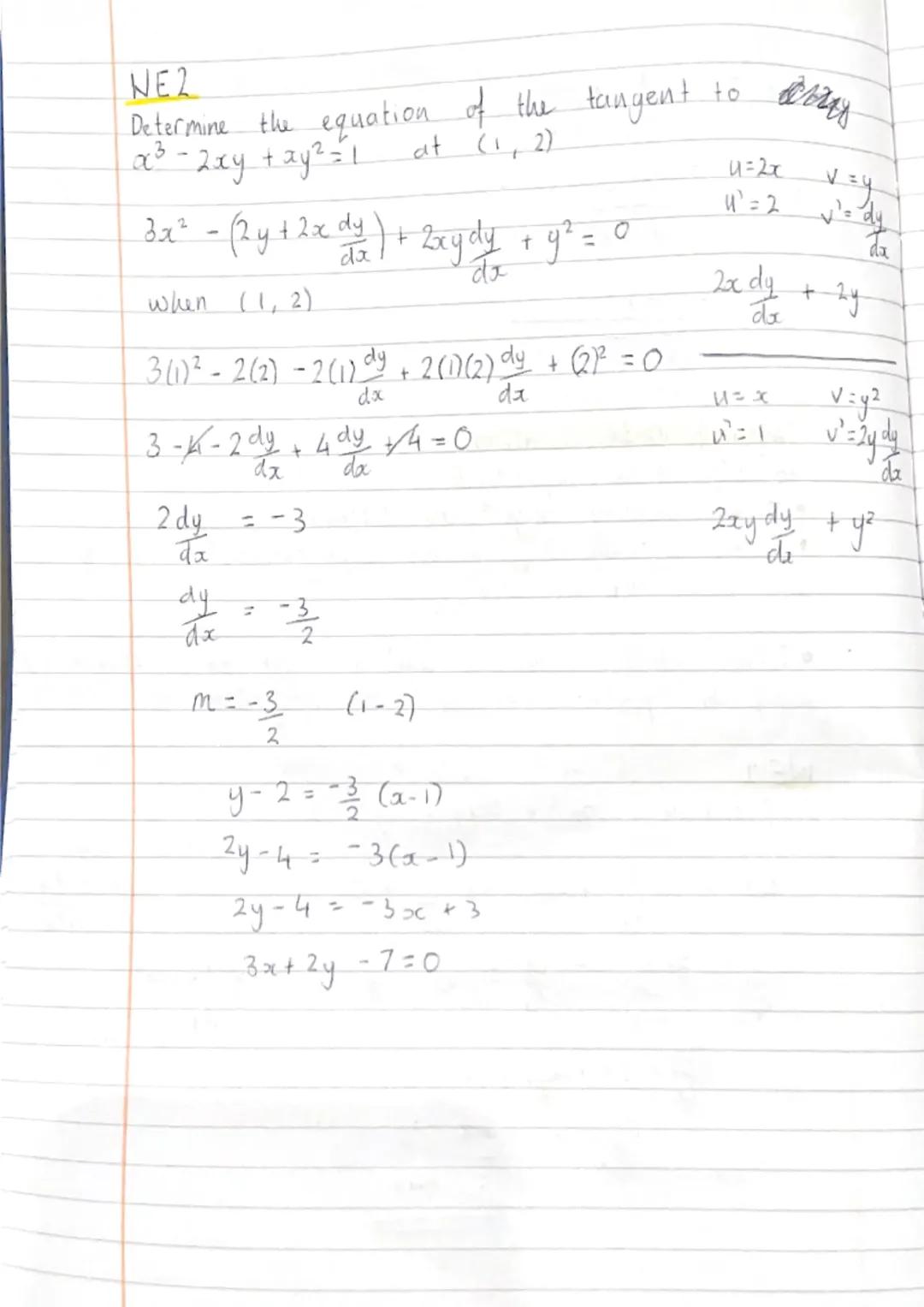Finding Tangent Lines Using Implicit Differentiation
Once you've mastered basic implicit differentiation, you can tackle tangent line equations - a common exam question that's actually quite straightforward.
For the curve x³ - 2xy + xy² = 1 at point (1, 2), start by differentiating implicitly. This gives: 3x² - 2y+2x(dy/dx) + 2xydy/dx + y² = 0. The tricky bit is remembering to use the product rule for mixed terms like xy².
Substitute your point (1, 2) into the differentiated equation: 3(1)² - 2(2) - 2(1)dy/dx + 2(1)(2)dy/dx + (2)² = 0. Simplifying gives dy/dx = -3/2, which is your gradient.
Finally, use the point-gradient form: y - 2 = -3/2x−1, which rearranges to 3x + 2y - 7 = 0.
Exam Success: Always check your tangent line passes through the given point by substituting back!