Structure and Function of DNA and RNA in Biology-... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Responding to change (a2 only)
Infection and response
Homeostasis and response
Energy transfers (a2 only)
Cell biology
Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments (a-level only)
Biological molecules
Organisation
Substance exchange
Bioenergetics
Genetic information & variation
Inheritance, variation and evolution
Genetics & ecosystems (a2 only)
Ecology
Cells
Show all topics
Britain & the wider world: 1745 -1901
1l the quest for political stability: germany, 1871-1991
The cold war
Inter-war germany
Medieval period: 1066 -1509
2d religious conflict and the church in england, c1529-c1570
2o democracy and nazism: germany, 1918-1945
1f industrialisation and the people: britain, c1783-1885
1c the tudors: england, 1485-1603
2m wars and welfare: britain in transition, 1906-1957
World war two & the holocaust
2n revolution and dictatorship: russia, 1917-1953
2s the making of modern britain, 1951-2007
World war one
Britain: 1509 -1745
Show all topics
720
•
25 Dec 2025
•
Lucy
@lucy_sldh
Structure and Function of DNA and RNA in Biology-... Show more



Nucleotide Composition and Structure
This section details the specific components of DNA and RNA nucleotides, highlighting the key differences in their structure of DNA and RNA a level biology.
Example: The four DNA bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), while RNA replaces thymine with uracil (U).
Definition: A polynucleotide is formed when multiple nucleotides join together through condensation reactions.
Highlight: The sugar-phosphate backbone is created when nucleotides join via phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another.

DNA Double Helix Structure and Base Pairing
This section explores the intricate details of DNA's double helix structure and the principles of base pairing, essential concepts in understanding structure of DNA a level biology AQA.
Definition: Complementary base pairing is the specific matching of bases where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine .
Highlight: The DNA double helix is formed by two antiparallel polynucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
Example: Base pairing follows specific rules: A-T pairs form two hydrogen bonds, while C-G pairs form three hydrogen bonds, contributing to DNA stability.

Fundamentals of DNA and RNA Structure
This section introduces the basic components and functions of nucleic acids in biological systems. The text explains how DNA function a level biology relates to information storage, while RNA serves as an information transfer molecule.
Definition: Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides that carry genetic information in all living cells.
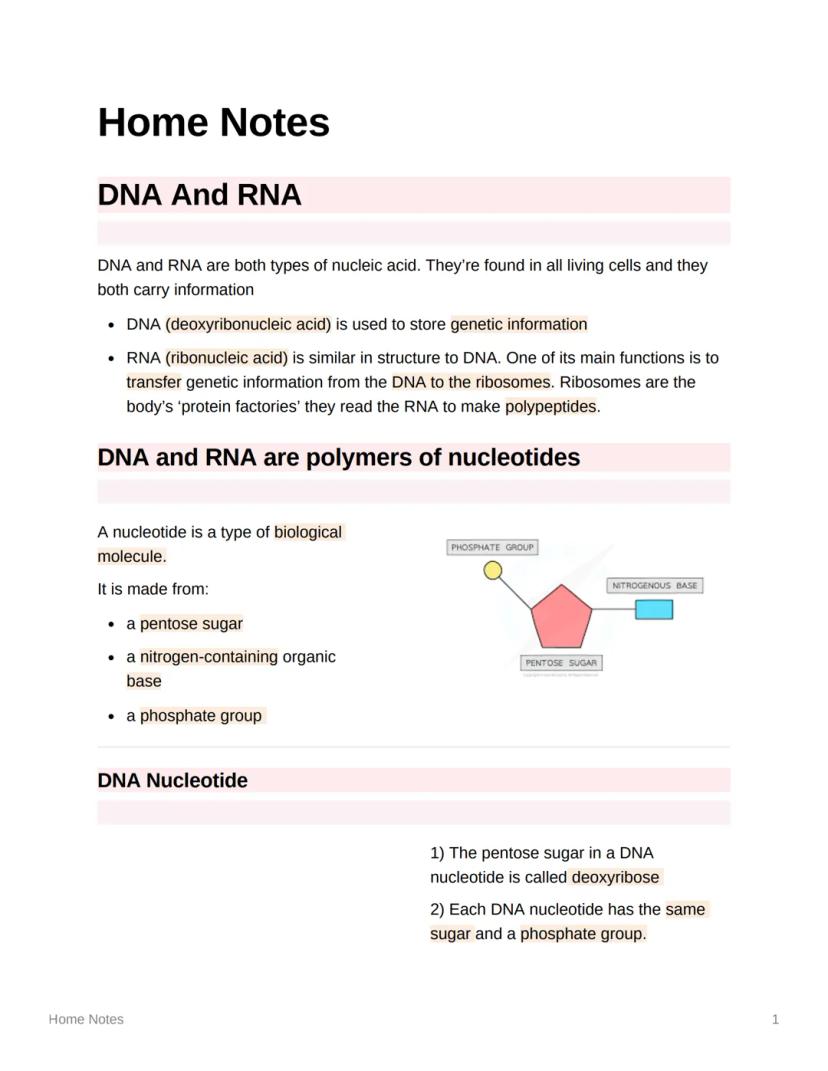
Vocabulary: A nucleotide consists of three components: a pentose sugar, a nitrogen-containing organic base, and a phosphate group.
Highlight: DNA nucleotides specifically contain deoxyribose sugar, while all nucleotides share the common feature of having a phosphate group.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
Lucy
@lucy_sldh
Structure and Function of DNA and RNA in Biology - A comprehensive guide exploring the fundamental components, structures, and roles of nucleic acids in living organisms.
• DNA and RNAare essential nucleic acids found in all living cells, with... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Nucleotide Composition and Structure
This section details the specific components of DNA and RNA nucleotides, highlighting the key differences in their structure of DNA and RNA a level biology.
Example: The four DNA bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), while RNA replaces thymine with uracil (U).
Definition: A polynucleotide is formed when multiple nucleotides join together through condensation reactions.
Highlight: The sugar-phosphate backbone is created when nucleotides join via phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
DNA Double Helix Structure and Base Pairing
This section explores the intricate details of DNA's double helix structure and the principles of base pairing, essential concepts in understanding structure of DNA a level biology AQA.
Definition: Complementary base pairing is the specific matching of bases where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine .
Highlight: The DNA double helix is formed by two antiparallel polynucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
Example: Base pairing follows specific rules: A-T pairs form two hydrogen bonds, while C-G pairs form three hydrogen bonds, contributing to DNA stability.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Fundamentals of DNA and RNA Structure
This section introduces the basic components and functions of nucleic acids in biological systems. The text explains how DNA function a level biology relates to information storage, while RNA serves as an information transfer molecule.
Definition: Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides that carry genetic information in all living cells.
Vocabulary: A nucleotide consists of three components: a pentose sugar, a nitrogen-containing organic base, and a phosphate group.
Highlight: DNA nucleotides specifically contain deoxyribose sugar, while all nucleotides share the common feature of having a phosphate group.
Our AI Companion is a student-focused AI tool that offers more than just answers. Built on millions of Knowunity resources, it provides relevant information, personalised study plans, quizzes, and content directly in the chat, adapting to your individual learning journey.
You can download the app from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
18
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore the detailed mechanisms of RNA transcription, including initiation, elongation, and termination. This study note covers the roles of RNA polymerase, the significance of the promoter and terminator regions, and the splicing of pre-mRNA into functional mRNA. Ideal for AQA A-level biology students seeking to understand the intricacies of gene expression.
Paper 1. The Function and structure of DNA & RNA.
Explore the structure and function of DNA and RNA, including key concepts such as nucleotides, base pairing, and the double helix. This summary highlights the differences between DNA and RNA, their roles in information storage, and the significance of hydrogen bonds in molecular interactions. Ideal for students studying molecular biology.
Explore the essential processes of DNA replication and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in this concise summary. Understand the roles of key enzymes like DNA polymerase and ligase, the significance of leading and lagging strands, and the steps involved in PCR. Ideal for Higher Biology students preparing for SQA assessments.
Explore the essential processes of DNA replication and the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). This study note covers the steps of DNA replication, the role of enzymes like DNA polymerase and ligase, and the requirements for PCR. Additionally, learn about practical applications of PCR in crime solving, paternity testing, and genetic disorder diagnosis, as well as the technique of gel electrophoresis for DNA fragment analysis.
Explore the groundbreaking Meselson and Stahl experiment that demonstrated semi-conservative DNA replication using nitrogen isotopes N-15 and N-14. Understand the process of DNA replication, including the roles of helicase, DNA polymerase, and the significance of complementary base pairing. This summary covers key concepts such as the structure of DNA, replication mechanisms, and the implications of the experiment for molecular biology.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
Best app on earth! no words because it’s too good
Thomas R
iOS user
Just amazing. Let's me revise 10x better, this app is a quick 10/10. I highly recommend it to anyone. I can watch and search for notes. I can save them in the subject folder. I can revise it any time when I come back. If you haven't tried this app, you're really missing out.
Basil
Android user
This app has made me feel so much more confident in my exam prep, not only through boosting my own self confidence through the features that allow you to connect with others and feel less alone, but also through the way the app itself is centred around making you feel better. It is easy to navigate, fun to use, and helpful to anyone struggling in absolutely any way.
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
very reliable app to help and grow your ideas of Maths, English and other related topics in your works. please use this app if your struggling in areas, this app is key for that. wish I'd of done a review before. and it's also free so don't worry about that.
Rohan U
Android user
I know a lot of apps use fake accounts to boost their reviews but this app deserves it all. Originally I was getting 4 in my English exams and this time I got a grade 7. I didn’t even know about this app three days until the exam and it has helped A LOT. Please actually trust me and use it as I’m sure you too will see developments.
Xander S
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This apps acc the goat. I find revision so boring but this app makes it so easy to organize it all and then you can ask the freeeee ai to test yourself so good and you can easily upload your own stuff. highly recommend as someone taking mocks now
Paul T
iOS user