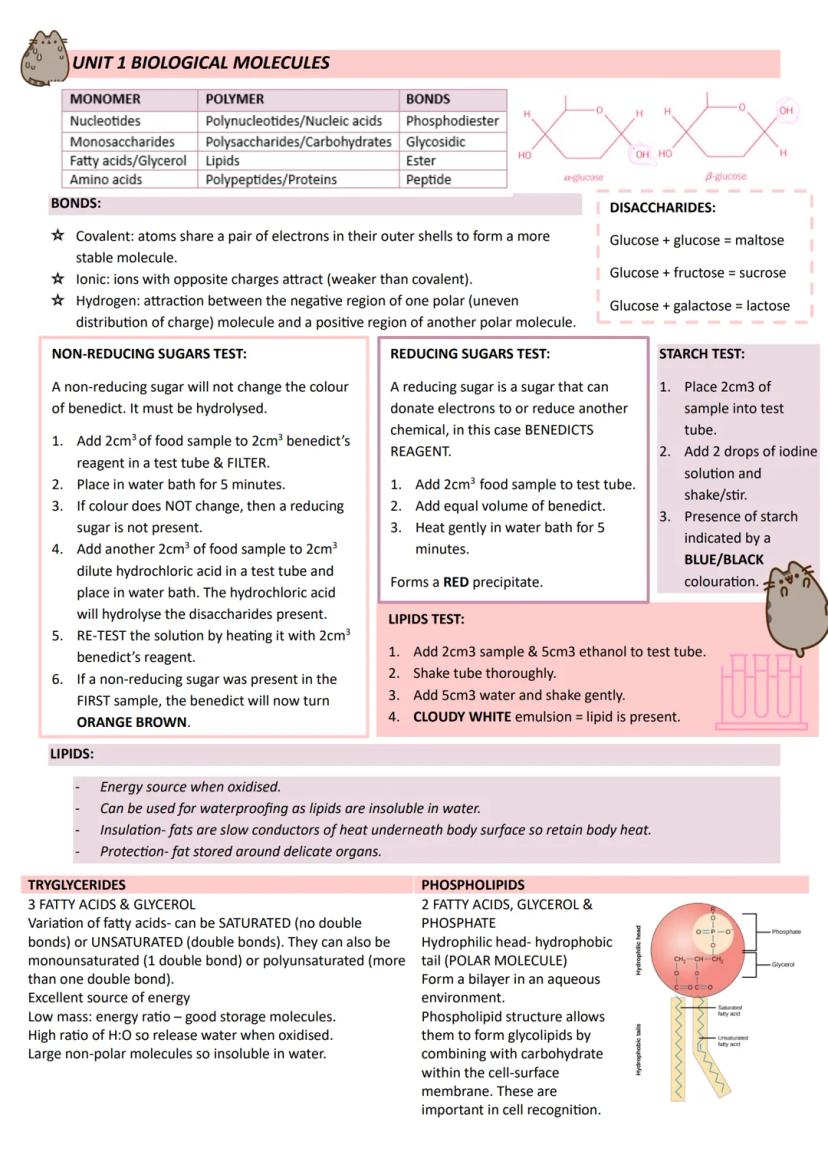
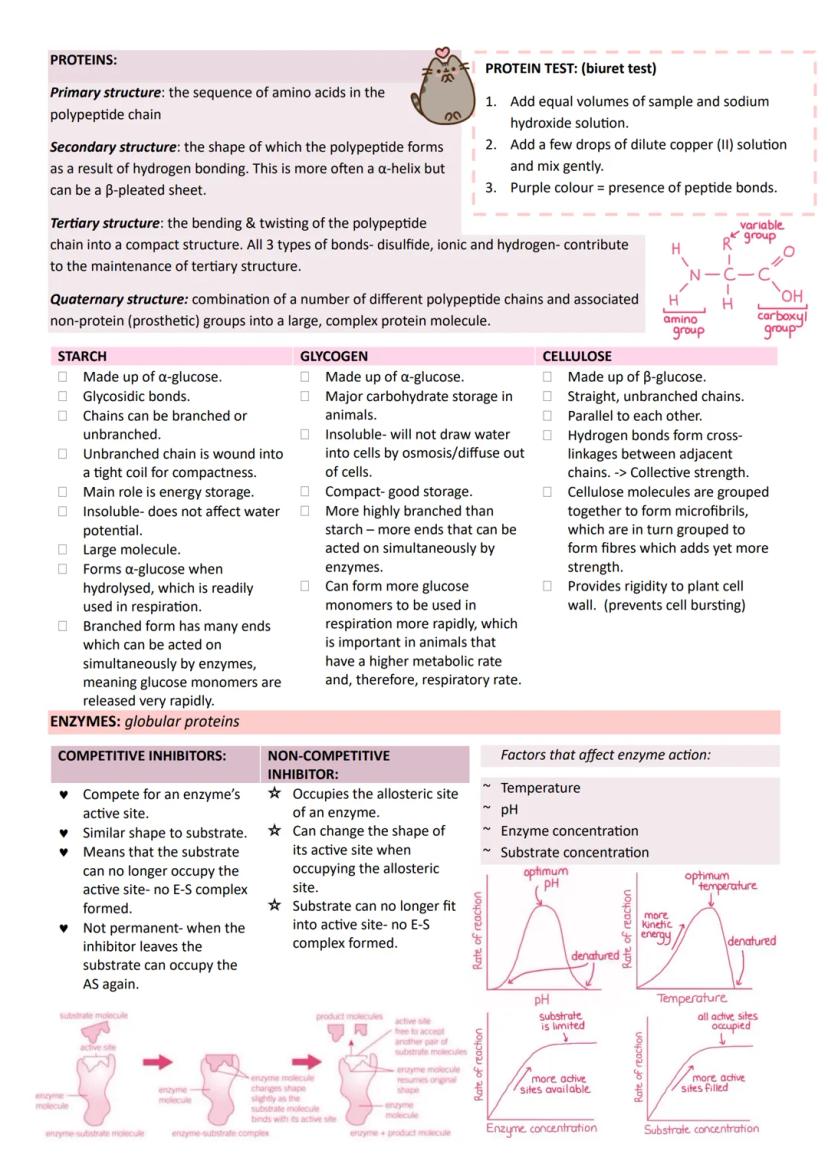
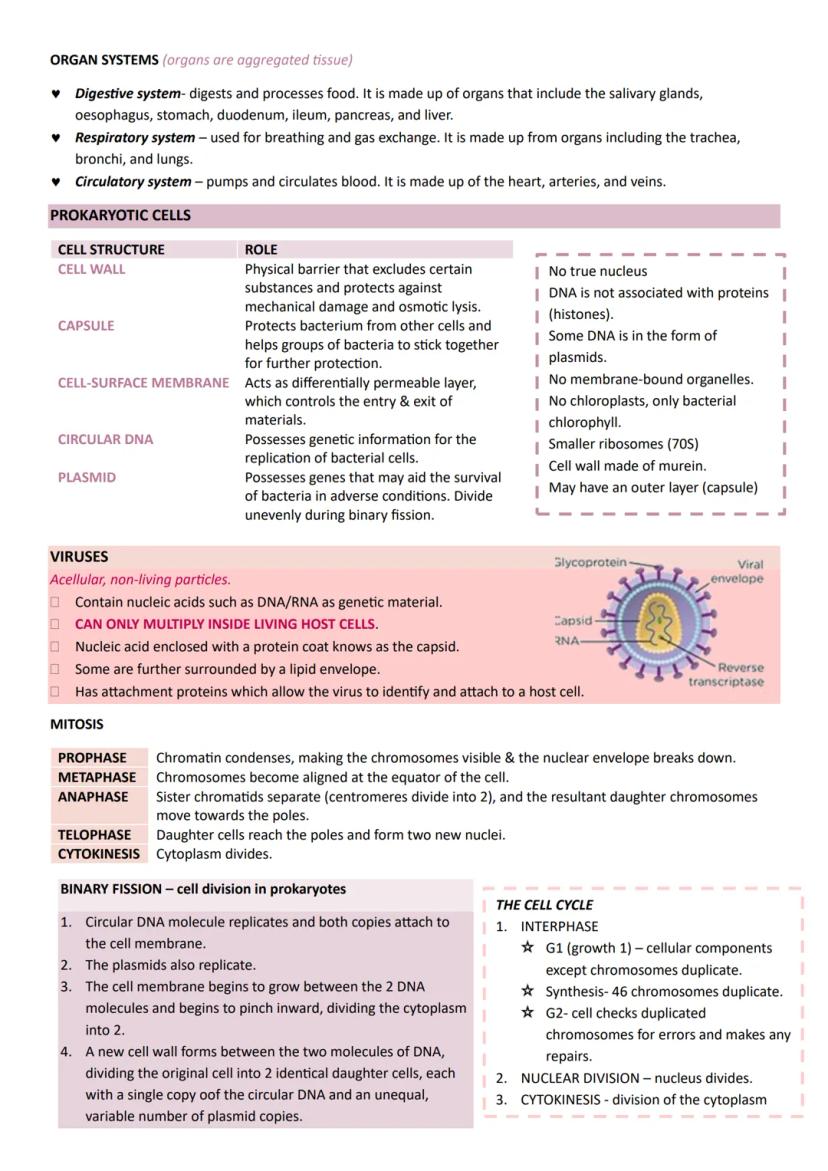
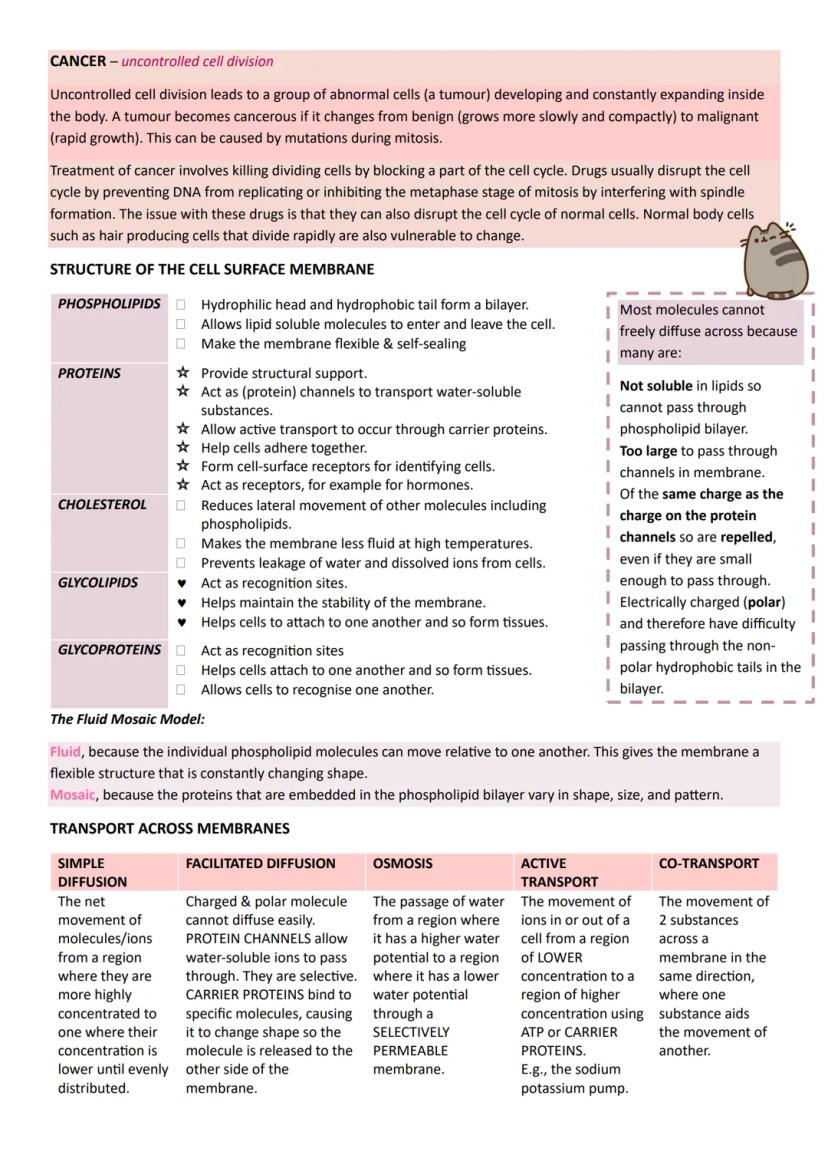
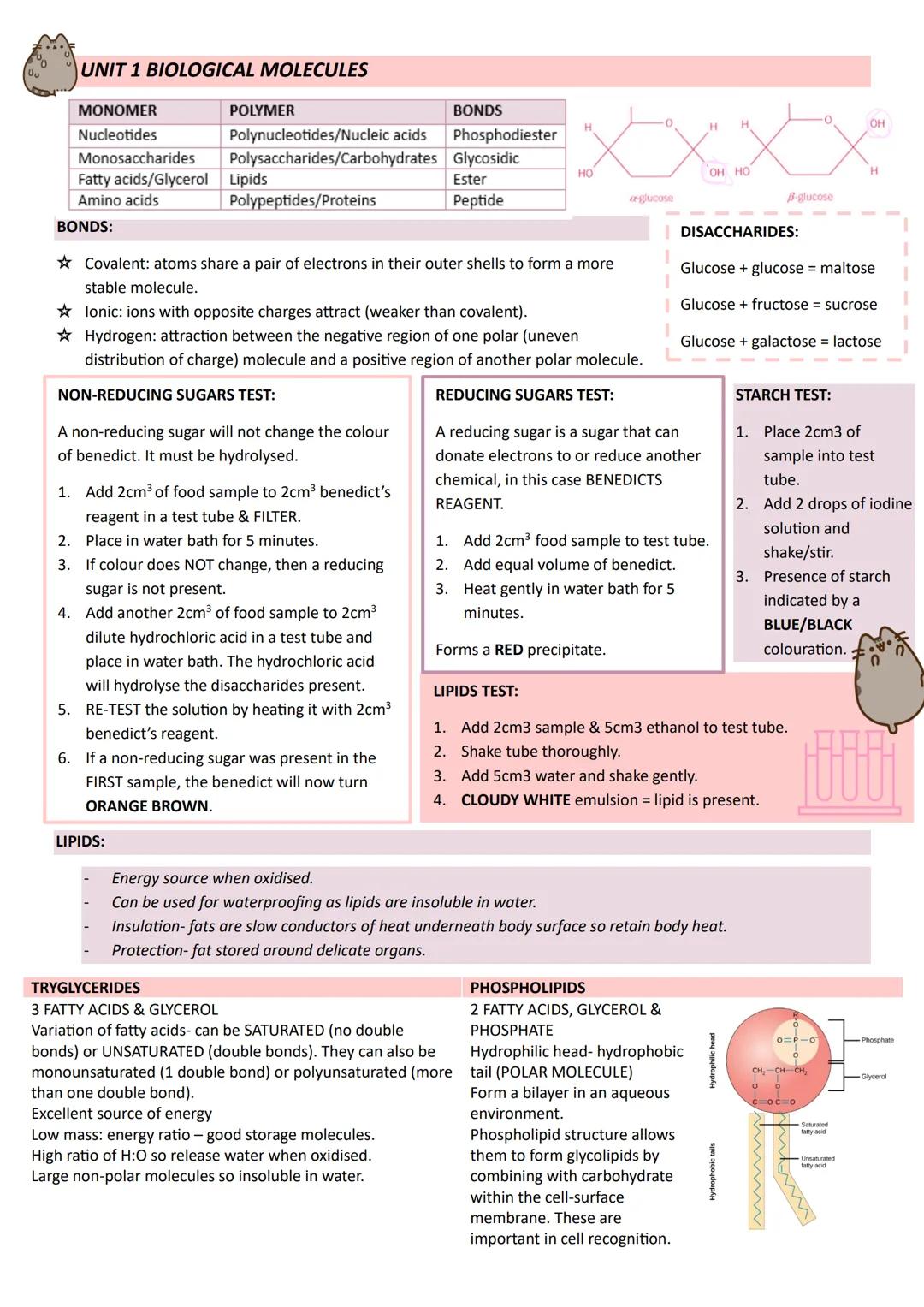
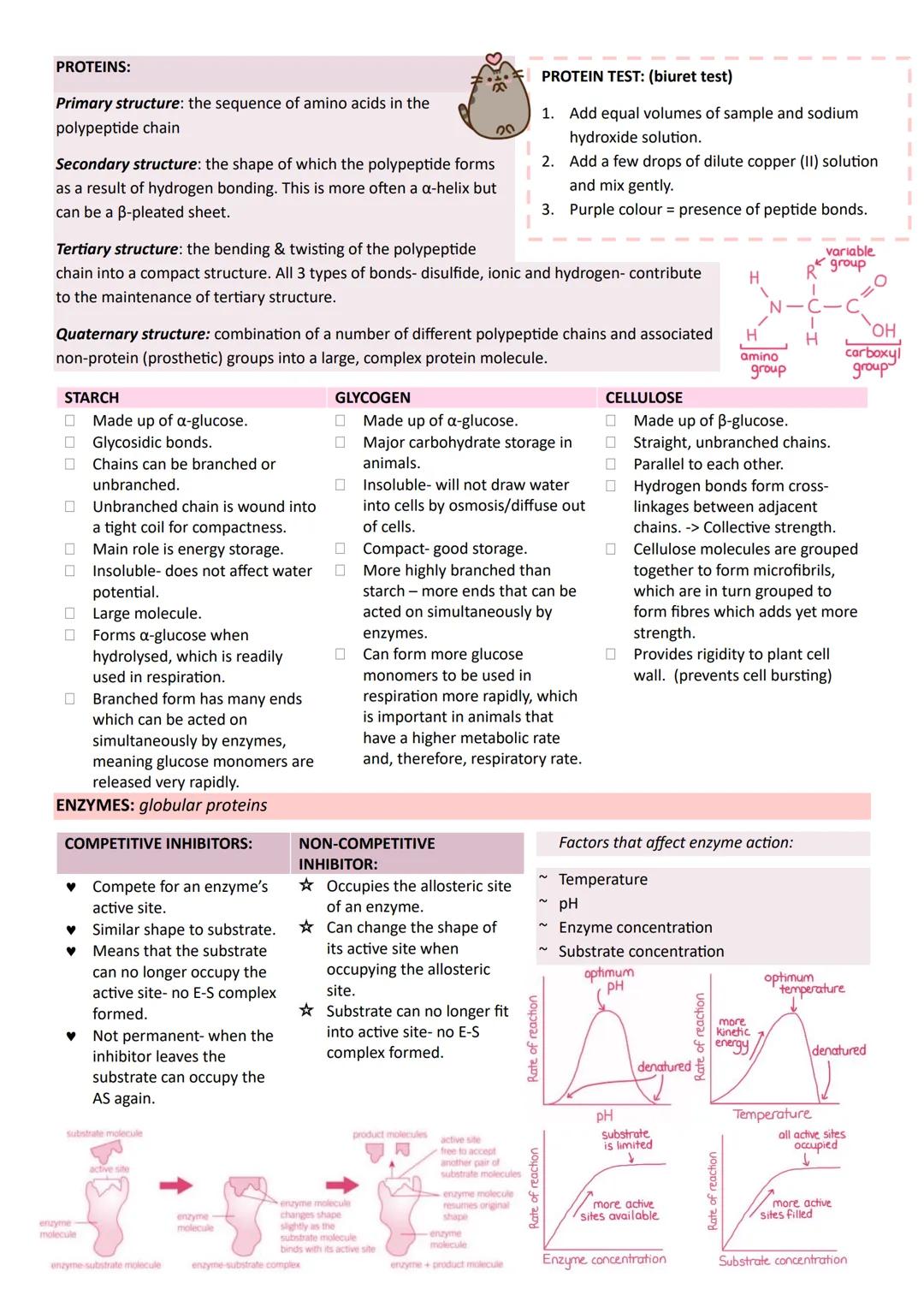
Medical Applications and HIV
Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by fusing B cells with tumour cells, creating immortal hybridomas. These have medical applications in pregnancy tests, disease diagnosis, and targeted drug delivery.
ELISA testing detects specific antibodies or antigens using enzyme-linked reactions. HIV testing uses indirect ELISA to detect HIV antibodies, whilst pregnancy tests detect hCG hormone using monoclonal antibodies and colour changes.
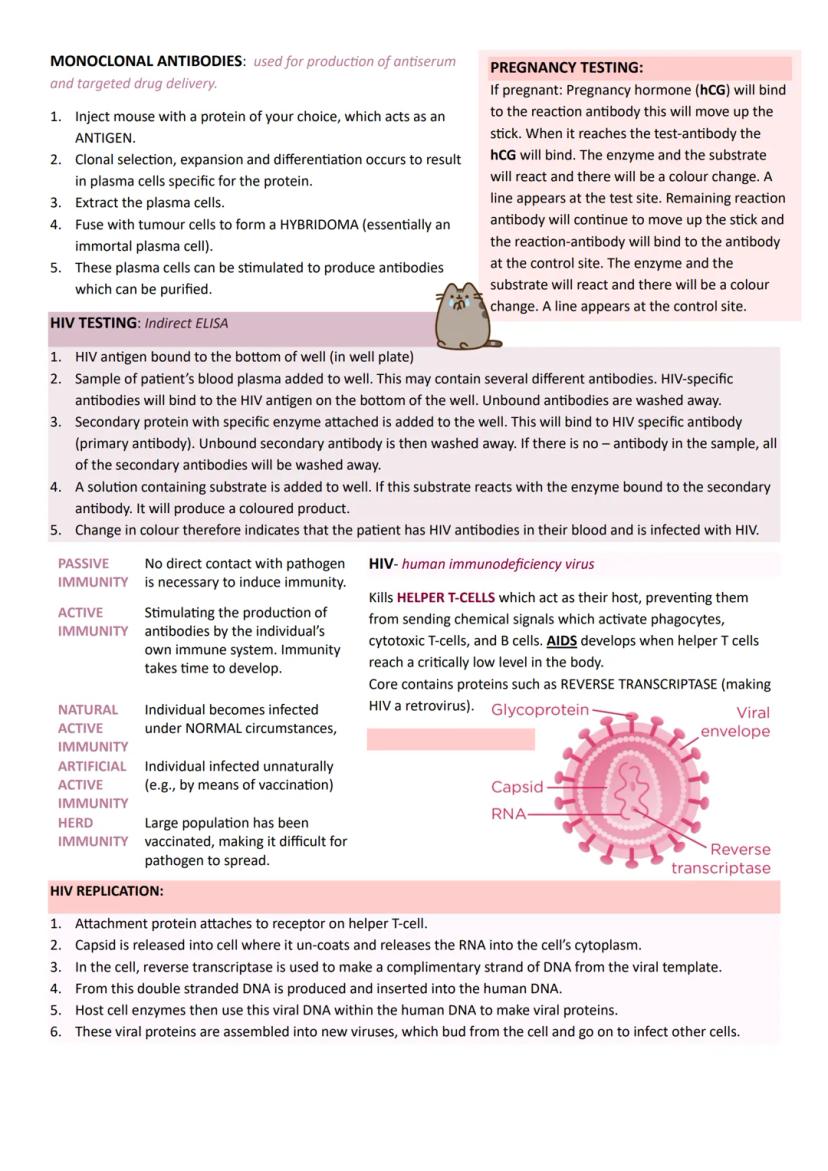
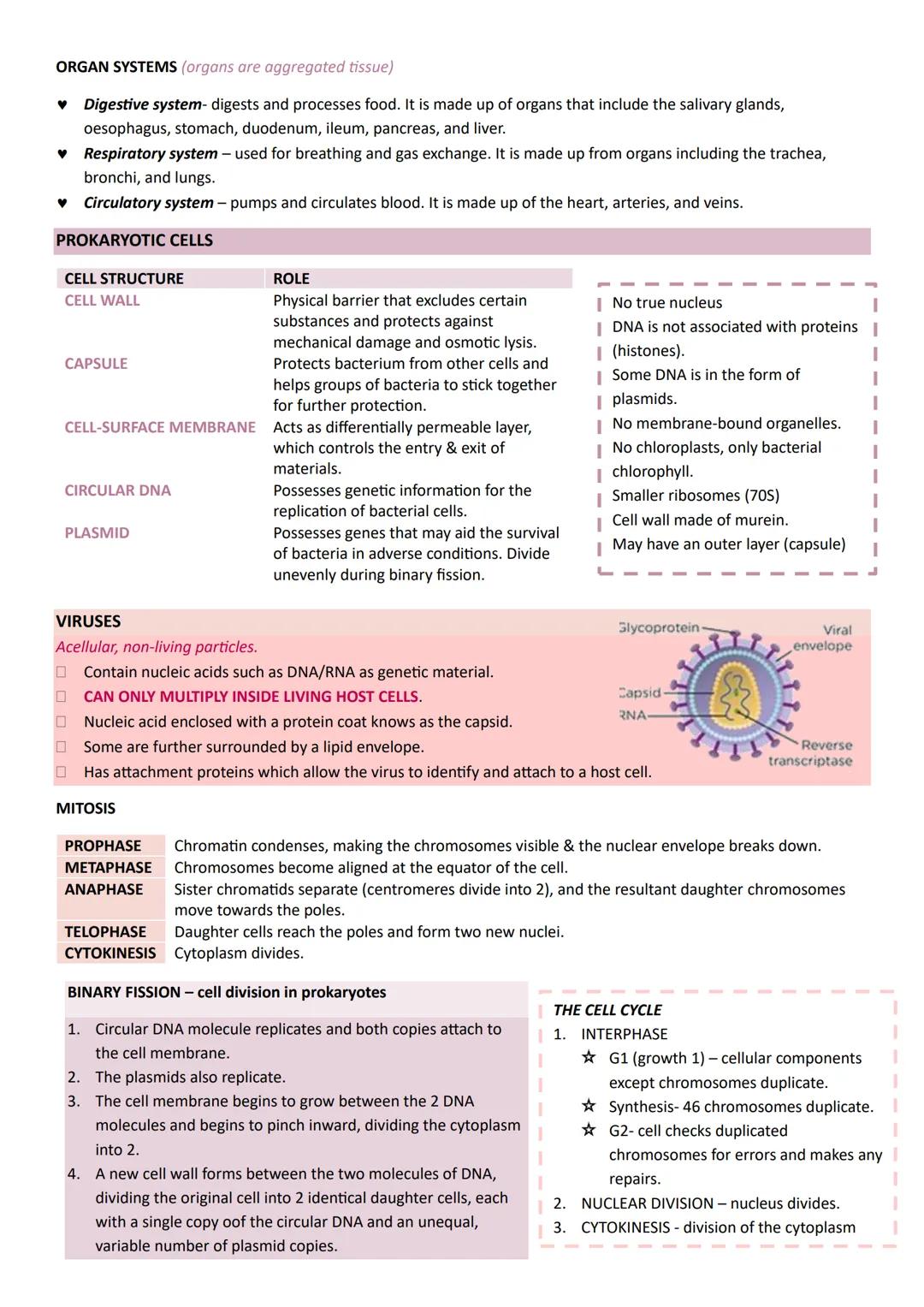
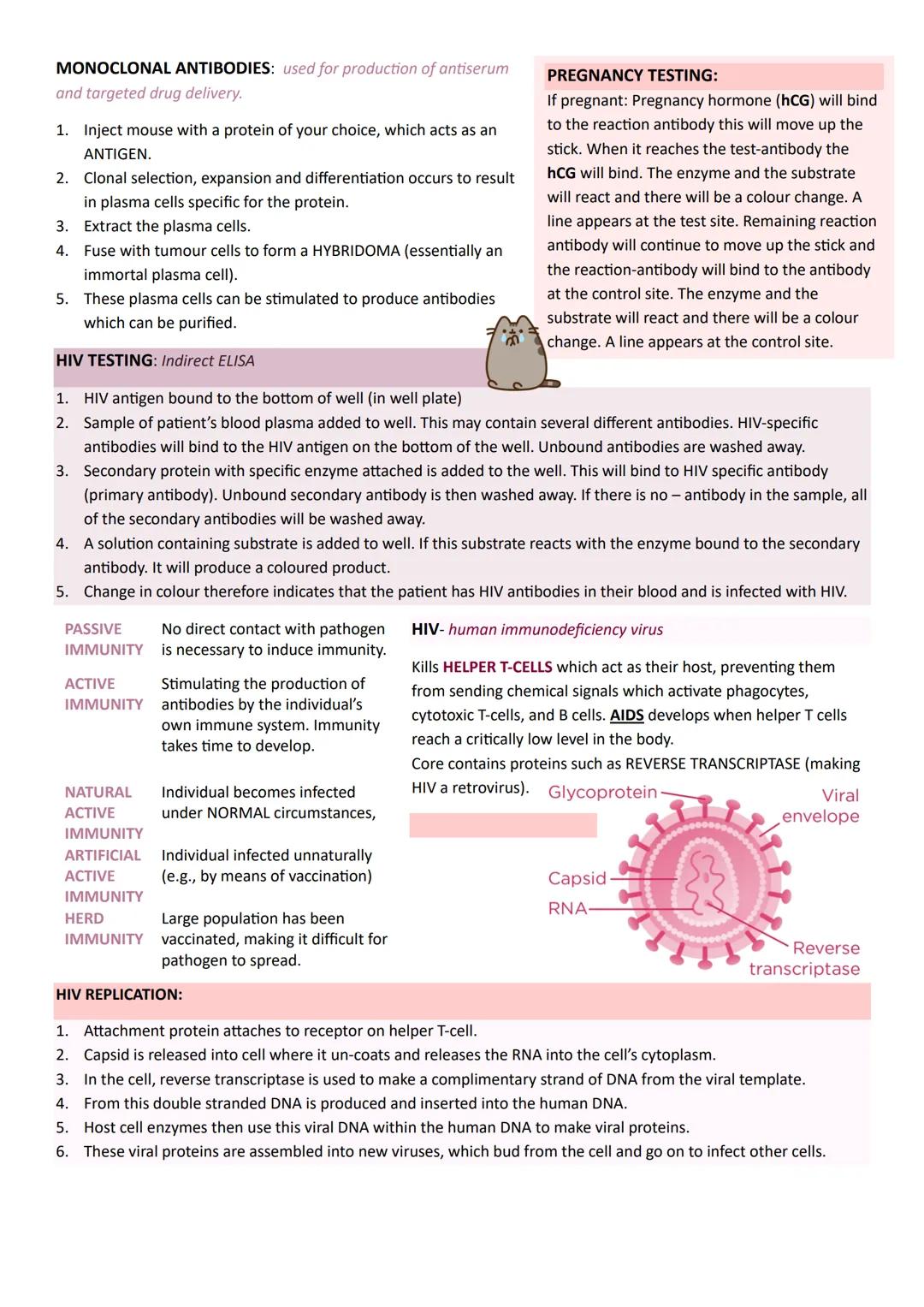
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) specifically targets helper T cells, gradually destroying immune system coordination. It contains reverse transcriptase enzyme, making it a retrovirus that converts RNA into DNA and integrates into host cell chromosomes.
HIV replication involves attachment, capsid release, reverse transcription, DNA integration, protein synthesis, and viral assembly. The virus then buds from cells to infect others, eventually leading to AIDS when helper T cell numbers become critically low.
Immunity types include active (body produces own antibodies) versus passive receivingready−madeantibodies, and natural versus artificial (vaccination). Herd immunity protects populations when enough individuals are vaccinated.
Understanding HIV's mechanism helps explain why it's so dangerous - by destroying the cells that coordinate immune responses, it leaves the body defenseless against other infections.
Global Health: HIV research has advanced our understanding of immunity and led to better treatments and prevention strategies worldwide.