorities, and whether vaccinations should be compulsory. Religious, medical, and personal objections also complicate universal vaccination efforts.
Real World: The COVID-19 pandemic showed both the power of vaccines and the challenges of achieving global vaccination coverage!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) specifically targets your helper T cells, the very cells that coordinate your immune response. Its structure includes a lipid envelope, protein matrix, and RNA core containing reverse transcriptase - an enzyme that converts viral RNA into DNA.
HIV replication is particularly clever and destructive. After attaching to helper T cells, the virus fuses with the cell membrane and inserts its genetic material. The reverse transcriptase creates viral DNA that integrates into the host cell's nucleus, hijacking cellular machinery to produce new viruses.
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) develops when HIV has destroyed enough helper T cells that your immune system can't function properly. Without these crucial coordinators, B cells can't produce antibodies and cytotoxic T cells can't be activated effectively.
Important: Antibiotics don't work against HIV because viruses lack cell walls and hide inside host cells where antibiotics can't reach them!
This immunodeficiency leaves patients vulnerable to opportunistic infections and cancers that healthy immune systems would easily defeat, ultimately leading to death if untreated.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
1
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user